Coughing up Phlegm
Have you been coughing up phlegm and the development is giving you a big challenge? Are you afraid you could be suffering from tuberculosis, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, or pneumonia? But let me quickly assure you that by the time you finish reading this article, you would have been able to come to term with what exactly the problem is.
Coughing up phlegm could represent so many things. While some could be potentially life-threatening, others are nothing to worry about – just a transient development that would get resolved in no time.
People always are alarmed each time they notice something strange about their health. Nobody wants to be debilitated, nobody wants to die untimely, and nobody loves to be seen as a potential source of infectious disease that could possibly spread to other people. You are not the only who is alarmed seeing such development in his health. Well, the reason we are here is to take care of that fear and get you the right information regarding your condition.
What is Phlegm?
Phlegm is the thick viscous liquid or substance secreted by the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract (not including the nasal passages), especially when they are produced in an unusually high quantity, and particularly that which is expelled through coughing. The cells in charge of the production of phlegm produce up to 1 – 1.5 liters of phlegm daily, even when you are healthy.
Most of the times, a higher quantity of phlegm is produced during an ongoing disease process. Therefore, it is likely to contain bacteria, sloughed-off inflammatory cells, and debris. There is usually an inflammatory process that results in the production of phlegm. If phlegm is coughed out or expectorated, it becomes sputum.
Why am I Coughing up Phlegm?

You can cough up phlegm for several reasons. But if you are interested in knowing why you have such challenge, then we shall quickly let you know a few reasons why it happens. So, here are some of the reasons behind your coughing up phlegm.
Smoking
Smoking leads to the inhalation of hot, dry, polluted air which results in the drying of the vocal cords. Each time you take in a puff of cigarette smoke, you pollute the larynx, making it difficult for the larynx to recover immediately and rehydrate itself within 3 hours. The vocal cord, on the other hand, needs to be fairly hydrated in order for it to function effectively. With the continual deprivation of the larynx of water, it gets inflamed and begins to swell. The inflammation and swelling of the vocal cord lead to the body trying to go into a compensatory mechanism in order to minimize the dryness. This eventually brings about the production of phlegm. Sometimes, one could still suffer from phlegm after giving up smoking, due to the effects of the toxins released from the cigarette over time. The toxins released from the cigarette can lead to chest pain, irritation of the lungs, sore throat or make you have bad taste.
Air pollution
This works almost the same way like smoking, in that, air pollution leads to the release of potentially harmful materials which cause the dryness and irritation of the respiratory tract. The body eventually responds by producing phlegm in an attempt to remedy the situation and reduce the level of dryness.
Illness
In the course of an illness like cold, flu or pneumonia, the amount of phlegm secreted becomes more as the body tries to overcome the foreign bodies (such as viruses, bacteria, etc) that are responsible for the assault on the body. One good example of an illness that leads to an excess secretion of phlegm is acute bronchitis. In acute bronchitis, the offending organism is usually a virus. In that case, it is not advisable to treat the illness with antibiotics except where it is established that it is being caused by bacteria. In the elderly, phlegm production during illness can be quite much, making them spit every now and then.
Abuse of the vocal cord
The vocal cord (voice) can be abused in different ways – screaming, yelling, clearing of the throat several times, singing with wrong notes or talking loudly. Screaming and yelling lead to the vocal cord vibrating and hitting against themselves, leading to inflammation and the secretion of phlegm. Clearing of throat works pretty the same manner as screaming and yelling. Throat clearing helps to loosen or remove phlegm. However, throat clearing leads to the vocal cord hitting against each other, leading to inflammation of the cord as well as phlegm production. Excessive screaming, yelling and using of the wrong music note to sing can also lead to inflammation and eventual formation of vocal nodules (a mass of tissue forming on the vocal fold, causing hoarseness, frequent vocal breaks, painful speech production, etc). The vocal nodules can sometimes be felt as a lump in throat.
Hay fever
In hay fever, the inner linings of the bronchioles are inflamed, leading to the excess secretion of phlegm. The phlegm secreted in high amount can sometimes lead to the clogging of the airway.
Asthma
The excess secretion of phlegm in asthma happens the way like it does in hay fever. In severe chronic asthma, there could be coughing up of jelly phlegm from the respiratory tract.
Gastro-esophageal reflux
Heartburn can lead to the secretion of more mucus in the throat also. People who have this problem usually find it difficult to tolerate highly oily foods, some forms of proteins, etc.
Whooping cough
This is another medical condition known to cause persistent coughing with the hypersecretion of mucus. The condition is common in children, but can be prevented with regular vaccination.
Croup cough
This is a viral infection of the larynx or voice box and the tracheal, with visible signs and symptoms associated with viral infection, such as a runny nose, cough and high secretion of mucus.
How to Stop Coughing up Phlegm?
There are several ways you can reduce the secretion of phlegm and totally stop the embarrassment it brings to you. Have you been faced with the issues of excess phlegm secretion lately? Here are some of the things you can easily do to take care of and arrest the situation.
- Drink plenty of water: Water is a good liquefier. So, while your body’s immune system tries to take care of the offending organism, water is required to assist the system in getting rid of the offender.
- Spit out the mucus: Get ready to spit out the mucus when they are formed and accumulate in your throat. Don’t ever swallow the phlegm in order not to cause more harm to your body. Keep a toilet paper or handkerchief close by and make use of them to receive the sputum.
- Minimize exposure to hazardous fumes: Since hazardous fumes play a role in causing hypersecretion of phlegm, one way to get rid of the problem, therefore, is to minimize or entirely stop your exposure to the fumes.
- Stop consuming dairy foods: Individuals differ a lot. While dairy products like milk, yogurt, and others may not directly cause the secretion of phlegm in people, the fatty content in them makes the secretion of mucus thicker in some people.
- Stay away from smoking: We have earlier explained how smoking leads to excess production of mucus or phlegm. If you want to reduce or completely eradicate the problem, therefore, you need to stay away from smoking.
- See the doctor: if you are not too sure what the cause of the problem is or if the condition is what you cannot handle, it is better to see the doctor who would prescribe the right drugs for you.
Coughing up Yellow Phlegm
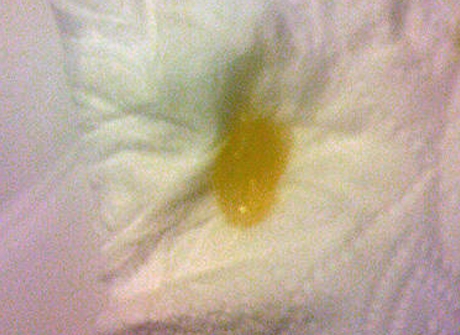
Coughing up yellow phlegm is a sign of something wrong going on in the respiratory system. Oftentimes, they are signs of lower respiratory tract infection, sinus infection, bacterial infection, bronchitis, allergy, flu or cold. This can, in some cases, be followed by wheezing, chest pain, and you may find it hard to breathe.
What do you do when you have yellow phlegm? It is always better to see the doctor since the problem may be deep-seated. The doctor knows exactly the kinds of investigations to carry out in order to determine the root cause of the problem, and then how to cure the problem.
Coughing up Rusty or Brown Phlegm

Respiratory tract infections are not limited to only yellow phlegm secretion. Occasionally, one can be amazed to see oneself coughing up rusty or brown phlegm. But what exactly does rusty or brown phlegm stand for? That may just be your greatest headache. But, don’t worry! We are here for you.
Rusty or brown phlegm occurs with too much inhalation of smog or dust. It is common in people who are exposed to dust such as bricklayers, construction workers or block molders. However, rusty phlegm can also indicate the presence of an infection or blood in the respiratory tract. When there is bleeding into the respiratory tract, some enzymes work on it if it stays there for a long time. This changes the color to brown or rusty color. It can occasionally come with black spots in the phlegm.
It is also present in people who smoke a lot. This is as a result of the excessive resin, tar and other particulate matters present in cigarette, which the body tries to reject by coughing them up. It can also result from the type of food one has eaten.
If you work in an area that requires regular exposure to dust particles, it is advisable to use special masks that make it difficult for dust particles to penetrate into your respiratory system. But when you see such development, see the doctor immediately for help.
Coughing up Bloody Phlegm
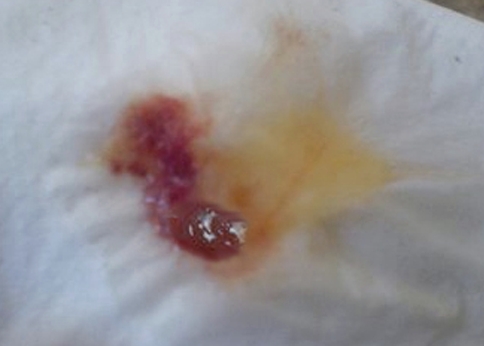
Bloody phlegm usually comes from bleeding within the respiratory tract. This is an indication that an organ has been injured. This can manifest as brightly colored phlegm or pink phlegm. Periodically, there could also be red spots in the coughed up mucus showing that blood is present in the mucus.
The main causes of bloody phlegm include injury to the respiratory organs, tuberculosis, pulmonary embolism, cancer, mitral valve stenosis, lung abscess, cystic fibrosis, parasitic infection, etc. If you have been involved in an accident and then started seeing bloody phlegm or you have been having a cough that won’t just go, it is good to see a doctor to find out if there has been major organ damage.
Dark green Phlegm
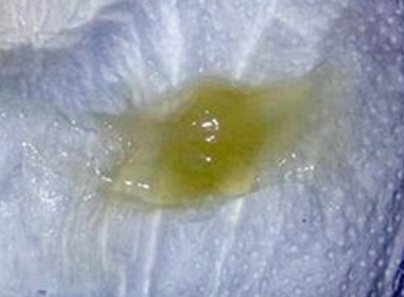
Phlegm could also come in dark green color. When such occurs, it most of the times, signifies the presence of bacterial, viral or other forms of infection such as pneumonia. Pneumonia is caused by bacteria, viruses, chemicals, aspiration of foreign bodies and lot of other things.
When the infection occurs, the body tries to get rid of it by sending its white blood cells (neutrophils) to the area. However, the presence of green proteins in the white blood cells could turn the phlegm to dark green, especially if the number of white blood cells deployed is much.
Pneumonia or other lower respiratory tract infections can be quite disturbing and could be potentially life-threatening especially if not handled in time. Once you see your sputum turning green, it is time to quickly see a doctor without further waste of time.
White or Grey Phlegm

White phlegm also stands for something different from what we have already talked about so far. It is a sign of upper respiratory tract infection or sinus congestion. Infection in the sinus (viral or bacterial) will cause it to be inflamed and drain phlegm into your throat.
But when you have grey phlegm, it could be that the body is trying to overcome accumulated resin or tar from excessive cigarette smoking or from the inhalation of air pollutants like smog and dust.
Pink Phlegm

Pink phlegm results from the presence of edema (swelling) in the lungs which are caused by the accumulation of fluids. Periodically, it can show up as streaks or stains when there is mild bleeding in the respiratory tract. In people with a pre-existing heart problem, the pink phlegm could come with a frothy texture. In any case, you are advised to see the doctor for investigation and management.
Home Remedies
There are a lot of things you can do at home in order to ease the discomfort of the excess phlegm secretion. Here are a few ones to help you.
- Drink lemon tea with honey: Lemon tea is quite helpful in relieving phlegm secretion. Add 2 teaspoons of lemon into a cup of warm water. Add a teaspoon of honey to the mixture and sip. The acidity of the lemon juice helps to break up the phlegm or mucus, while the honey plays a role in soothing your throat.
- Eat spicy foods: Spicy foods like wasabi, chili pepper or horseradish are known to decongest the respiratory tract. That is why you start having a runny nose after eating them. If you are faced with excess phlegm secretion, one good way to decongest the system, therefore, is to take any of the aforementioned spices.
- Gargle with salt water: Gargling with salt water helps to decongest the respiratory tract too and make it easy to cough up the mucus. Simply add ½ teaspoon of salt to a cup of warm water and use it to gargle, while your head is tilted backward.
- Drink warm liquids/fluids: Warm liquids or fluids play an important part in helping to relieve the symptoms of excess phlegm secretion. Fluids that can help out include pepper soup, warm chicken soup, tea, etc. They play a dual role of nourishing the body as well as assisting in breaking up the phlegm in your throat.
- Use turmeric drink: Turmeric helps to make your immune system stronger. It also has antiseptic properties that can assist in killing the offending bacteria thereby reducing the rate of the production of the phlegm. Add 1 teaspoon of turmeric to 1 glass of hot milk. Drink it twice daily. You can as well mix a tablespoon of turmeric and a pinch of salt in a glass of hot water and use it to gargle as many times as you can daily.
- Drink cider vinegar: You only need to take a teaspoon at a time. The taste may not be palatable but it sure helps in breaking that nasty phlegm. Swallow the teaspoon of cider as fast as you can and then wait for 5 – 10 seconds for the taste to clear off. But if the taste still remains after the time elapses, take some water to clear it off.
- Use ginger: Ginger is a natural decongestant and can help you clear the throat of that mucus. Add 1 teaspoon of fresh ginger slices to 1 cup of boiled water and steep for a few minutes. Add 2 teaspoons of honey, and drink it several times a day. This will help loosen the phlegm and even assist in fighting the infection since ginger is known to possess some antibacterial and antiviral properties. You can as well chew raw ginger if you can, or you can add it to your dishes.
- Inhale steam: Inhaling steam helps to loosen the mucus and make it easy to cough it up. You can make use of a vaporizer if there is one handy.
- Eat toast: Toast can really help get the phlegm off your throat fast. Toast removes the phlegm as it softly scrapes the throat while being swallowed.
Coughing up Phlegm in the Morning
Phlegm could be coughed up any time of the day. But specific times could stand for different things. So, coughing up phlegm in the morning is mainly a sign of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). As is common with the condition, the cough is worse off in the mornings with high mucus or phlegm production. But symptoms ease in severity as the day progresses. You may find it hard to breathe especially when involved in a physical activity. Other symptoms include wheezing, chest tightness, fatigue, and sometimes, your chest hurts.
One major cause of COPD is smoking. COPD could include chronic bronchitis and emphysema. With emphysema, the elasticity of the air sacs of the lungs is gradually lost and the condition gets worse. But in chronic bronchitis, there is swelling in the linings of the lungs, which is the reason you find it hard to breathe.
Coughing up Phlegm but Not Sick
Understandably, phlegm secretion is made worse in illness. However, are you coughing up phlegm but not sick and with no other symptoms? Here are the possible reasons this is happening to you. It could be the normal production of phlegm by the respiratory tract which could be slightly more in some people than in others.
You may not be having any visible signs and symptoms of illness, but there could be something else going on in the system. Such conditions can be early pregnancy, irritants from the surrounding environment, allergy to dander, or after giving up smoking.
Coughing up Phlegm after Eating
The kind of food you eat can lead to coughing up of phlegm after eating. This is mostly common with eating oily foods, fried foods, caffeinated drinks, yeast infection of the vocal cord, and alcohol. They cause irritation of the throat thereby leading to more phlegm secretion into the throat.
The color of the mucus secreted and coughed up after food would, to a large extent, depend on the type of food eaten. For instance, it could be brownish after eating chocolate, drinking red wine or coffee.
Coughing up Phlegm for Days, Weeks and Months
It is expected that phlegm should last for just a few days and then be resolved. However, a few cases of the phlegm lasting for several days to weeks and months exist. In that case, there is either something the body is rejecting in the environment such as allergens, or the condition is as a result of other chronic illnesses like COPD, bronchitis or infections like tuberculosis, pulmonary emphysema, etc.
So long as the root cause is not addressed, the cough will continue to remain. If you suspect an allergen, then find out exactly what the allergen is and get rid of it. If due to a disease condition, see the doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Conclusion
Coughing up phlegm comes in different forms, colors, and gravity. It could be the body’s normal secretion or a sign of an infection, inhalation of pollutants or injury to the respiratory tract. Whatever the reason, we have outlined a lot of things you could do to alleviate the symptoms (home remedies and treatments). If you apply any of the suggestions we have made, you will surely get rid of the challenge.










 The main function of hemosiderin is to contribute to the repairs that are necessary after an acute hemorrhage. When a blood vessel has ruptured, the red blood cells will die and the hemoglobin (part of the red blood cell) is going to be released into the extracellular space. The reticulo-endothelial system has cells with phagocytic properties; these are also known as macrophages and they will consume the released hemoglobin, leading to the production of biliverdin and hemosiderin.
The main function of hemosiderin is to contribute to the repairs that are necessary after an acute hemorrhage. When a blood vessel has ruptured, the red blood cells will die and the hemoglobin (part of the red blood cell) is going to be released into the extracellular space. The reticulo-endothelial system has cells with phagocytic properties; these are also known as macrophages and they will consume the released hemoglobin, leading to the production of biliverdin and hemosiderin.