Pseudofolliculitis Barbae
What is Pseudofolliculitis Barbae?
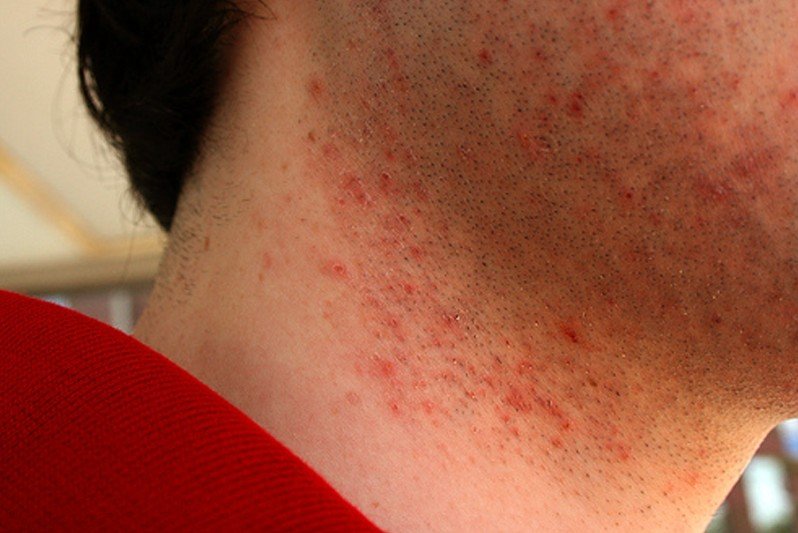
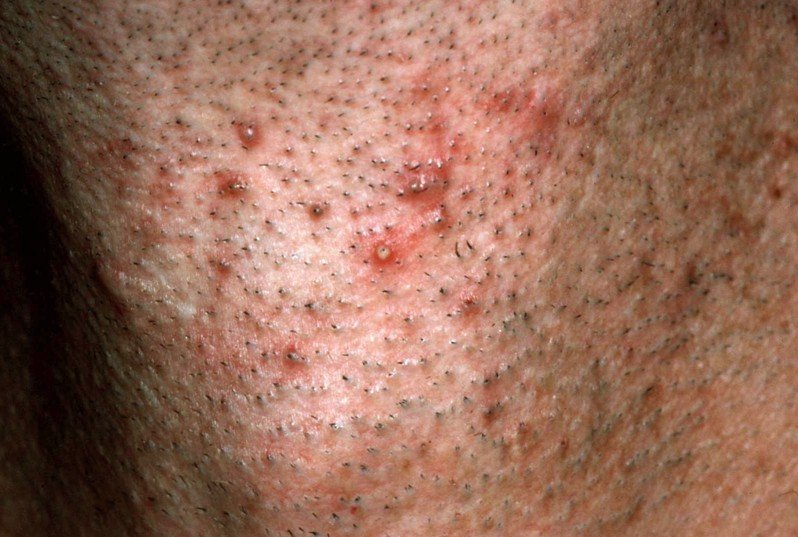
Pseudofolliculitis barbae also known as shaving bumps or razor bumps is a condition characterized by the development of papules and pustules resulting from an inflammatory reaction against a foreign body.
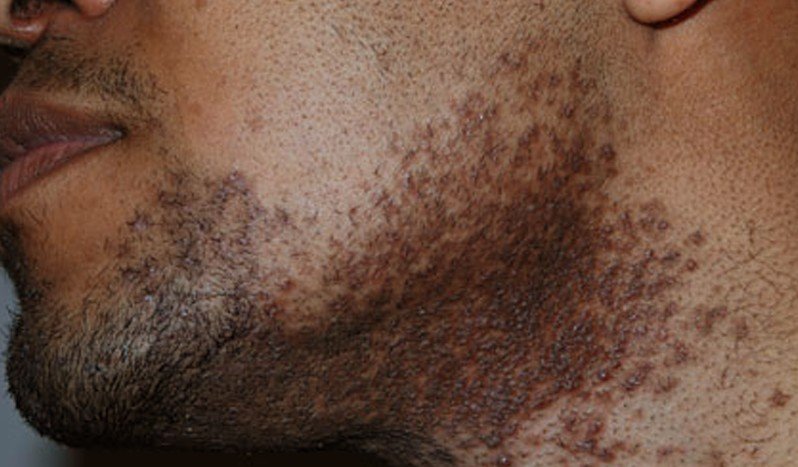
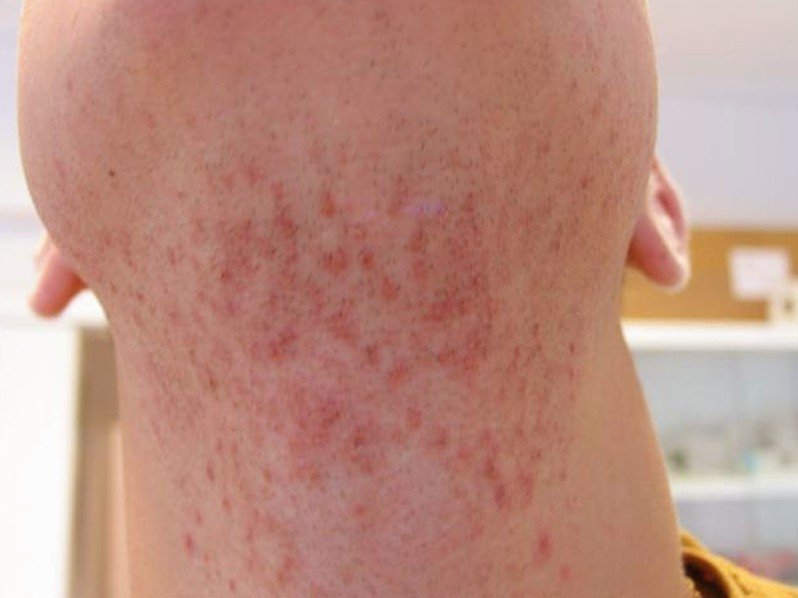
Pseudofolliculitis barbae is a skin condition known to exist commonly in curly haired individual particularly dark skinned individuals. The inflammatory reaction against foreign body is the consequence of shaving. It is a type of folliculitis that developed from a shaved hair that grows and curves back into the skin. Overtime, the papules or pustules that developed will later become a keloidal scarring which appears to be hard bumps in the areas of the beard and neck. Pseudofolliculitis barbae often occurs in the beard portion and in the neck.
Pseudofolliculitis barbae is common among black men especially those who regularly shave their beard. It can also affect white men although the incidence is rather seldom. The prevalence of the incidence among black men is in relation to their tightly curled hair which most black people have. The curly hair after it has been shaved has the tendency to grow back in a curly fashion thereby piercing the follicle wall or reentering the skin.
Pseudofolliculitis is especially a problem among black men in the military where they are required to have a clean shaven face. The skin condition is common in men although women can also get affected with pseudofolliculitis barbae. In women, however, pseudofolliculitis barbae is more commonly found in the axillary and the pubic areas where women often shave. Pseudofolliculitis not only occurs in the beard area but can also occur in the pubic area but is more aptly termed as pseudofolliculitis pubis.
The onset of pseudofolliculitis is post puberty when a person started to grow hair in different areas of the body as part of the development or transformation of the body. The skin condition is generally not serious or life-threatening but it can cause significant deformity in the cosmetic aspect particularly when the inflamed papules has hardened or formed into keloid.
Pseudofolliculitis Barbae Symptoms
Pseudofolliculitis barbae is characterized by tiny bumps or pimple-like bumps irritation of the skin in the beard area. This skin condition is also marked by hyperpigmentation or dark spots in the skin of the beard area of the face. The growth of the papules may also extend to the neck, chin, cheeks and the mandibular areas. Overtime, these papules may become keloids.
Pseudofolliculitis barbae is not a serious skin condition but can generally affect the appearance of the affected individual. This can be very distressing to the part of the patient as the lesions of Pseudofolliculitis barbae are unsightly. Pseudofolliculitis barbae can therefore affect the quality of life aside from its potential for secondary infection.
Causes of Pseudofolliculitis Barbae
Pseudofolliculitis barbae is the consequence of regular shaving of the beard. The skin condition is common among men with tightly curled hair particularly the African-American and those who are dark skinned and have curly hair.
The hair is a vital component in making up the appearance of an individual. It generally grows anywhere in the body and is the only structure in the body that constantly undergoes renewal without leaving a visible scar in the body. The structure of the hair is divided into two parts known as the follicles and the shafts. The follicles are a tube that contains several layers that have different functions. At the bottom of the follicle is a structure called papilla. This papilla contains all the tiny blood vessels which are responsible for feeding the cells. The bulb is the living part of the hair and is located at the bottom of that surrounds the papilla.
The shaft is another structure of the hair composed of keratin which is a hard protein. The shaft is also composed of the inner and outer sheath. The outer sheath is surrounded by a fibrous layer where a gland below it is where the erector pili muscle is conjoined. The hair stands up because of the contraction of the erector pili muscle. In curly or kinky hair, the shape of the shaft is more elliptical and flattened.
The hair in the beard has a short active phase that they are much shorter than the scalp hair. As the new hair is formed during the anagen phase, the club hair is pushed upward the follicle and out onto the surface.
The mechanism of the Pseudofolliculitis barbae can either be extrafollicular penetration or transfollicular penetration. When the hair is cut or shaved, the hair tip is left with a sharp end. In the extrafollicular penetration, the sharp tip of the hair pierces the skin as it leaves the follicles and reenters the skin. The pierce in the skin will cause the irritation and inflammation as the body is naturally trying to ward off the foreign body. In transfollicular penetration, the hair basically remains in the follicle or is not pushed out onto the surface. The curly hair will naturally curve inside the follicle resulting to fluid buildup due to an obstruction in the hair follicle. All ingrown hairs are generally considered as a foreign object of the body, thus, the inflammatory reaction.
The manner of shaving the hair and beard for that matter will generally affect the pattern of the hair regrowth. Dark spots or pimple-like bumps occur with frequent cycle of the skin condition in either extrafollicular or transfollicular penetration. The mechanisms of Pseudofolliculitis barbae are often true among dark skinned individuals who have tightly curled or kinky hair.
Treatment
The best treatment for Pseudofolliculitis barbae is to let the beard grow again and to refrain from shaving after a period of time or until the condition has resolved. If shaving is necessary, proper steps in shaving and the right blades or razor to be used should be followed.
Treatment of Pseudofolliculitis barbae depends on the extent or severity of the condition. Topical retinoid, topical antibiotics and low-potency corticosteroid are often prescribed to treat Pseudofolliculitis barbae.
Chemical depilatories are used as an alternative to shaving, especially when shaving is necessary, such as in the military where a clean-shaven face is required.
Laser hair removal is an effective and permanent method of removing facial hair. Although costly, this method of removing hair is found to be effective.
Pseudofolliculitis Barbae Pictures
Collection of Photos, Images and Pictures of Pseudofolliculitis Barbae…