Pharyngitis
What is Pharyngitis?
Pharyngitis is defined as the inflammation of the pharynx that often results in the condition known as a sore throat. The condition involves the pharynx which can be found immediately at the back of the mouth and the nasal cavity and just above the esophagus and the larynx.
The pharynx is an important part of the body for it is vital in respiration and deglutition. It serves as a channel from the mouth and nose down to the esophagus and the larynx and thus, a common channel for deglutition and respiration. The pharynx is also vital to the production of speech which enables communication.
Pharyngitis is a very common condition that is experienced internationally although this disease is seldom serious or life-threatening. It is prevalent among school age children from 5 to 18 years and rarely occurs in infants while adults may also get affected.
The onset of Pharyngitis can also be classified as either acute or chronic.
Acute pharyngitis
Acute pharyngitis is a type of pharyngitis that rapidly occurred although this usually lasts for a brief period of time. It is often the result of viral infection and commonly linked with acute nasal infection.
Chronic pharyngitis
Chronic pharyngitis on the other hand is more common in adults and is often associated with the disease of the upper respiratory tract.
Pharyngitis Symptoms
The symptoms of pharyngitis vary and greatly depend on the underlying condition that caused the inflammation. The symptoms also depend on the extent of the inflammation including the causative agent of the infection.
The sore throat is the primary and common manifestation of Pharyngitis. The terms sore throat and pharyngitis however are used interchangeably. Sore throat on the other hand is a manifestation of pharyngitis and is characterized by pain and irritation of the throat that is usually aggravated by swallowing.
The general symptoms of Pharyngitis on the other hand include the following:
- Difficulty in swallowing
- Onset of fever which is generally above 38 degrees Celsius in temperature
- Difficulty in speaking
- Swollen throat which is reddish and enlarged.
- Itchiness of the pharynx
- Visible white patches or pus on the covering of the tonsils or the throat
- Hoarseness of voice
- Difficulty in breathing
- Dryness of throat
- Coughing, which may cause the patient to expel mucus that may be clear, whitish, brownish, greenish or yellowish in color.
Other signs and symptoms of Pharyngitis may include the following depending on the condition that triggered the inflammation:
- Fever and chills
- Body aches
- Weakness and fatigue
- Onset of fever which may be high grade or low grade depending on the cause of the inflammation of the pharynx
- Onset of runny nose
- Frequent sneezing
- Development of rashes
- General malaise
- Sudden loss of appetite
- Problem with taste or an unusual taste in the mouth
- Nausea and vomiting
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Earache and sore neck and jaw
Pharyngitis that is left untreated on the other hand may cause serious complications such as infection in the blood and rheumatic fever. The symptoms of pharyngitis associated with serious medical complications may be accompanied with life-threatening symptoms that require a medical emergency.
- Onset of high grade fever that is greater than 101 degrees Fahrenheit
- Sudden change in the levels of consciousness
- Sudden loss of consciousness
- Joint pain associated with an erratic movement of the body
- Tachycardia or the rapid heart rate
- Difficulty in breathing
- Shortness of breath
- Choking
- Rapid swelling of the tongue or the throat
- An extreme pain
Pharyngitis Causes
Various factors can trigger the onset of Pharyngitis although infectious organisms are the most common cause. Viral infection is regarded as the most common cause of Pharyngitis while bacterial infection is less in occurrence. Pharyngitis is often caused by viruses commonly causing colds and flu while most viral illnesses can result to the inflammation of the pharynx.
Numerous types of virus can cause Pharyngitis and such include the following:
Adenovirus
Adenovirus is the most common pathogen that causes inflammation of the pharynx among children and adults. It is regarded as the largest non-enveloped virus which can be transmitted through respiratory droplets or can also be transmitted via fecal means.
Orthomyxoviridae
Orthomyxoviridae is the type of virus that commonly causes influenza. This virus belongs to the family of RNA viruses that is composed of six genera. Influenza A and B are among the six genera of RNA viruses that cause influenza in humans and other vertebrates and other mammals.
Other viruses that can cause Pharyngitis are the following:
- Herpes simplex virus
- Coronavirus
- Rhinovirus
- Parainfluenza virus
- Epsteinn-Barr virus
- Cytomegalovirus
Bacterial infection is also another cause of Pharyngitis although this occurs less frequently. There are numerous types of bacteria that can infect the throat subsequent inflammation of the Pharynx.
Group A Streptococcus
Group A Streptococcus is the most common cause of throat infection and the condition is also referred to as strep throat. Pharyngitis with this etiology rarely occurs in children below the age of 3 years old and is common among adult patients.
Other bacteria that can cause Pharyngitis include the following:
- Haemophilus influenza
- Corynebacterium diptheriae
- Neisseria gonnorrhoeaea
- Moraxella catarrhalis
- Bordetella pertussis
- Bacillus anthracis
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- Chlamydophila pneumoniae
Pharyngitis can also arise from non-infectious disease and may be caused by several factors such as:
- Irritation from thermal or chemical exposure
- Cold climate or during cold season
- Cold air
- GERD or the gastroesophagegal reflux disease.
Pharyngitis Diagnosis
Pharyngitis is rather difficult to distinguish the cause whether it is from a viral infection or bacterial infection due to the similarities in signs and symptoms.
Laboratory studies to identify Pharyngitis include the following:
Throat culture
Throat culture is the standard diagnostic utilized in identifying Pharyngitis from Streptococcus infection. The test achieved through collection of culture from the secretions of the throat via the throat swabs. This test is generally done to rule out Pharyngitis caused by a bacterial infection.
Blood test
Blood test is also another diagnostic procedure for Pharyngitis that is caused by another factor aside from viral infection. The procedure is generally done by taking a small sample of blood drawn from the arms or from the hands.
Imaging test is not necessary in determining or diagnosing Pharyngitis except for cases where airway obstruction is occurring or there may be a suspicion of epiglottitis.
Pharyngitis Treatment
Pharyngitis is a common disease that generally affects children although adults may also get affected. It is however not a serious disease and is basically non-life threatening. The goal of treatment is directed towards the relief of symptoms and prevention of further medical complications.
Pharyngitis caused by bacterial infection and fungal infection are generally addressed through medications such as:
- Antibiotics prescribed by doctors and which should be properly administered to avoid recurrence of infection
- Analgesics and acetaminophen are both useful in relieving pain and reducing fever
- Penicillin G benzathine and Penicillin V are both recommended therapies for Pharyngitis of bacterial infection
- Cephalexin or Cefadroxil are the prescribed therapy for patients with allergy in Penicillin treatment.
Pharyngitis caused by viral infection usually does not respond to antibiotics and the treatment is basically symptomatic. Viral pharyngitis on the other hand usually resolves within 3 to 7 days from the time of infection. Home remedies can generally help viral pharyngitis.
Is Pharyngitis Contagious?
Pharyngitis is a condition characterized by the inflammation of the pharynx. It is mostly caused by viral infection and which can be transmitted from one person to another. The mode of transmission or spread of the disease is basically through respiratory droplets such as from sneezing and coughing. Fecal route is also another method of transmitting the disease. The spread of the disease is prevalent in close communities and to those living in places such as military barracks where close contact is common.
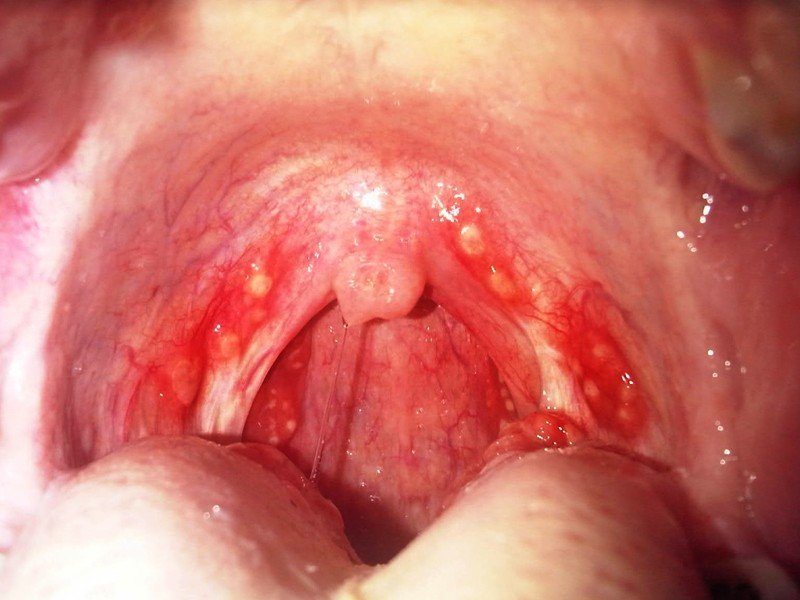
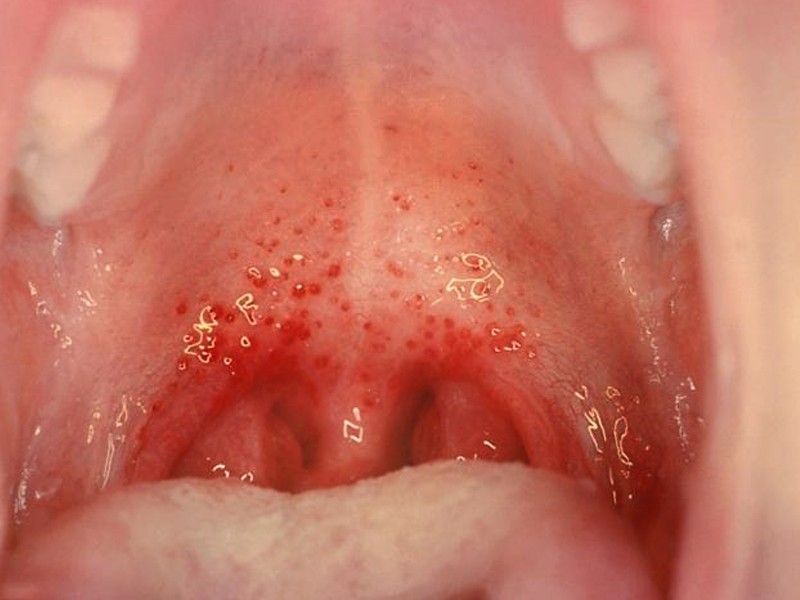
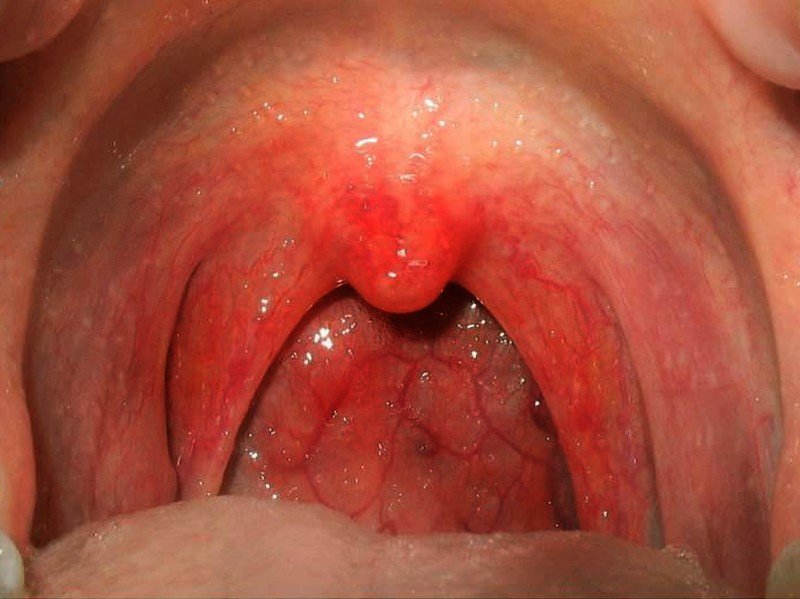
Pharyngitis Pictures
Pictures of Pharyngitis…