Thrombophlebitis
What is Thrombophlebitis?
This is the inflammation of one or more of your veins. Breaking the word down, “Thrombo” means blood clot and “Phlebitis” means inflammation of vein. It is also called phlebitis for short.
Types
There are two different types of thrombophlebitis, which are:
Superficial vein thrombophlebitis
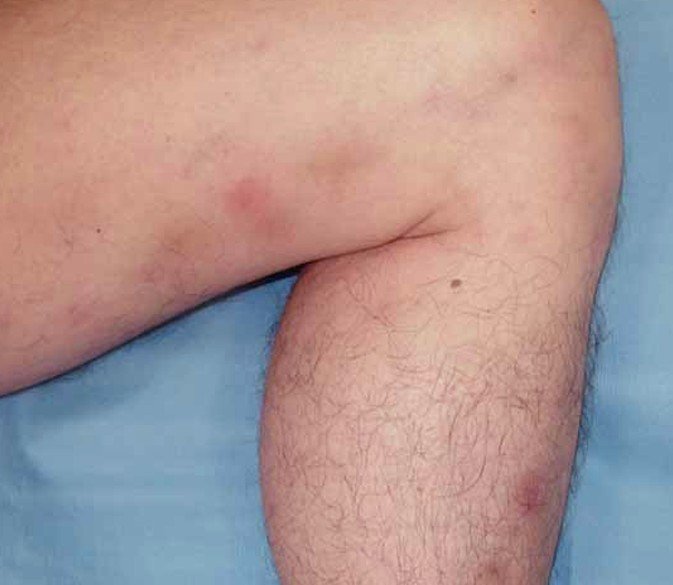
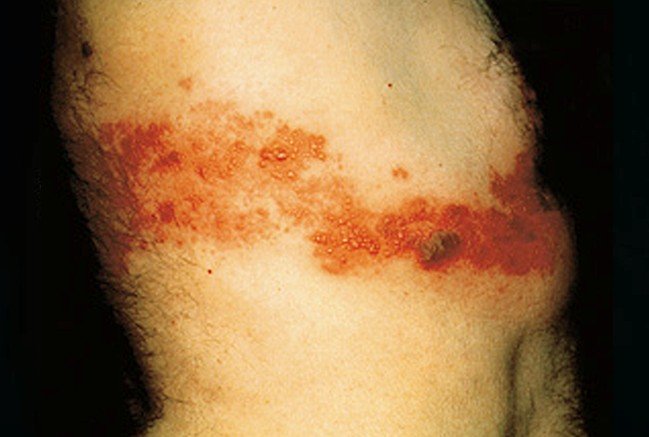
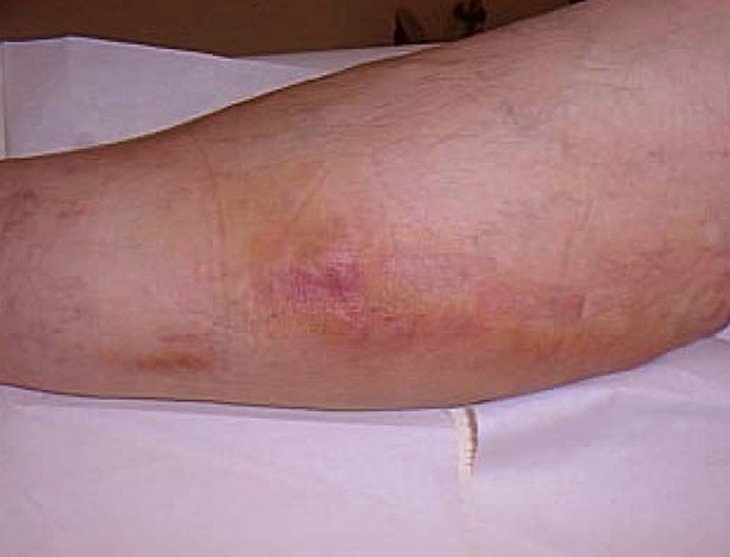
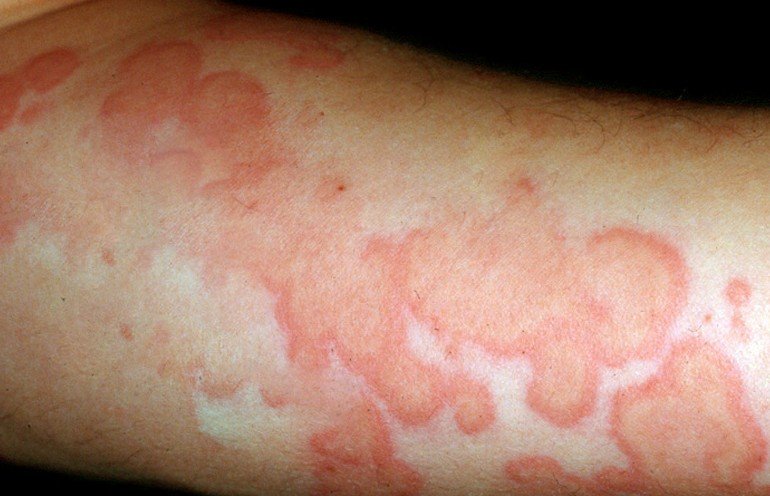
This is when the inflammation is just below the surface of the skin. This type of thrombophlebitis will usually cause no pain and are harmless. The clots will gradually break apart as they flow along with the blood. They could also be a symptom of deep vein thrombophlebitis.
Deep vein thrombophlebitis
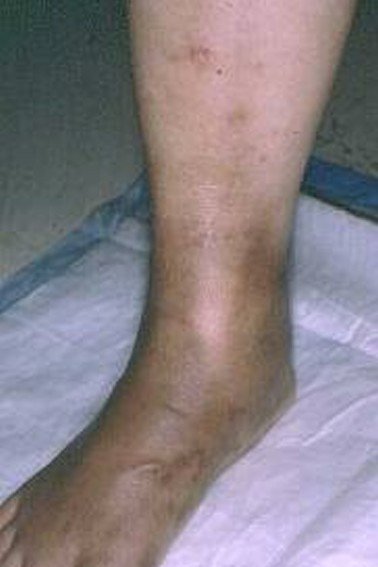
This is when the inflammation is in a deep vein, normally in your abdomen or lower area of your legs, and implanted in your muscles. They are harmful and can lead to damage of your vein that is permanent.
Thrombophlebitis Symptoms
The main symptoms of thrombophlebitis are:
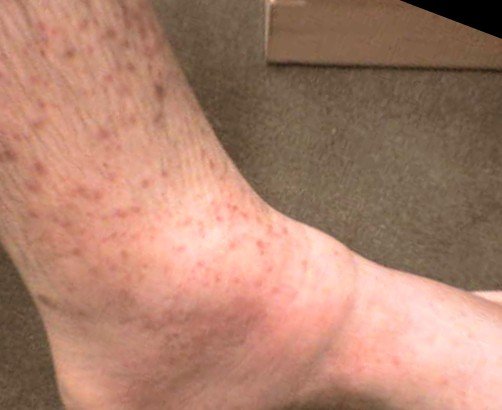
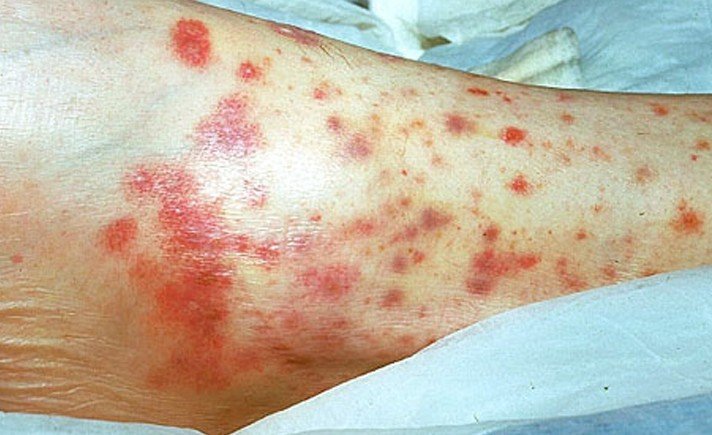
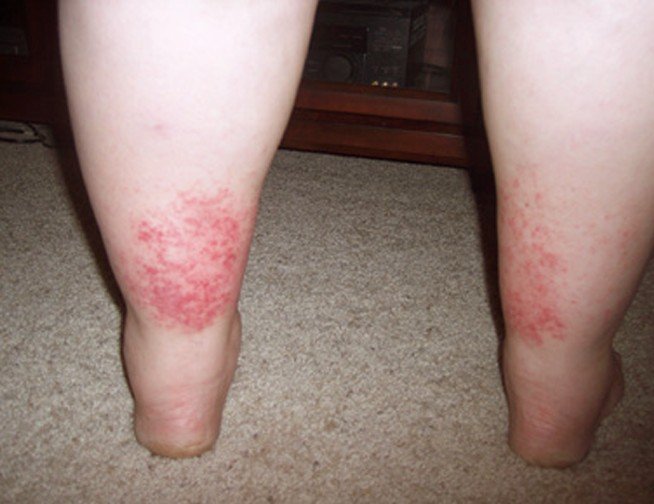
- In the affected area you will notice pain, warmth, and tenderness.
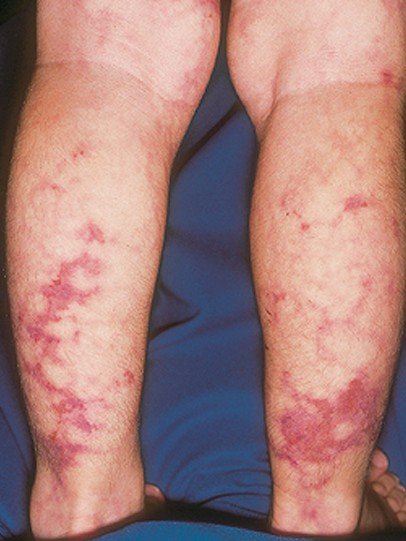
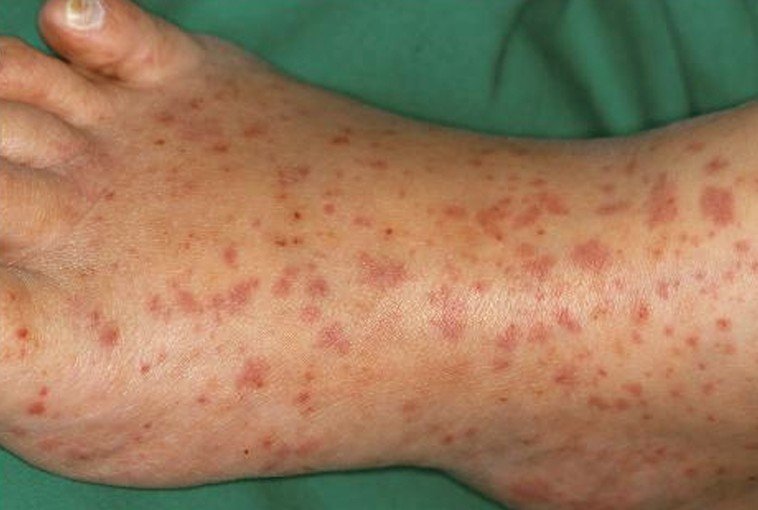
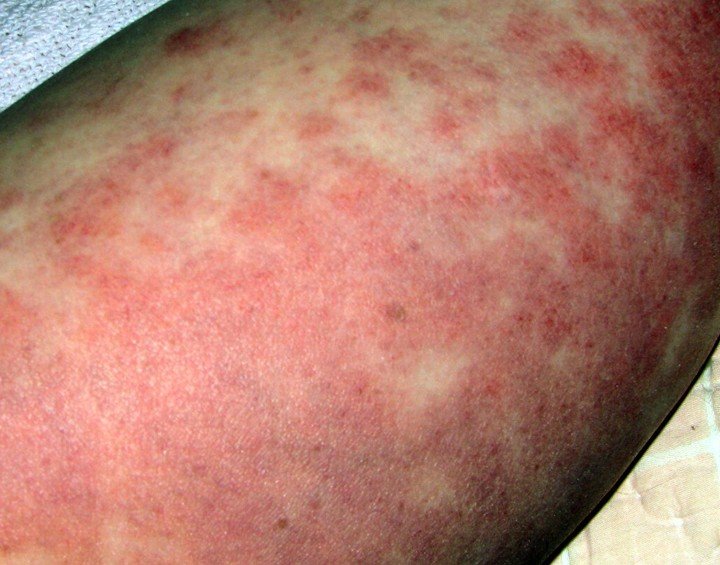
- Swelling and redness and irritated tissue and skin around the area.
- You may have a fever.
- Having pain when flexing your ankle.
- Having a swollen ankle or foot especially if it is just one side that is swollen.
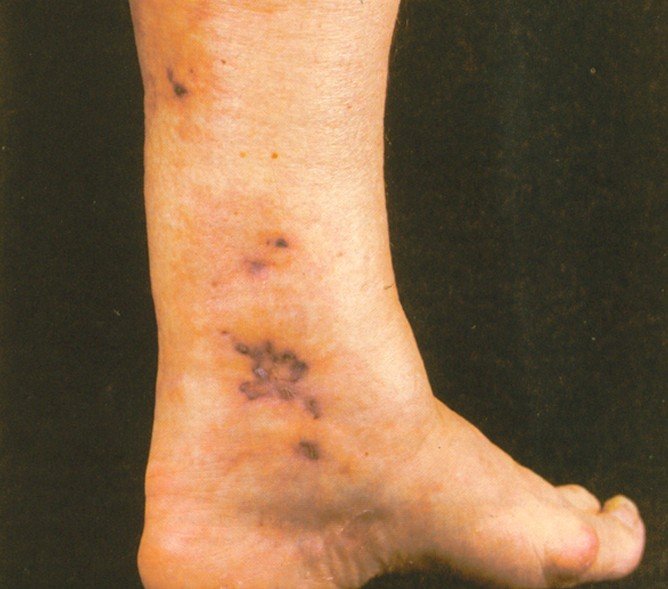
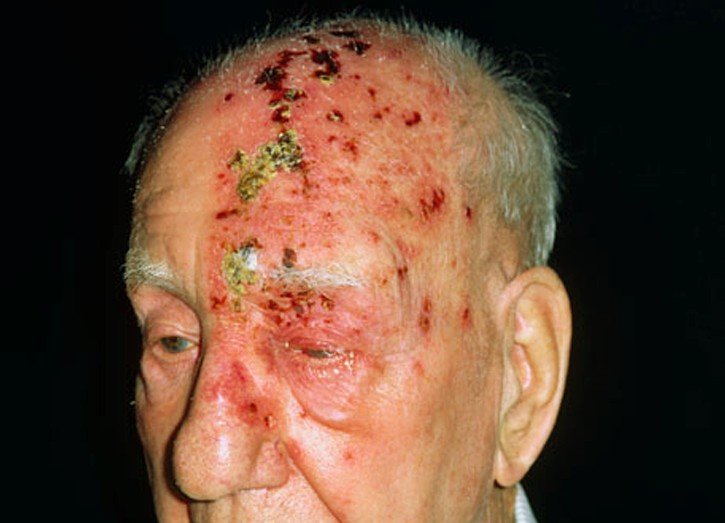
If it is superficial vein thrombophlebitis and the skin is affected you may notice a hard, tender, red cord just underneath the surface of the skin. Both of the above symptoms are more common in deep vein thrombophlebitis but can happen in superficial vein thrombophlebitis. Many times a person with deep vein thrombophlebitis you will not symptoms at all. You mostly notice these symptoms when you are walking or standing.
There is a possibility that in a deep vein thrombophlebitis that the blood clot will travel to other parts of your body such as your lungs, heart, etc. This could cause an embolism, which is a blockage of you blood vessel. It this happens a person may show these symptoms.
- Heart rate that is increased
- Being short of breath
- Having chest pains
If they have any of these symptoms you should see immediate medical attention because the blood can become dislodged and cause death if it settles in the wrong place.
Thrombophlebitis Causes
The main cause of thrombophlebitis is the formation of a blood clot or clots. These clots will usually affect the veins in your legs but they can also affect the veins in your neck and arms. Basically anything that causes your blood not to circulate the right way can cause a clot. There are several risk factors that can cause a person to form a blood clot.
- Having any type of injury to the vein that can lead to a blood clot forming.
- Using birth control pills.
- Being required to be on bed rest for a long period of time after having surgery of any type, having a heart attack, injury, etc.
- Smoking
- Type 2 diabetes
- Sitting in the same position or being inactive for a long period of time like sitting in a car or on an airplane.
- Having a deficiency in your blood that will prevent the normal dissolution of the blood clot. This could be a deficiency such as vitamin B-12 deficiency.
- A blood clotting disorder that is inherited.
- Having cancer like pancreatic cancer that causes an increase of pro-coagulants, which is necessary for your blood to clot.
- Having a stroke that caused your legs or arms to be paralyzed.
- Having a catheter in a central vein for treating a medical condition and it irritates your blood vessel wall causing a decrease in blood flow or having a pacemaker.
- Having just had a baby or are pregnant possibly causing an increased pressure in the veins of your legs and pelvis.
- Using hormone replacement therapy.
- Having the tendency to easily form blood clots.
- Being obese or just overweight.
- Being over the age of sixty.
Thrombophlebitis Treatment
What treatment plan your physician decides to use will depend on were the blood clot is and the type of thrombophlebitis it is. If it is a superficial vein thrombophlebitis it can be cured by externally treating the area but with a deep vein thrombophlebitis you need urgent treatment to prevent an embolism from developing. Your physician may prescribe medications like anti-coagulants to help prevent the clots from enlarging. They may also prescribe pain medication or over-the-counter pain relief medications.
For treating superficial vein thrombophlebitis elevating and bandaging the area can sometimes help. The physician will use clot busters to treat deep vein thrombophlebitis to help in dissolving the blood clot. If there is an infection the physician will prescribe antibiotics. Wearing support hose can help with the discomfort. If the vein is severely affected by thrombophlebitis the physician may have the affected vein or blood clot surgically removed.
You should also avoid sitting for long periods of time. On long car rides stop several times so you can get out and stretch and walk around. Normally a case of superficial vein thrombophlebitis will improve within seven to fourteen days and usually does not require hospitalization.

 Many times when you have Leukocytosis you may or may not have any symptoms. If you do have any symptoms they are usually caused by the disease that is causing the increase in your white blood cell production. Some of the common symptoms you could have include:
Many times when you have Leukocytosis you may or may not have any symptoms. If you do have any symptoms they are usually caused by the disease that is causing the increase in your white blood cell production. Some of the common symptoms you could have include: