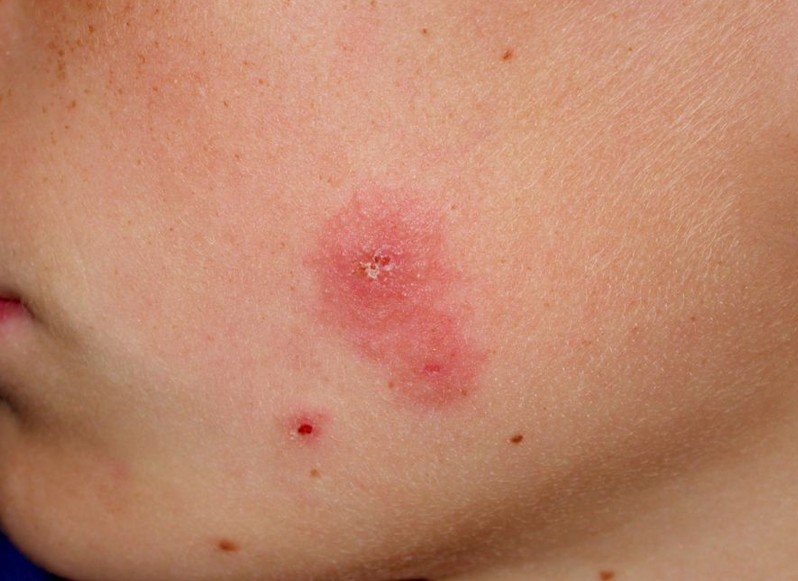
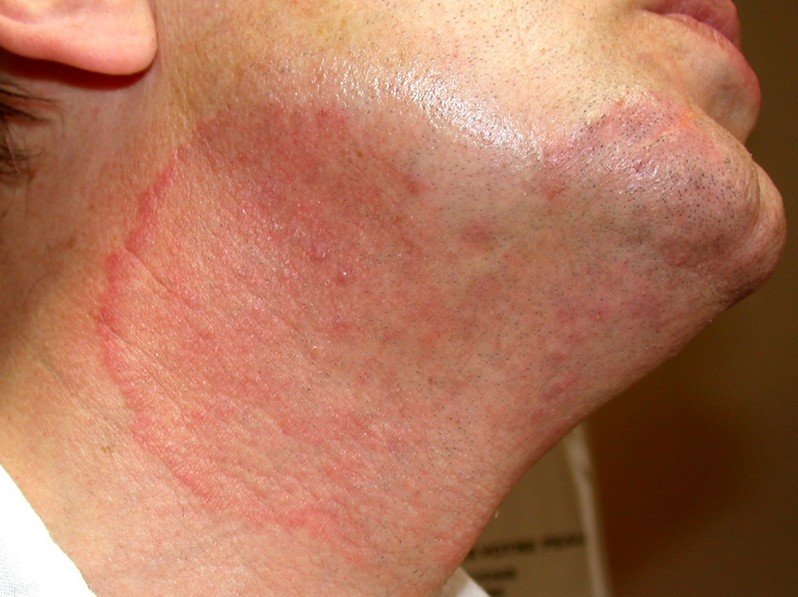
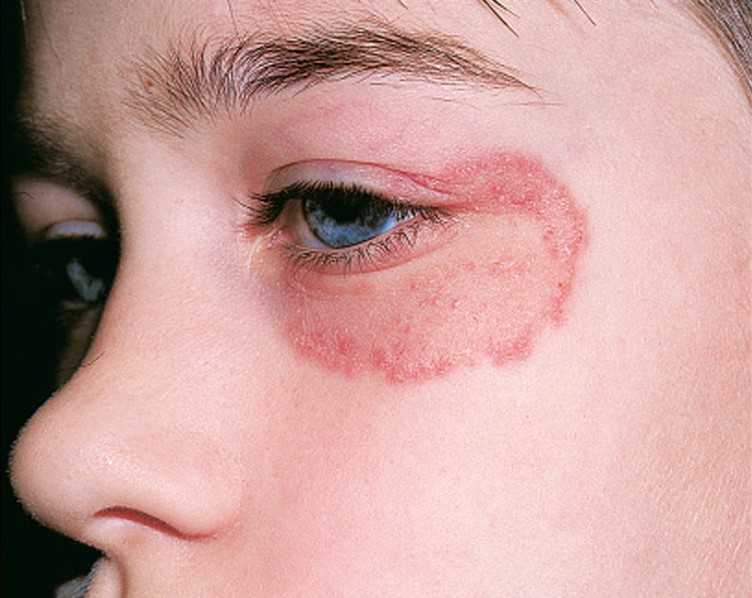
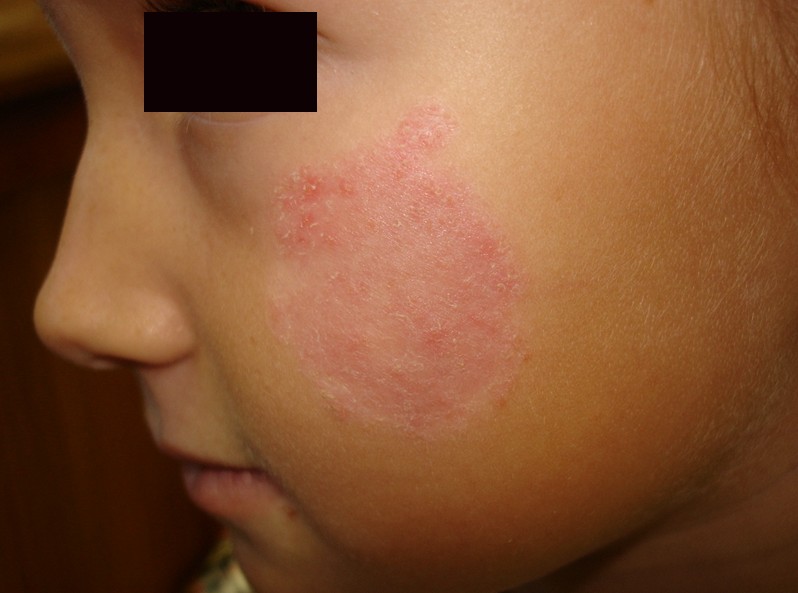
Tinea Faciei
Tinea faciei is a superficial infection of the skin. It is part of the dermatophyte skin infections and it can affect people of different sexes and ages. In children and in women, tinea faciei affects the skin on the face, including the chin and the upper lip. In the male population, this infection is known as tinea barbae, as it occurs only on areas that have hair (such as the beard area).
What happens is that the dermatophytes (which are actually keratinophilic fungi) will release enzymes (known as keratinases). These enzymes are going to invade the upper layer of the epidermis, causing the lesions on the skin and an inflammatory reaction. Tinea faciei occurs all over the world but it has a higher frequency in the tropical regions. This is because the high temperatures and the constant humidity are considered to be triggering factors.
What are the Symptoms of Tinea Faciei?
These are the most common symptoms of tinea faciei:
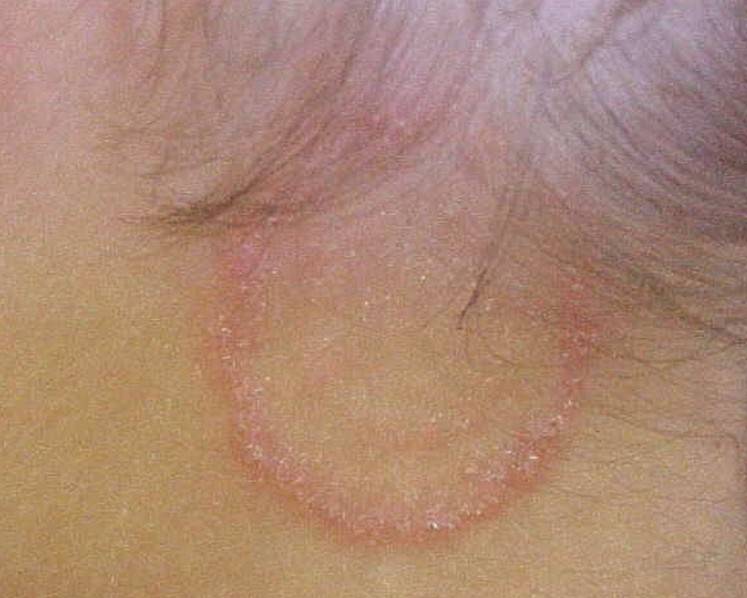
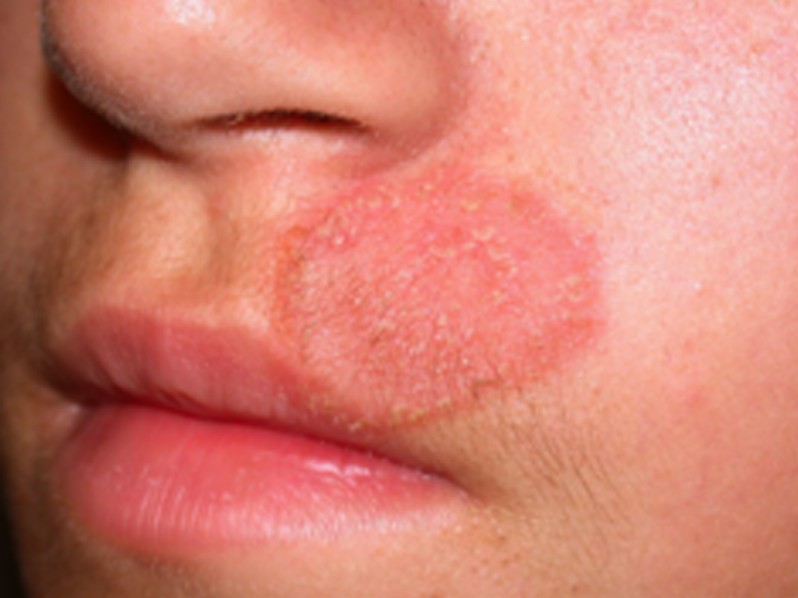
- Atypical features on the glabrous skin of the face
- Lesions are single or multiple in number
- The lesions are in form of red patches, papules or vesicles
- The patches can be round or oval as shape
- No annular structure of the lesions
- Resemble the lesions from other dermatoses or the ones from tinea corporis (ringworm infection)
- The lesions might be associated with itchiness
- The patches might be linear, red and scaly
- Active border
- Crusting may appear
- Most commonly affected areas on the face: cheeks, nose, periorbital area, chin, forehead
- The onset can be:
- Sudden onset with quick spreading of the lesions
- Delayed onset with slow spreading of the lesions (inflammation is minimum, the rash on the skin is reduced)
- Lesions are frequently aggravated by sun exposure
- Skin may peel after the treatment is begun
- Lesions are contagious to the touch.
What are the Causes of Tinea Faciei?
These are the most common causes of tinea faciei:
Fungal infection – zoophilic dermatophytes (Microsporum canis)
- Acquired infection from pets or livestock
- Transmission from one person to the other is possible, as the lesions are highly contagious to the touch
- In Asia – common infections with Trichophyton mentagrophytes and Trichophyton rubrum
- In North America – common infection with Trichophyton tonsurans.
Diagnosis
These are the most common methods used for the diagnosis of tinea faciei:
Mycological investigation
- Microscopic examination of the skin
- Skin cultures (surface scraping)
- Keratinocytes will dissolve and the fungal elements are going to be exposed
- The cultures allow for the positive identification of the fungal infectious agent
- Special media can be used for faster detection of the dermatophytes
Histological examination
- Used sometimes for the confirmation of the diagnosis
- Histological modifications resembles the ones from psoriasis
- Cutaneous fungal elements will be revealed in the epidermis
- Certain fungal infectious agents might also infect the hair follicle (aspect revealed through histological examination)
- Infiltratory inflammation might be present in the dermis as well
Differential diagnosis
- Cutaneous infection with Candida
- Allergic contact dermatitis
- Irritant contact dermatitis
- Perioral dermatitis
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Granuloma
- Lupus erythematosus (acute/bullous/discoid/drug-induced/sub-acute cutaneous/neonatal)
- Pityriasis (alba/rosea)
- Rosacea
- Sarcoidosis
- Syphilis.
Treatment
These are the most common courses of treatment undertaken for tinea faciei:
Topical treatment
- Anti-fungal medication
- Recommended if the hair follicles are not affected
- Topical corticosteroids can be recommended to reduce the inflammation and itchiness
- Ciclopirox/terbinafine
- Recommended for the anti-inflammatory properties
- Given as treatment in cases of tinea faciei caused by zoophilic dermatophytes
- Can reduce the common, yet severe, inflammatory reaction commonly associated with this condition
- Azoles
- Topical application as well
- Have a direct effect on the wall of the fungal cell
- Reduces the reproduction of the fungal cells
- Allylamines
- Leads to the death of fungal cells
- Topical and systemic administration
- Isoconazole nitrate in combination with diflucortolone valerate
- The combination of these two topical preparations has shown promising results in reducing the symptoms of tinea faciei
- More severe cases can benefit from systemic administration of corticosteroids. However, these should not be administered for prolonged periods of time, as they can have serious consequences on a person’s health and they can cause severe withdrawal symptoms. The treatment with systemic corticosteroids should be reduced gradually, not stopped all of a sudden
- Systemic therapy is recommended in the following cases:
- Rare, atypical lesions
- Chronic cases
- Multiple lesions.
- Systemic therapy is recommended in the following cases:
Home Remedies
These are the most common home remedies recommended for tinea faciei:
Tea tree oil
- Recommended for tinea faciei because of its anti-fungal and anti-septic properties
- Topical applications are recommended with the help of a cotton ball
- Daily repetitions are indicated until the first results become noticeable
- It is recommended to warm the tea tree oil a little before actually applying it on the skin
Garlic or garlic extract
- Recommended because of its anti-fungal properties
- Regular use is indicated for effective results
- If you decide to use regular garlic, then cut it into slices, apply it directly on the skin and bandage the area
- The best results are when the garlic is made into a paste, applied on the skin and left there over the night
Apple cider vinegar
- Natural anti-fungal properties
- Topical applications are recommended with the help of a cotton ball
- Daily repetitions are indicated until the first results become noticeable
- Complete removal of the fungal infectious agent
Coconut oil
- Natural healing properties
- Recommended for cases with intense itchiness
- Overnight applications are most recommended
Jojoba/lavender oil
- Mix the jojoba oil with the lavender oil
- Topical applications are recommended with the help of a cotton ball
- Lavender oil is indicated because of its powerful anti-fungal properties
Mustard seeds
- Soak them into water and crush them into a paste
- Direct application on the skin
Turmeric
- Apply fresh turmeric on the skin with the help of a cotton ball
- Daily repetition of application
Tinea Faciei Pictures
Collection of photos, images and pictures of the skin infection Tinea Faciei…