Tinea Capitis
What is Tinea Capitis?
Tinea capitis is a fungal infection involving the superficial layer of the scalp and the hair shafts. It is also termed as ringworm of the scalp, scalp ringworm and ringworm of the hair.
Tinea capitis is a mild dermatophytosis affects the scalp and the hair shafts and is clinically presented as single or multiple patches of skin. This skin condition is commonly known as ringworm of the hair although the worm has nothing to do with the condition. Tinea capitis may occur as a scaly and non-inflammatory dermatosis resembling the appearance of a seborrheic dermatitis. It may also occur as an inflammatory disease clinically presented with scaly erythema associated with hair loss.
Tinea capitis is known to affect people from all parts of the world without racial predilection. The infection is found to be prevalent in pre-school children affecting both boys and girls although it is found to have a slight prevalence among boys.
The fungi that can cause the infection vary according to geographical region. There are at least eight species of the fungi that can cause tinea capitis and all are generally termed as dermatophytes. Tinea capitis is not a serious or life-threatening condition but it tends to become chronic and linger until adult life. The severity of the infection, however, depends on the site of infection. Tinea capitis on the other hand is a contagious skin condition which can be spread from either a direct or indirect contact with an infected person. Direct contact with an infected animal is also another way of spreading the disease.
Tinea Capitis Symptoms
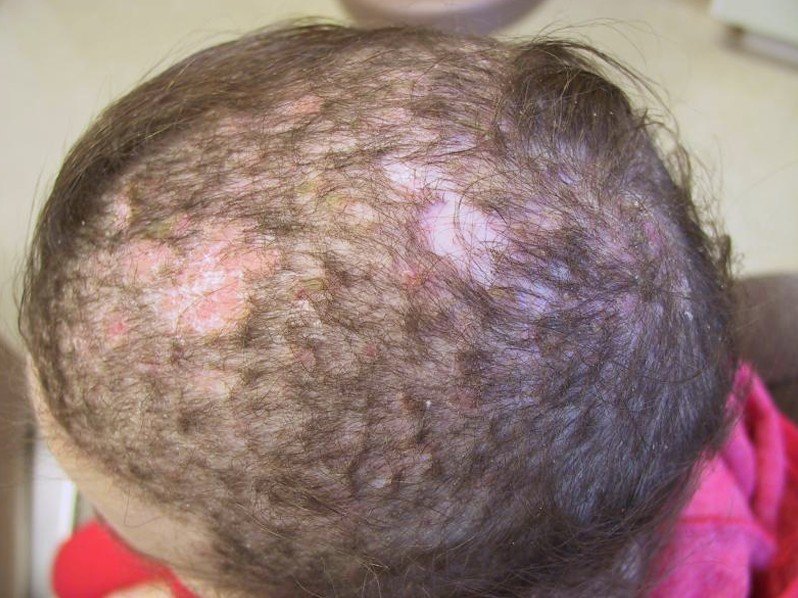
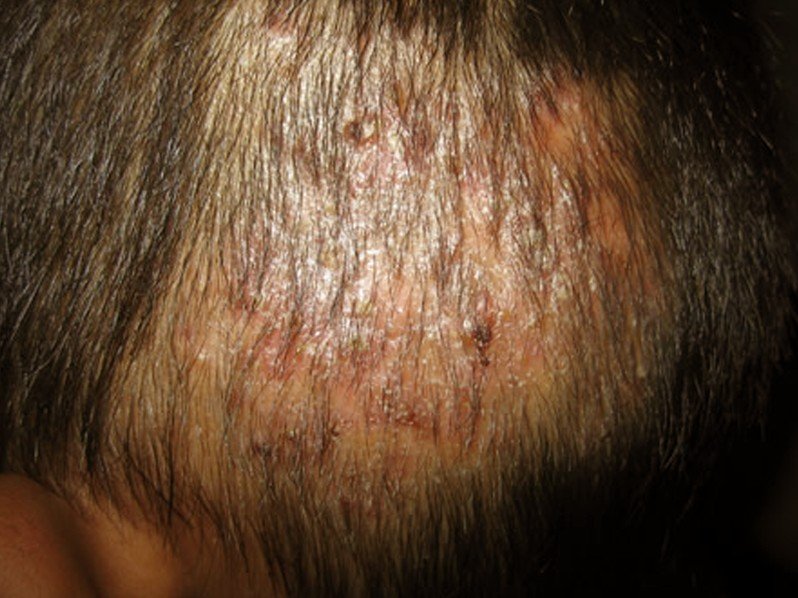
Tinea capitis is generally marked by the formation of itchy and scaly patches on the skin surface of the scalp and on the hair shafts. The section of the hair that is affected will eventually break off and will leave the scalp scaly and reddish. The affected area will also create a bald spot which will gradually increase in size if no treatment is applied.
Tinea capitis is clinically presented in several ways.
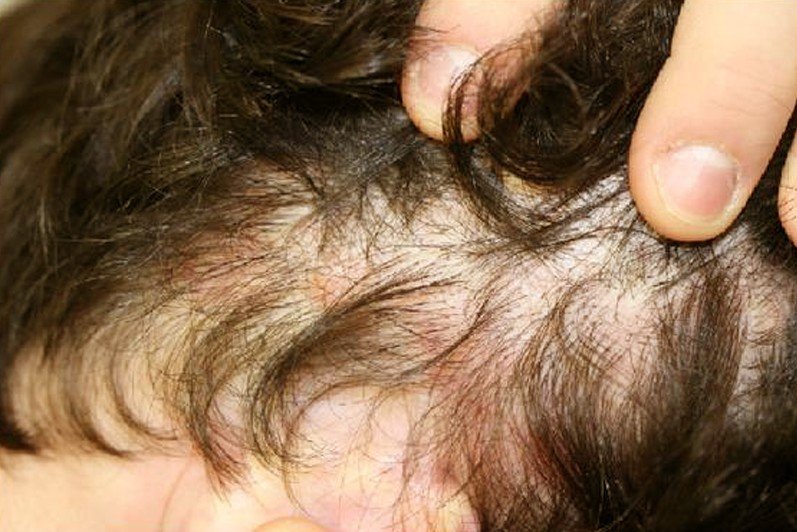
- Black dots – describes the tiny capitis as scaly where the hair has broken away from the surface of the scalp.
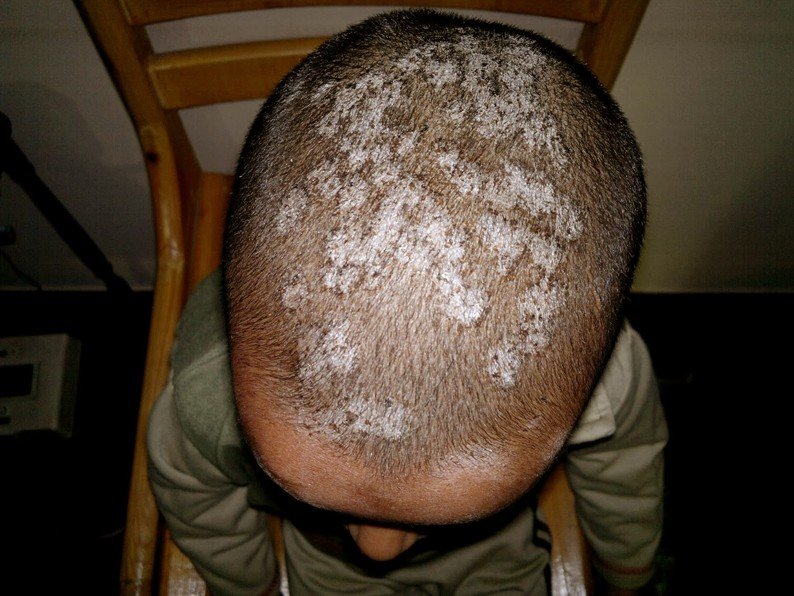
- Dry scaling – is tinea capitis similar to the appearance of dandruff with hair loss as if eaten by an insect
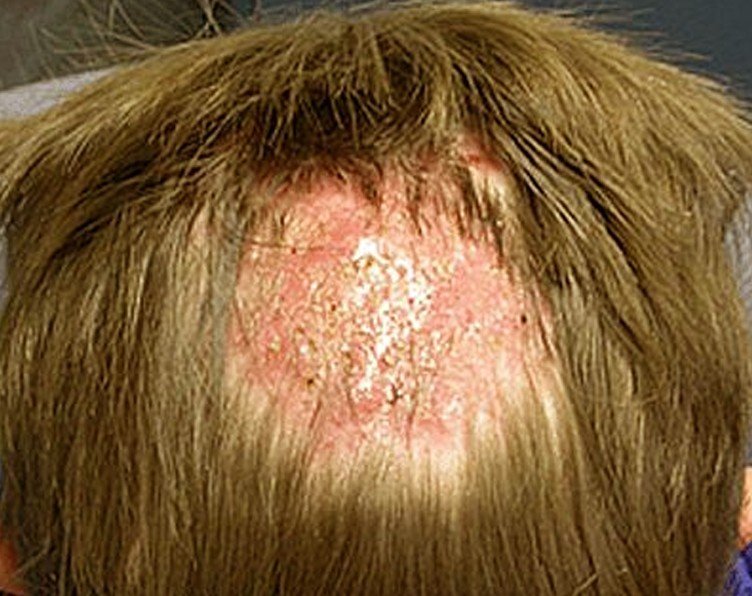
- Kerion – describes tinea capitis as severely inflamed and resembles an abscess
- Favus – is characterized by matted hair with yellowish crusts
Tinea capitis can also appear as sections of bald spots with smooth texture while there are cases of tinea capitis which remains asymptomatic and is presented only with mild scaling.
The common signs and symptoms of tinea capitis include the following:
- Growth of single or multiple scaly patches on the surface area of the scalp or in the areas where the hair has broken off
- The affected area is somewhat reddish or grayish in color and is scaly
- The skin patches may have black dots in the area where the hair has broken off
- The hair is characteristically brittle that it can be easily pulled out
- The scalp may be tender or may have pain
- Swollen lymph glands may occur at the back or on the sides of the neck
- Tinea capitis may also result to an allergic or id reaction
Tinea Capitis Causes
Tinea capitis is the result of infection from any of the several variants of dermatophytes. These dermatophytes are fungi that invade the outer layer skin of the scalp.
Tinea capitis is the consequence of an infection from either a Trichophyton or a Microsporum. Both are genus of fungi that can cause tinea corpus and other fungal infections of the skin. The source of fungi that can cause tinea capitis can be anthropophilic, zoophilic or geophilic.
Microsporum canis is one of the most common fungi dermatophyte that can cause tinea capitis. The source of this fungus is zoophilic or which that is normally found in animals. Microsporum canis is often found in kittens.
Trichophyton tonsurans is the anthropophilic source of fungi and is among the most common cause of tinea capitis. This dermatophyte is spread from one person to another as the fungi generally favor humans over animals.
Tinea capitis can also be caused by fungi that thrive in the soil or the source is rather geophilic. This, however, seldom happens.
Common zoophilic fungi that cause tinea capitis are the following:
- Microsporum nanum
- Trichophyton verrucosum
- Microsporum distortum
- Trichophyton mentagrophytes var. equinum
Anthropophilic fungi causing tinea capitis is the following:
- Trichophyton rubrum
- Trichophyton violaceum
- Trichophyton megnini
- Microsporum ferrugineum
Tinea capitis is also classified according to the manner the fungus has infected the hair shaft.
Endothrix infection
Endothrix infection is characterized by the infiltration or filling in of the hair shaft with the fungal spores and branches. This type of infection is commonly caused by Trichophyton tonsurans, Trichophyton soudanense and Trichophyton violaceum.
Ectothrix infection
Ectothrix infection is described with infection covering only the outside of the hair shaft. This type of infection is commonly caused by Microsporum canis, Microsporum ferrugineum.
Tinea Capitis Pictures
Collection of Photos, Images and Pictures of Tinea Capitis…
Tinea Capitis Treatment
Tinea capitis is generally treated with an antifungal medication given orally. Griseofulvin is the drug of choice for the treatment of tinea capitis. It acts by stopping the fungal cell from dividing and is especially effective when the infection is caused by Microsporum canis. It is generally recommended for children as the medicine is well tolerated. Griseofulvin has been in use since 1958 although this drug does not kill fungi right away and treatment is necessary to be taken for several weeks to several months.
Terbinafine, Lamisil is the new drug of choice for treating children with tinea capitis. This drug was approved in the year 2007 and is prescribed for children ages 4 years and above. This drug is also to be taken for several weeks.
Is Tinea Capitis contagious?
Tinea capitis is a highly contagious disease which can be spread through the following:
- Direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person
- The fungi causing tinea capitis can be acquired through contact with a contaminated surface such as sharing of hair brushes and comb
- The fungi of tinea capitis also thrive in animals that the infection can be spread through petting or coming into close contact with an infected animal