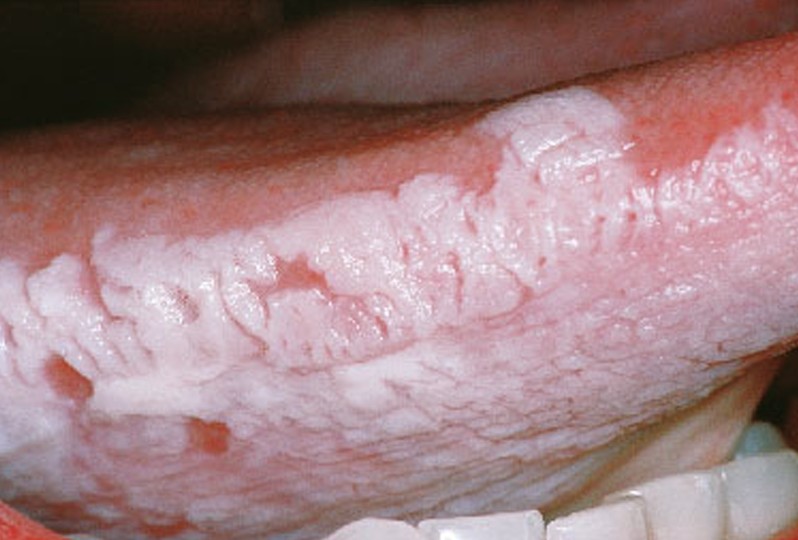
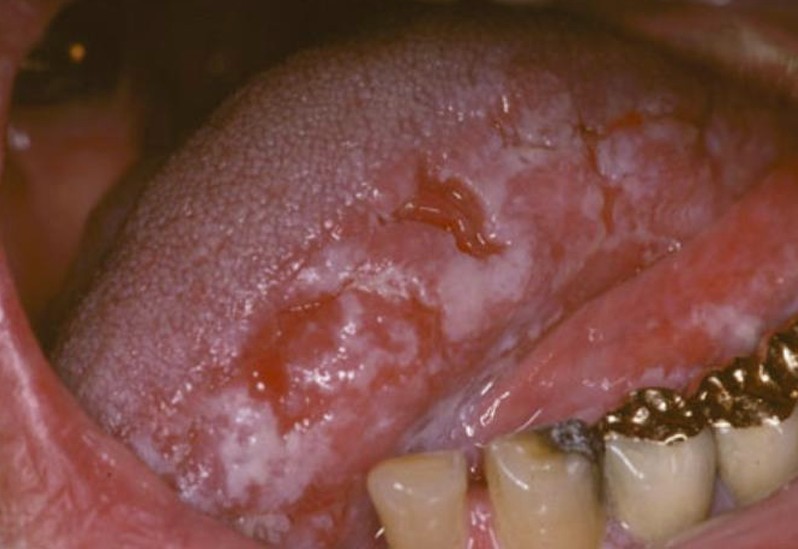
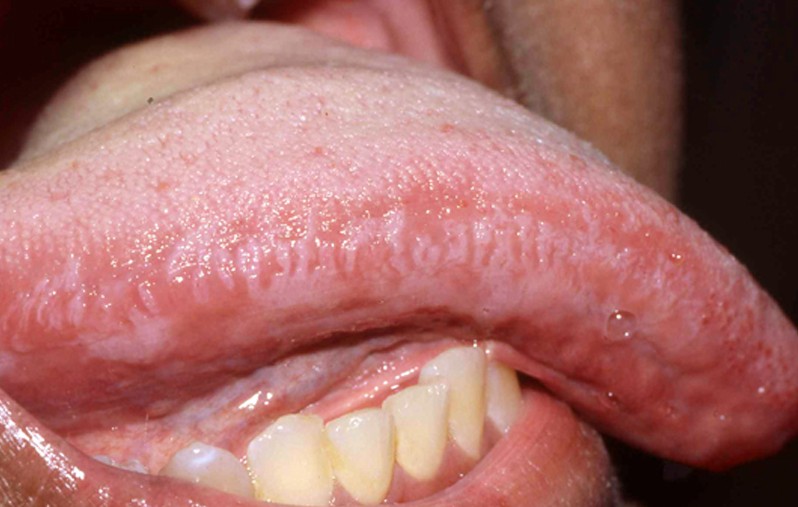
Oral Hairy Leukoplakia
Oral hairy leukoplakia is a disease of the oral mucosa that was first described in 1984. It is strongly associated with the HIV infection; this is why it is also known as HIV-associated hairy leukoplakia. This condition is primarily characterized by the appearance of a white patch on the sides of the tongue; this patch has a hairy-like appearance, hence the name. The lesion cannot be scraped off but it is benign.
The main culprit behind the diagnosis of oral hairy leukoplakia is the infection with the Epstein-Barr virus. Once infected, this virus stays inside the body for the entire lifetime and it becomes activated when the immune system is weakened. This is the reason why there is such a strong association between HIV/AIDS and this medical condition. In many cases, the appearance of the white patch on the tongue is a clear sign that the treatment administered against the HIV virus does not provide the desired results. It may also be the first sign that suggests an infection with the HIV virus or the first sign of an infection with another virus (however, it generally suggests that the immune system has been weakened).
Oral hairy leukoplakia appears in HIV negative patients as well, especially those that have a compromised immune system due to other types of infection or various medical conditions (for example, in patients who have undergone organ transplants or who have received chemotherapy for different types of cancer). Even though its name is similar to the one of hairy tongue, these two should not be confused. Oral hairy leukoplakia and hairy tongue are two separate medical conditions, with different symptoms and treatments.
What does Oral Hairy Leukoplakia look like?
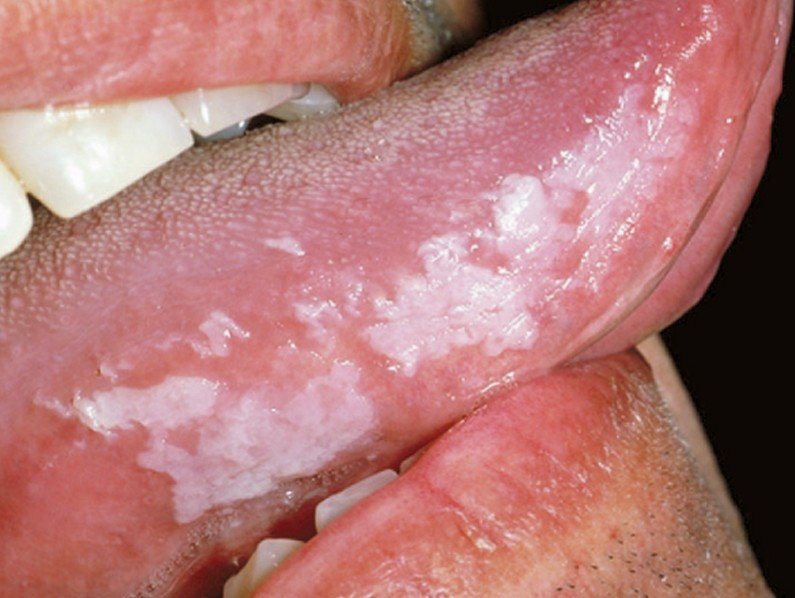
The primary lesion in this medical condition is a white patch on the sides of the tongue. The patch can appear on one side or on both sides of the tongue. The hairy like appearance is characteristic for this condition.
Symptoms of Oral Hairy Leukoplakia
These are the most common symptoms of oral hairy leukoplakia:
- White patch on the lateral borders of the tongue
- Often asymptomatic (no pain)
- Daily change of appearance
- Spontaneous appearance and disappearance of the lesions
- Unilateral or bilateral involvement, not necessarily symmetric
- The lesions are continuous or discontinuous along the tongue lateral borders
- The lesions cannot be scraped off, as they are adherent (scraping will only remove the superficial layers)
- Can also affect the dorsal or ventral surface of the tongue and the buccal mucosa or the gums
- In rare occasions, it can affect the soft palate, the pharynx or the esophagus
- Lesions can become thickened or hardened in some areas
- The lesions look similar to the ones that appear in cases of candida infections (oral thrush), the difference being that they cannot be scraped off
- Lesions can be:
- Small, flat and smooth (this type of lesion is characteristic for the appearance on the ventral surface of the tongue, the buccal mucosa or gums)
- Hairy appearance (prominent folds)
- Red prominent lesions – these are a sign of potential malignancy (pre-cancerous lesions) and they appear quite rarely
- Mild pain
- Abnormal sensations in the tongue
- Taste alteration
- No associated inflammation or redness
- Psychological impact (cosmetic concern)
What are the Causes of Oral Hairy Leukoplakia?
These are the most common causes that lead to the appearance of oral hairy leukoplakia:
- The white patch appears because of the increased keratin production and the hyperplasia of the epithelium
- Infection with the Epstein-Barr virus – the virus enters a person’s body and will remain there for the entire life, waiting for the weakening of the immune system in order to be reactivated.
- Frequent association with HIV/AIDS
- General immune-suppression (viral infections)
- Association with organ transplants and treatments for cancer and especially leukemia (chemotherapy, immunosuppressive medication)
- Association with Behçet syndrome and ulcerative colitis
- Appears in rare cases in otherwise healthy people, with a competent immune system
- Chewing tobacco, drinking excessive quantities of alcohol and smoking are considered risk factors (especially in men who have already received a diagnosis of HIV infection)
Treatment
The lesions in oral hairy leukoplakia are benign, so they do not require any particular treatment. However, these are the most common courses of treatment in case of associated symptoms:
- Antiviral drugs – the administration of this medication in high doses leads to the rapid disappearance of the lesion but the white patch will re-appear just as fast the moment the treatment is discontinued or the immune system becomes more and more compromised. The most often administered antiviral drugs are:
- Acyclovir
- Desciclovir
- Ganciclovir
- Foscarnet
- Valacyclovir/Famciclovir – new drugs, higher oral bioavailability, can be taken less often
- Topical treatments – these provide temporary remission as well. The most commonly recommended topical treatments are:
- Podophyllum resin (cytotoxic agent) – the treatment has the following adverse effects: pain in the local area of application, discomfort and taste alteration
- Retinoids
- Antiretroviral drugs – these guarantee the most promising results when it comes to the regression of oral hairy leukoplakia lesions. The recommended choice for anti-retroviral medication is:
- Zidovudine
- Ablative therapy – this treatment is recommended only in case of small lesions.
- Cryotherapy – even though it has shown promising results for the treatment of oral hairy leukoplakia, this is not a common course of treatment.
- Topical applications with gentian violet have also shown to improve the lesions in this medical condition.
- Treatment of secondary infections (Candida) should be provided as well. This should be done with the proper anti-fungal medication.
- In rare cases, the surgical removal of the lesions is recommended. However, this is not often the primary choice of treatment and it may be done only on large patches.
- Ongoing medical treatment is necessary to prevent the lesions from occurring. It is recommended that you go to the doctor’s office for follow-up every three months.
- This condition can be prevented by reducing the alcohol and tobacco intake.
- The treatment for the HIV infection should be re-considered and a new treatment plan should be devised, as the presence of oral hairy leukoplakia is often a sign that the actual treatment is not working.
Oral Hairy Leukoplakia Pictures
Here are some of the pictures collection of the medical condition Oral Hairy Leukoplakia…