Herpes Gladiatorum
Herpes gladiatorum is an infectious condition, caused by the herpes viruses and easily transmitted from one person to the other (skin-to-skin contact). The condition was first described more than fifty years ago, being presented in medicine journals. The main culprit behind this infectious condition is the human herpes simplex virus type 1 (commonly causes oral herpes or cold sores, as they are also known). The infection can also be caused by the human herpes simplex virus type 2, which is commonly responsible for the appearance of genital herpes. However, it is important to remember that both types of viruses can contribute to the appearance of herpes gladiatorum.
Given the increased contagiousness through skin contact, herpes gladiatorum is a common complaint in sport communities. It is frequently encountered in those who play contact sports, in rugby players and wrestlers. The association with those who play sports has caused this condition to receive other names, such as herpes rugbiorum or scrumpox. Herpes gladiatorum is also known as the herpes of the wrestlers or mat pox.
On average, those who are diagnosed with herpes gladiatorum experience between one and ten outbreaks each year. However, it is believed that there are certain factors that can trigger a herpetic outbreak, such as intense stress, anxiety or a compromised immune system due to different illnesses (temporary or permanent). Some people become infected with the strains of the herpetic virus, without exhibiting any symptoms. These are the carriers of the virus and they can easily transmit it to other people, through a process which is known as asymptomatic shedding. This means that the virus is active on the skin but there are no obvious symptoms present, such as the characteristic skin rash or the liquid-filled blisters.
Is Herpes gladiatorum an STD?
It is important not to mistake herpes gladiatorum for a sexually transmitted disease. There are a lot of people who believe that this condition is transmitted only through sexual contact but, in reality, it is the skin-to-skin contact that favors the transmission of the virus from one person to the other.
Symptoms
These are the most common symptoms that are encountered in patients diagnosed with herpes gladiatorum:
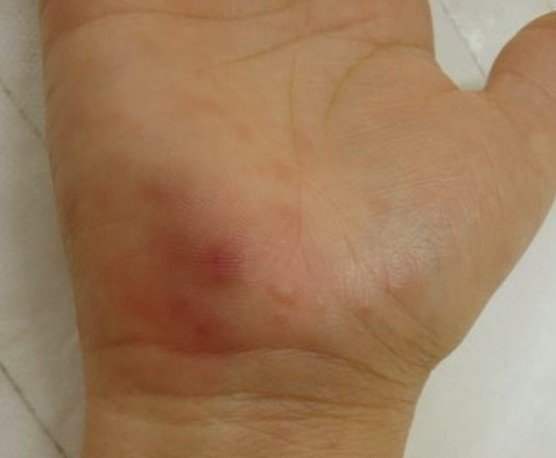
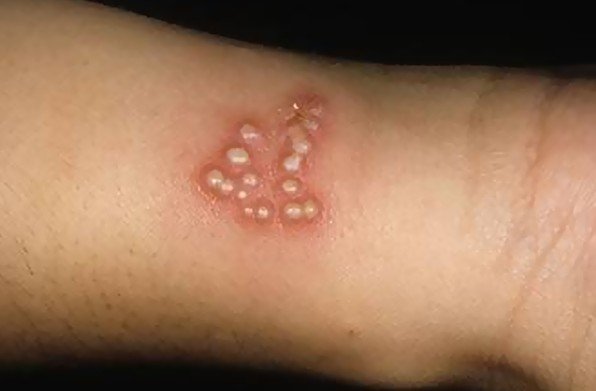
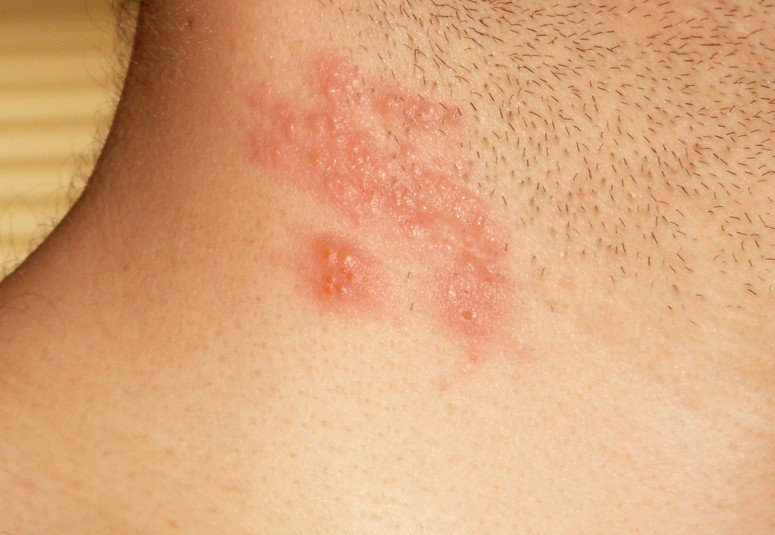
- Rash on the skin
- The lesions appear formed in clusters
- Among the lesions, blisters filled with liquid can appear on the skin, causing a lot of pain (these blisters contain small infectious particles – in contact sports, these are easily broken and the infection is thus transmitted from person to the other)
- Most common regions where the lesions appear include: neck area, thorax, face, abdomen and inferior limbs
- Systemic symptoms are also present:
- Swelling of the lymph nodes (lymphadenopathy appears as the body tries to fight the infection)
- Fever (moderate to high-running)
- Sore throat
- Nausea or vomiting
- Headaches
- Symptoms last for a couple of weeks
- The symptoms are more intense at the first outbreak of viral infection
- In case of recurrent herpetic infections, the lesions heal faster and scabs are formed at approximately three days (however, it should be mentioned that even though the lesions heal, the patient will remain infectious for a couple of days after starting the treatment with antiviral medication)
- The lesions heal on the skin without scarring
- In some patients, there are no symptoms present (asymptomatic viral infection).
Causes
As it was already mentioned, herpes gladiatorum is caused by the infection with the herpes simplex virus (more commonly type 1 and rarely type 2).
Treatment
The infection caused by the herpes simplex virus is treated with antiviral medication. The most commonly recommended medication chosen for herpes gladiatorum includes: famciclovir, valacyclovir and acyclovir. For the best outcome, the medication is administered orally, as tablets. In many patients, antiviral medication is administered orally, with the purpose of prophylaxis. Studies have demonstrated that the administration of this medication can reduce the risk of recurring herpetic infections. Plus, this medication reduces the chances of transmitting the virus to another person – there are a lot of people who are carriers of herpetic viruses, presenting no symptoms whatsoever (except for the outbreak periods).
Is herpes gladiatorum contagious?
Herpes gladiatorum is a highly contagious condition, being transmitted through skin-to-skin contact. As it was already mentioned, the blisters on the skin contain small viral particles. Upon forceful contact, these blisters break and the virus is transmitted to the skin of the other person. The level of contagiousness is just as increased in those who are carriers of the virus – not presenting any symptoms, these people easily transmit the infection to other people. It is also important to remember that a person remains contagious even after the lesions on the skin have healed. During the outbreak, the level of contagiousness is even more increased, so you need to protect yourself and not come into contact with those who have been infected.
Herpes gladiatorum vs Shingles
The difference between herpes gladiatorum and shingles is given by the type of virus that is behind the actual infection. Herpes gladiatorum is caused by the infection with the human herpes simplex virus, type 1 and type 2. Shingles, on the other hand, are caused by a reactivation of the varicella zoster virus. This is also a herpetic virus, which is known to cause varicella during the first impact. Once infected, the virus will remain for the rest of the life in the body. During periods of low immunity, the virus can become re-activated and causing the condition known as shingles.
Patients who are diagnosed with shingles present really painful lesions on the skin, commonly following a nerve pathway. As opposed to herpes gladiatorum, this condition can become quite debilitating – because of the intense pain, patients can enter into depression and the overall quality of life can become really affected. Also, it should be mentioned that shingles does not present such a high risk of contagiousness, especially in comparison to the herpes gladiatorum condition. However, outbreaks in both cases can be triggered by intense stress, low immunity or other similar factors. Taking vitamin C and zinc supplements can improve the strength of the immunity system, reducing the risk for outbreaks in both cases.
Herpes Gladiatorum Pictures
Here are some of the pictures of Herpes Gladiatorum…