Green Tongue
Why is my Tongue Green?
We all know that, in healthy individuals, the tongue has a common pink color, with a smooth texture. However, it is possible that certain conditions lead to the modification of both the color and the texture of the tongue. As you will have the opportunity to read below, the green tongue can appear as the result of an oral infection, after trauma or due to sores.
A healthy individual can be recognized after the state of the oral cavity. If a person’s tongue has gone green, this is suggestive of an underlying health problem. It is highly important to make the correct diagnosis, so as to recommend the best treatment.
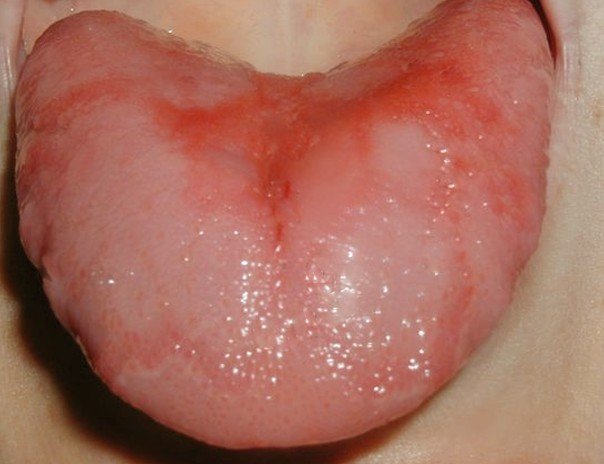
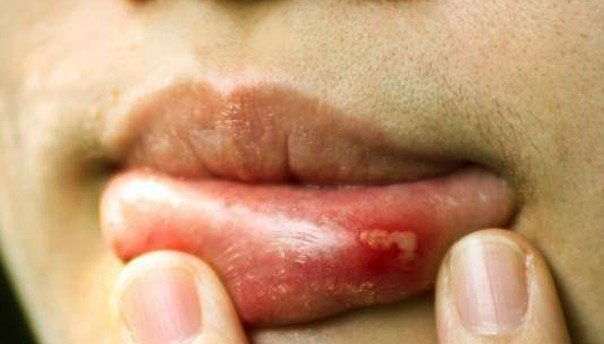
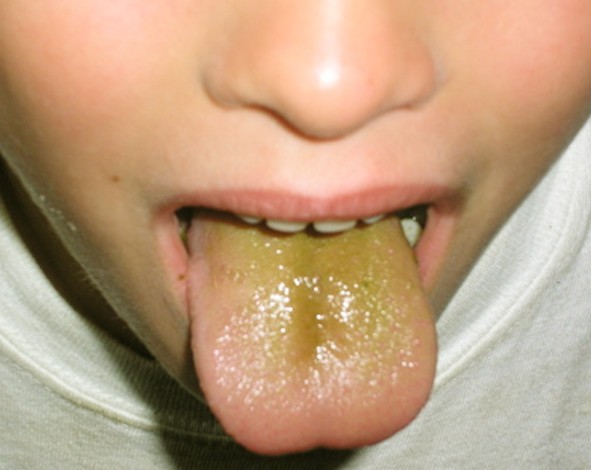
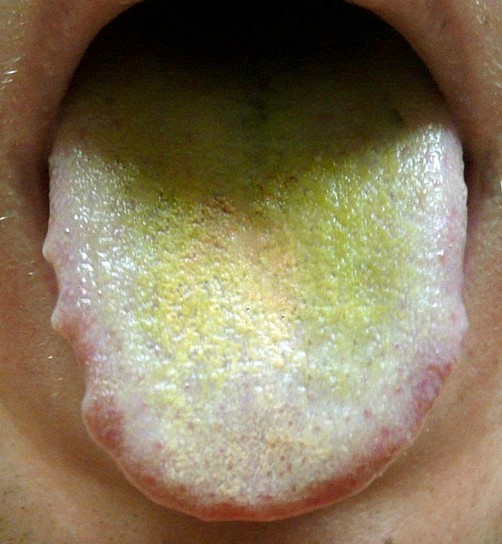
Pictures of a Green tongue
Here is how a green tongue looks like:
Symptoms Signs of a Green Tongue
These are the most common symptoms associated with the green tongue:
In case of oral candidiasis:
- White tongue in the initial stage
- Color changes to green, after treatment or food
- Underneath the initial colored layer, the tongue is red and may even bleed (upon scraping)
- The dorsal surface of the tongue is affected (in the majority of the cases); however, the infection can be encountered in any part of the tongue
- Bad breath
- Burning sensation at the level of the mouth
- Pain/discomfort (especially after eating food that is spicy or hot)
In case of the hairy tongue syndrome:
- Hair-like structures are present on the surface of the tongue (dorsal surface)
- Bacterial contamination can case these strands to become green or even black in color
- Metallic taste in the mouth
- Bad breath
- Dry mouth.
What Causes a Green tongue?
These are the most common causes that can cause the tongue to become green:
Oral candidiasis (oral thrush)
- Most common cause
- Fungal infection (caused by Candida albicans)
- Often encountered in individuals whose immune system is weak
- Also seen in those wearing ill-fitted prostheses or dentures (prolonged wear)
Hairy tongue syndrome
- Exact cause has yet to be identified
- These are the risk factors associated with the appearance of this condition:
- Smoking
- Excessive mouthwash rinsing
- Poor dental hygiene
- Weak immune system
Other causes
- Upper respiratory tract infection (sore throat) – extension of the infection to the tongue
- Prolonged treatments with antibiotics
- Toothpaste/mouthwash – the ingredients contained in these products can cause the tongue to become green (temporary)
- Green colorants contained in candy and other sweets can lead to the appearance of a green tongue (temporary)
- Drugs/marijuana consumption
- Tongue piercing (green color of the tongue is suggestive of an infection, especially if there is associated discharge and pain).
Diagnosis
These are the most common methods used for the diagnosis of the green tongue:
Medical history of the patient
- When did the color of the tongue change?
- Are there other symptoms present?
- Previous health problems (and treatments)
Physical examination
- Microscopic examination of the tongue
- Identification of abnormal long papillae strands (hairy tongue syndrome)
Laboratory testing
- CBC (Complete blood count) – level of white blood cells
- Tongue culture – identification of microorganisms (fungus or bacteria).
Green tongue Treatment
These are the treatments recommended for the green tongue, according to the main cause:
Oral candidiasis
- Anti-fungal medication (topical administration)
- Increased water intake
- Balanced diet (fresh fruits and vegetables)
Hairy tongue syndrome
- Treatment for the underlying cause
- Lifestyle changes
- Avoid smoking
- Excellent dental hygiene (daily brushing)
- Dislodgment of the surface epithelium of the tongue
- Frequent brushing of the tongue surface
- Avoid mouthwash or other products that may stimulate the growth of the tongue surface tissue (such as hydrogen peroxide or other oxygenating products)
- Avoid products that cause the staining of the tongue (toothpaste, mouthwash, candy, chewing gum etc.).
Apart from the specific treatment for the underlying cause, one must also make a change in the diet. For example, you should make sure that the diet is rich in fiber, so that the colon is clean and free of toxins. Also, you need to maintain an excellent oral hygiene and quit smoking.
The water intake should be increased, in order to keep the tongue clean and prevent the food debris from depositing in the small papillae of the tongue. Gargling with warm water is also recommended, especially after a meal. Crunchy fruits and vegetables should be included within the diet, as they guarantee a natural cleaning process for the surface of the tongue. When brushing the teeth, make sure that you use the other side of the toothbrush in order to clean the tongue as well. A tongue scraper can be used at home, in order to eliminate the green coating and promote a faster healing process. Sugary foods and dairy should be eliminated from the diet, as these lead to increased mucus production at the level of the tongue.
Natural remedies
These are the most common natural remedies that are recommended for the symptoms associated with the green tongue:
- Turmeric and honey
- Mix the two natural remedies into a paste
- Both have strong antibacterial properties
- Can be used to keep the oral thrush under control
- Mint/clove
- Recommended for the bad breath (halitosis) associated with the green tongue
- Vitamin C
- Enhanced immune system
- Prevention/elimination of oral thrush
- Baking soda
- Exfoliating properties
- Maintain a good pH level in the mouth (acid neutralization)
- Mix it with lemon juice and apply the resulting paste to the tongue
- Rinse afterwards with water
- Salt
- Brush your tongue gently with salt (natural tongue scraper – remove debris and dead cells)
- Antiseptic properties (elimination of bacteria)
- Probiotics
- A capsule should be mixed with water, the solution being used instead of mouthwash
- Glycerin
- Apply the vegetable glycerin to the tongue and brush it gently
- Be sure to rinse with warm water afterwards
- The procedure should be repeated until the tongue regains its natural color
- Aloe vera
- Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties
- May remove the coating on the tongue, as well as eliminate the bad breath
- Recommended choice – fresh aloe vera juice
- Colloidal silver
- Recommended in the situation of yeast overgrowth at the level of the mouth
- Natural antifungal properties, also helps with the bad breath
- Should be diluted with water before usage
- Neem (Indian lilac)
- Antifungal and antibacterial properties
- Blood purifier (toxin removal)
- Recommended – boiled in water, used for gargle
- A thorough rinse with water is required to complete the process.