Red Moles
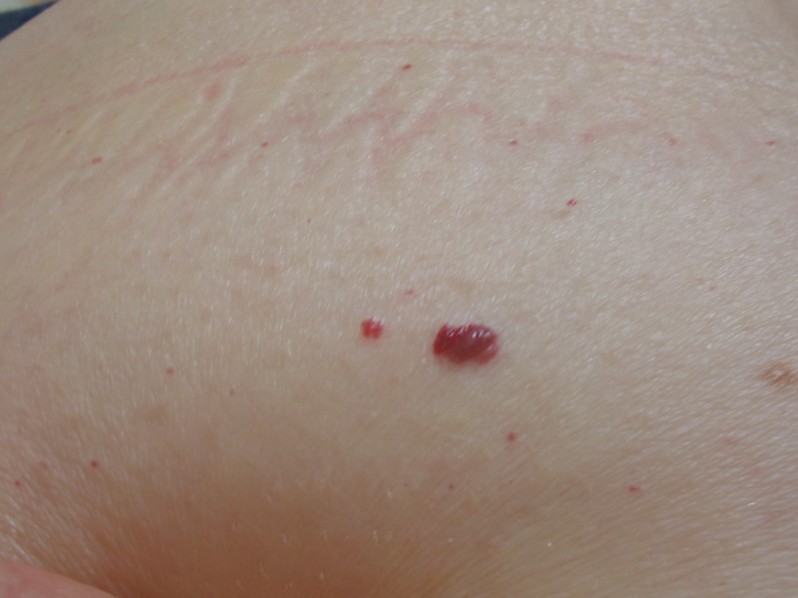
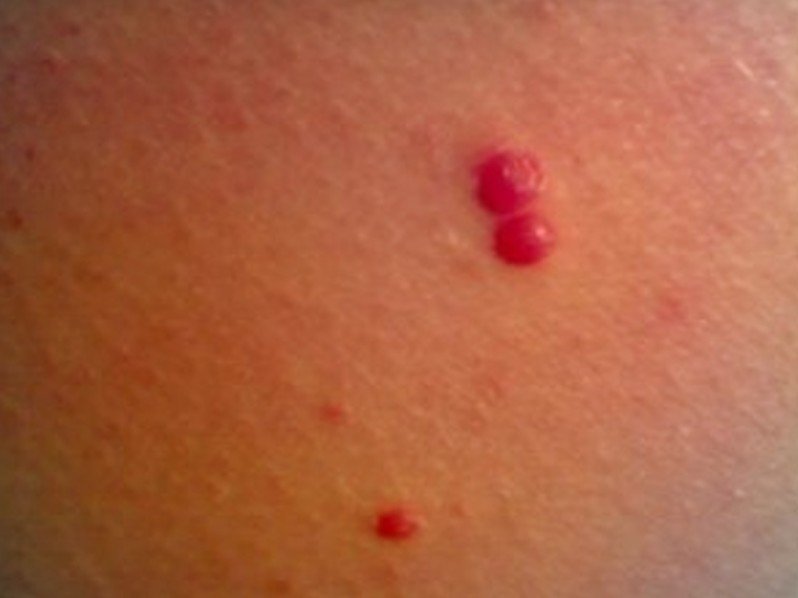
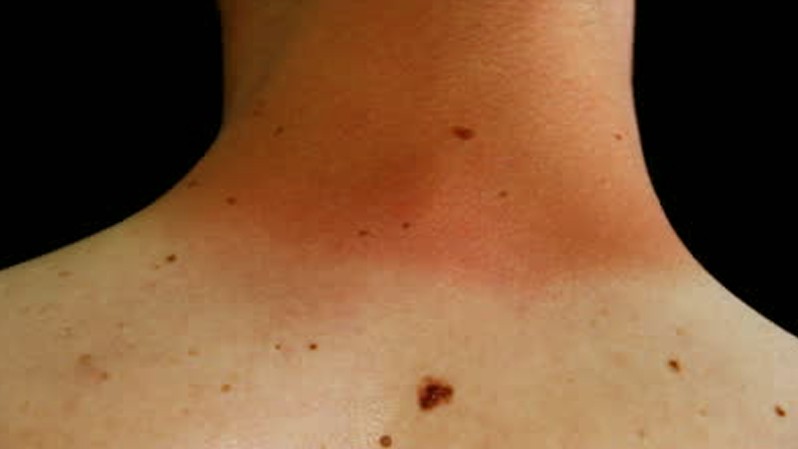
The red mole is also known as a cherry angioma and at first sight it might seem like a serious medical problem. However, unlike other types of moles, these red ones are benign and they do not pose any threat to a person’s health. Keep in mind that red moles are not a sign of cancer and they most commonly indicate that the skin is aging. While moles in general are formed out of skin tissue (with melatonin as primary component), red moles consist of an accumulation of blood vessels. They are known as Campbell de Morgan spots in the medical literature.
Red moles can appear on any part of the human body but they have a tendency to be more numerous on the thorax. There is no gender predisposition and, as for age, it seems that people over 30 years develop them. Just like with regular moles, red moles can be quite different from one person to the other. Their size might range from small to big and their color might vary from fading to bright red. The growth of a red mole is appreciated in terms of width and diameter. Sometimes, at a closer look, one can notice that the red moles consist of clusters of blood vessels.
If you are worried that your red mole might turn into a cancerous one, it is important to look for other signs, besides the color. The features you should be checking are: symmetry (asymmetrical moles present a high risk for cancer), borders (irregular borders – sign of malignancy) and diameter (large and still growing mole – malignant).
Causes of Red Moles
These are the most probable causes that lead to the appearance of red moles:
- Living in a sunny, warm climate
- Frequent and prolonged exposure to the sun
- Genetic predisposition/inheritance
- Pregnancy
- Exposure to harmful substances or chemicals
- Aging
- Malignancy.
Treatment
If the red mole does not suffer any modifications, then the doctor might decide not to treat it. However, in case of modified or large red moles, these are the most common courses of treatment undertaken for red moles:
Surgical removal
- Often performed for biopsy reasons – to determine whether the mole is benign or malignant
- Especially recommended if the red mole is bleeding or if it has been subjected to any kind of trauma.
Electrosurgery
- Cautery is one of the most often chosen methods of treatment for red moles
- By using this method, the doctor practically burns the red mole.
Cryotherapy
- Red moles can be easily removed with the aid of cryotherapy
- By using this method, the doctor practically freezes the red mole, the removal process being quite easy afterwards.
Laser
- One of the easiest methods to treat the red mole
- Easy procedure and better recovery
Shave excision
- Recommended in case of smaller red moles
- Higher risk of scarring.
Removal
Many people are interested in removing their red moles because of aesthetic reasons. The methods available for removal have already been presented. In the paragraphs below, you will find however a detailed explanation of each procedure used for removal.
Surgical removal
- The surgeon will prepare the area by applying iodine or other disinfectants
- The procedure is done by using local anesthetic
- The surgeon will use a scalpel to resect the red mole all at once and he will then keep a part of it for biopsy analysis
- Depending on how big the red mole was, a suture might be necessary
- For the last part, the doctor will apply a dressing with antibiotic ointment in order to prevent secondary infections.
Electrosurgery
- The surgeon will prepare the area by applying iodine or other disinfectants
- The procedure is done by using local anesthetic
- Using a small probe, the surgeon will burn the red mole with the help of electric current
- Because this procedure involves the usage of electric current, the surgeon will also place a lap on another part of your body, in order to protect you from the electricity
- A sterile dressing will be applied after the procedure has ended.
Cryosurgery
- The surgeon will freeze the red mole by using liquid nitrogen
- This is one of the simplest and quickest removal procedures, as the red mole does not withstand extreme cold temperatures
- Basically, the surgeon will spray the liquid nitrogen onto the red mole and the results are going to appear almost instantly
- This procedure guarantees faster recovery time
- Less chance of infection.
Laser
- Removal is performed with the help of pulsed dye laser
- The red mole is practically destroyed with the aid of the extreme heat
- Quick removal, no need to spend time in the hospital
- May require more than one session for complete removal (most patients require between one and three laser surgery sessions)
- The recently operated area might appear as if bruised; however, in the following days after the laser removal, the bruising will subside.
Shave excision
- The surgeon will prepare the area by applying iodine or other disinfectants
- The procedure is done by using local anesthetic
- Using a scalpel, the surgeon will remove the red mole in several stages. Basically, he will take the red mole and cut layer by layer.
- Less invasive than complete cutting
- As opposed to regular removal, the shave excision does not require sutures or stitches to keep the wound closed
- A sterile dressing will be applied after the procedure has ended.
In conclusion, red moles are benign growths on the skin and they do not pose any risk to transform into cancer. However, they may cause discomfort, especially if they are located in areas where there is a lot of friction. If you keep on rubbing the red mole on the collar of your shirt, then perhaps it might be for the best to pay your doctor a visit and discuss about your options for removal. Once the red moles are removed, they do not come back.
Pictures of Red Moles
Collection of images, pictures of red moles…