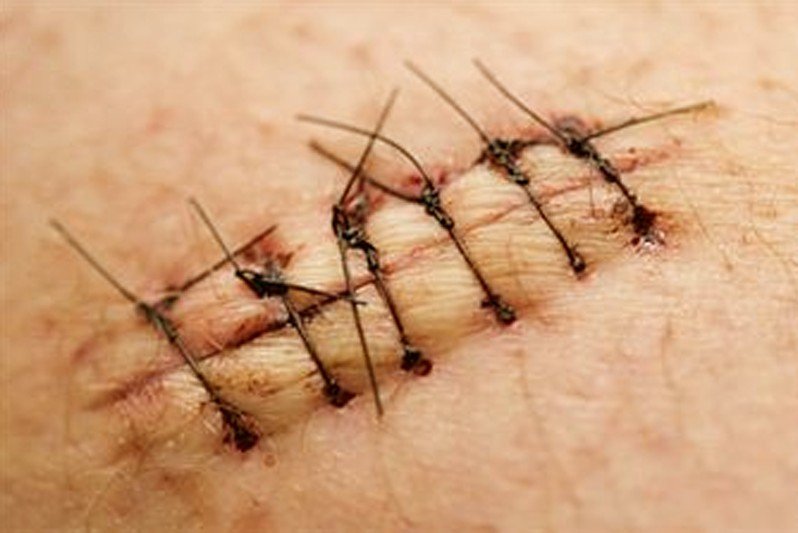
Dissolvable Stitches
What are Dissolvable Stitches?
Stitches are used in the surgical field, being made with the help of a threaded needle. The method is known as surgical suturing and it is used by a wide range of medical professionals, including oral surgeons, general surgeons and even doctors performing surgery on animals. The advancements in the medical field have allowed for new stitches to be used, the dissolvable stitches represent an often popular choice. These are also known as absorbable sutures and they are recommended for the suturing of both internal and external wounds.
Unlike the normal stitches, the dissolvable stitches will be absorbed by the body and they do not need to remove. This means that the recovery time after a surgery is considerably reduced and the patient will not need a second visit to the doctor’s office to have his stitches removed. Today, these kinds of stitches are chosen for the suturing of superficial wounds but also for complex surgeries that require internal stitching, such as the surgery on the heart or the transplantation of different organs. The main thing to keep in mind is that dissolvable stitches will allow for a wound (internal or external) to heal properly, being resorbed without any additional consequences.
What are dissolvable stitches made of?
 The human body is designed so as to eliminate any foreign substance, when coming into contact with it. This is the reason why dissolvable stitches are resorbed on their own, as the body tries to eliminate them as they are foreign substances. The materials chosen for the making of dissolvable stitches include collagen, hair or silk. A wide range of other artificial materials can be chosen for the making of these stitches – the important thing is that the right material is selected, so as it can be easily broken down by the human body.
The human body is designed so as to eliminate any foreign substance, when coming into contact with it. This is the reason why dissolvable stitches are resorbed on their own, as the body tries to eliminate them as they are foreign substances. The materials chosen for the making of dissolvable stitches include collagen, hair or silk. A wide range of other artificial materials can be chosen for the making of these stitches – the important thing is that the right material is selected, so as it can be easily broken down by the human body.
How long for dissolvable stitches to dissolve?
The necessary time for these stitches to dissolve is mainly influenced by the material from which they are made and the area in the body where they are used. Also, the surgeon might decide on stitches made from a particular material if he/she wants to use them internally/externally. It goes without saying that the stitches applied on an external wound will take less time to dissolve, as they are superficial. On the other hand, internal stitches may take a longer time to dissolve, as the wound is deeper located and it takes considerably more time to heal.
On average, it takes somewhere around one or two weeks for the stitches to dissolve. After the surgery has finished and you wake up from the anesthesia, the doctor will guide you through the healing process and he/she will take time to explain how long it will take for the stitches to dissolve. Also, it can happen that the stitches do not dissolve entirely and you will need to visit the doctor in order to have them removed. However, this occurs only on rare occasions and the removal procedure is quite simple.
Features
There are several features that dissolvable stitches present, such as:
- Decomposition rate – it is important to understand that this rate varies according to the wound and how deep it is. As it was already explained, the dissolvable stitches for international wounds take a longer time to dissolve. On the other hand, the ones used for superficial, external wounds are characterized by a rapid decomposition rate.
- Elasticity – the degree of elasticity varies according to the type of wound and its location on the body. Often times, the surgeon will choose dissolvable stitches that have a higher elasticity to offer, for wounds that are superficial and external. Also, if the wound has occurred in an area where is a lot of movement (for example, the elbow or the knee), it is important to choose dissolvable stitches with high elasticity. Otherwise, the wound will re-open and it will take considerably longer for it to heal.
- Thickness – the thickness of the dissolvable stitches depends on how deep a wound actually is. The surgeon will choose less thick stitches for external and superficial wounds, preferring however thicker stitches for the internal or deep wounds.
- These stitches are resorbed in a natural manner by the human body, as opposed to non-dissolvable stitches.
- Unlike non-dissolvable stitches which require further removal, these stitches go away on their own and they do not require a second visit to the doctor’s office.
How do dissolvable stitches work?
When a doctor performs a surgery, whether internal or external, the wound needs to be stitched up. The doctor will decide to use dissolvable stitches, as these are easily resorbed and they do not require follow-up. If you are wondering how do dissolvable stitches work, then you should know these are perceived by the body as an unknown substance. When an unknown substance is identified as present in the human body, regardless of its location, the body will try to dissolve it. This is the reason why dissolvable stitches are resorbed without effort.
Depending on the wound’s location and depth, the doctor might decide to apply a higher number of stitches. When applied, dissolvable stitches function by helping the wound remain closed and heal properly. They remain in the body for as long as it is necessary for the wound to heal and then they gradually fade. In plastic surgery, dissolvable stitches are often chosen for their ability to be resorbed. They work in the same way as it was explained above, the main advantage being that they present a reduced risk for scarring. On the other hand, on internal wounds, the surgeon might decide to choose thicker dissolvable stitches, as these will work by keeping incisions made on vital organs close together.
In conclusion, dissolvable stitches are recommended for both internal and external wounds, delivering the advantage of rapid decomposition. The doctor will decide whether the wound should be closed with the help of dissolvable stitches or not. Also, it is important to maintain the recently sutured area clean, so as to prevent secondary infections that might appear.
Pictures
Here are some of the pictures of dissolvable stitches…