Stucco Keratosis
What is Stucco Keratosis?
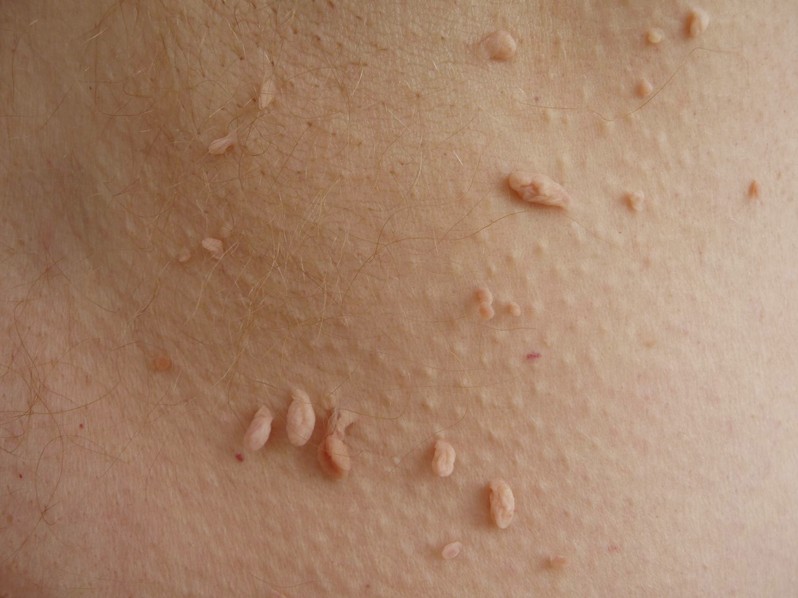
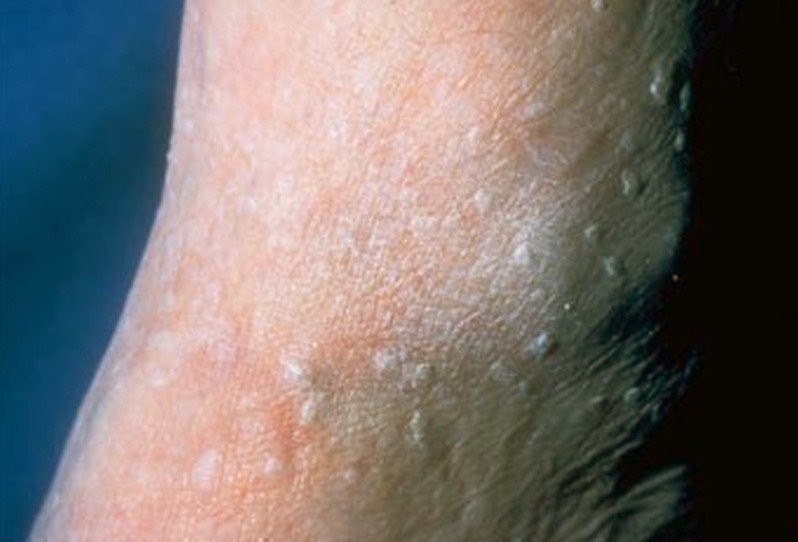
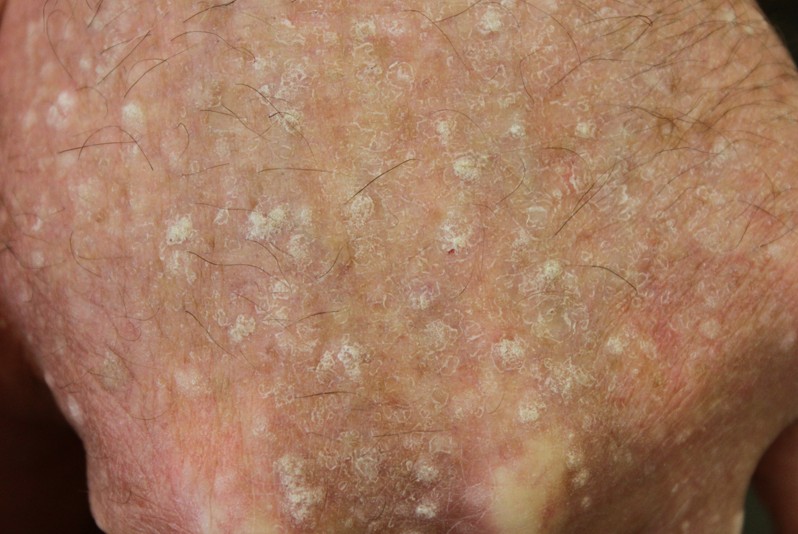
This is a skin disorder that has been first described in 1965. The primary characteristic of stucco keratosis is the presence of keratotic papule, present in the lower extremities. The interesting thing about this condition is that it affects the male population in general, without having any hereditary transmission. The condition is asymptomatic and most of the times the patient will not even notice the lesions present on the skin. However, there are many cases where the lesions are numerous, ranging from as few as 7 to as many as 100.
Stucco keratosis is also known as keratosis alba and, in older males, it is more frequent at the level of the ankles. This condition is benign and it does not have any infectious factors associated with it, which makes it 100% non-contagious.
What are the Symptoms of Stucco Keratosis?
These are the most common symptoms of stucco keratosis:
- Keratotic papule present on the distal lower acral extremities
- Lesions of different colors (gray white, pink, yellow)
- Minimal bleeding if the lesions are scraped
- The skin becomes thick and the lesions appear to be stuck on, hence the name stucco keratosis
- The skin has a riddled appearance
- Medium growth lesions can also appear (they resemble warts)
- Unique lesions are possible but usually the lesions are high in number and small in size
Causes of Stucco Keratosis
The exact cause that leads to the appearance of stucco keratosis has yet to be identified. However, it seems that a large percent of the male population diagnosed with this skin condition also presents an infection with the papilloma virus. Other incriminated factors in the appearance of stucco keratosis are:
- Prolonged and excessive sun exposure
- Aging
- Recent studies have also incriminated genetic mutations in the appearance of stucco keratosis
Diagnosis
These are the most common methods used to diagnose stucco keratosis:
- Histopathological examination – it will show the actual thickening of the skin, with the elongation of papillae and thickening of the corneum layer.
- Medical history – gender, age, lack of other symptoms.
- Clinical findings – lesion appearance and number, distribution (mainly on the lower part of the legs, ankles especially) and morphology (size, color etc.)
- Differential diagnosis – this can be made with seborrheic keratosis, acrokeratosis verruciformis or verrucae plana.
Treatment
The main purpose of the treatment is related to cosmetic reasons, but there are just as many cases in which the treatment will be imposed by the existence of symptomatic lesions, requiring removal. The main idea is to apply medical procedures such as curettage and local destruction, making sure that the lesions are completely removed.
These are the most common methods of treatment undertaken:
- Topical creams to suppress the immune system response (moderate success in research studies)
- Lesion scraping – the only downside to this procedure will be the minimal bleeding but this can be successfully handled by the patient
- Cryotherapy – applying cold temperatures to the site of the lesions is an effective treatment. The downside to cryotherapy, especially when applied on the lower parts of the legs, as it can cause ulcerations
- Electro-desiccation – this sounds a little bit scary but the procedure is actually simple. Basically, a needle-shaped electrode is used in order to dry the affected tissues with high-frequency electric current
- Retinoid drugs have also been chosen for the treatment of stucco keratosis. These are also used for the treatment of psoriasis and they should be taken only under the attentive supervision of a doctor. Taken for prolonged periods of time, they can have serious side-effects on your health
- In some cases, the lesions do not require any specific treatment
- UV protection is a very important thing to take into consideration. Patients are advised to wear sunblock with high SPF factors and wear clothing that covers the skin as much as possible
- Urea containing emollients and creams have also helped with the stucco keratosis lesions. The lesions soften with the application of these creams but they do not disappear completely
As you have seen for yourself, there are several methods of treatment for stucco keratosis, each presenting its own set of advantages and disadvantages. If you have been diagnosed with this skin condition, then you should not delay seeking specialized medication attention, even if the lesions present on your skin are asymptomatic. Also, it might be useful to get tested for the presence of papilloma virus, as this is often encountered in patients with stucco keratosis. The reason why you need to determine whether you have this virus or not has to do with the actual treatment that might be recommended. Aside from that, there are certain cautionary measures, such as using sunblock with high SPF factor that you have to take into consideration.
Stucco Keratosis Pictures
Here are some of the pictures of Stucco Keratosis…