Lipedema
What is Lipedema?
Lipedema is a chronic disorder, in which the excess adipose tissue is deposited on different parts of the body, such as legs or the arms. The condition can be transmitted from one generation to the other (inherited condition), affecting the female population almost exclusively. The excess adipose tissue can affect women of different ages and weights (from underweight to those who suffer from severe obesity – morbid obesity). The adipose tissue is deposited on the body in a specific pattern, affecting both sides of the body and being symmetrical. In general, it starts at the waist and it continues down to the ankles.
This type of excess adipose tissue is very difficult to be lost just through physical exercise and dieting. Lipedema has three main stages, depending on the quantity of excess adipose tissue but it is known that in none of the three stages the feet are affected. It is estimated that 11% of the general population suffers from lipedema, with more than 370 million women being diagnosed with this condition.
Lipedema Symptoms
These are the most common symptoms of the lipedema:
- Excess adipose tissue in the areas where fat is commonly stored (these are known as lipidemic areas)
- Reduced adipose tissue in areas where there is commonly no fat (these are known as non-lipidemic areas)
- Inner thigh pads – frequently one of the first signs of lipedema (when recognized, allows for the diagnosis of the condition since the pre-puberty period)
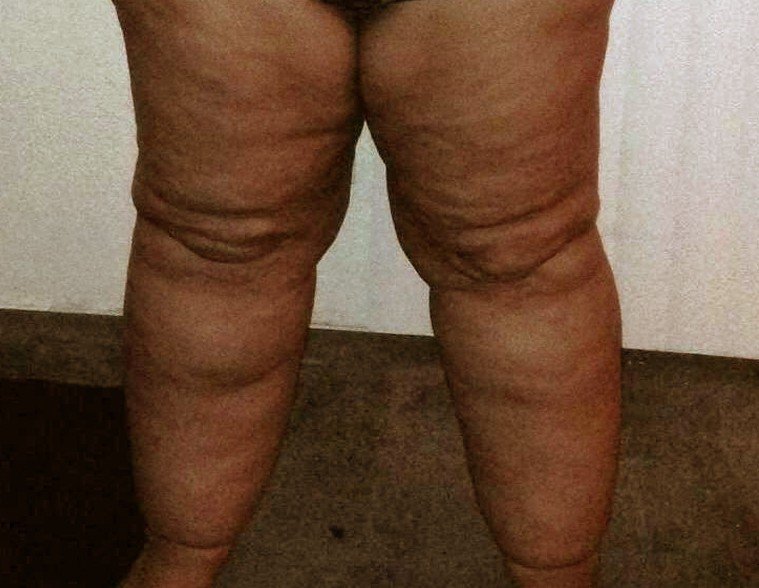
- Fat starts to build up around the knees – the appearance is of the excess adipose tissue draping over the knees
- The excess adipose tissue on the inferior limbs give a column-like appearance, with the greatest build-up being around the knees
- The fat is also distributed around the waistline, affecting primarily areas such as the hips, stomach or buttocks (disproportionate appearance)
- The majority of the excess adipose tissue is found in the lower part of the body
- The excess adipose tissue that continues to expand can have a negative impact on the lymphatic vessels, leading to the appearance of a condition that is known as lipo-lymphedema
- Lymphedema increases the risk for infection and fibrosis
- Lymphedema can also restrict the mobility of the patient.
Causes
At the moment, the exact cause that leads to the appearance of lipedema is not known. It is believed that the condition can be transmitted through the genetic inheritance, based on the idea that more women in a family can suffer from the same condition (especially if they are first or second degree relatives). Researchers have also found that a connection between lipedema and the hormonal imbalances (estrogen and progesterone) – this is based on the fact that the condition occurs for the large part in women and especially in those who have gone through puberty already.
In the majority of the cases, the condition is triggered by puberty but there are other factors that can trigger or worsen the condition, such as: pregnancy, the period before entering menopause (peri-menopause) and surgical interventions (especially those in the gynecological sphere – surgery of the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries). Some studies have demonstrated that any surgical intervention that has been made with general anesthesia can trigger the appearance of lipedema but further research is required to confirm such associations.
It is also believed that situations of extreme stress can trigger the appearance of lipedema, such as the death of a loved one or even getting a divorce. This occurs as the stress has a negative impact on the adrenal glands, leading to an increase in the cortisol levels – as the condition is just at the beginning, most people mistake it for the common weight gain and try to solve it through dieting. Even though it is very hard to diagnose lipedema at the first stages, a successful diagnosis at that moment can help patients manage their condition in a more efficient manner. This leads to a reduced expansion of the excess adipose tissue and thus to reduced consequences on the overall health.
Treatment
These are the most common courses of treatment taken for patients who suffer from lipedema and lymphedema:
- Manual lymphatic drainage
- Application of special bandages – these are usually recommended and applied by a drainage specialist
- Custom-fitted compression garments – stockings/biker shorts
- Prevent the recurrence of lymphedema
- Reduce the pain caused by the excess adipose tissue (compressing blood vessels, nerves and lymph vessels)
- Physical therapy
- Frequent and gentle exercises to improve the blood circulation in the legs
- Newer therapies include:
- Diet + low impact exercise + herbal protocol
- Benefit – inflammation reduction
- Change of eating habits and food choices
- Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) antagonists or blockers
- Complex decongestive therapy
- Pneumatic compression
- Diet + low impact exercise + herbal protocol
- Surgical intervention
- Lymphatic-sparing gentle water-jet-assisted liposuction
- Performed with tumescent local anesthesia
- Integrity of the lymphatic system is preserved
- The excess adipose tissue can be removed in an efficient manner.
- Lymphatic-sparing gentle water-jet-assisted liposuction
Natural Cure
These are the most common natural cures that can be used for lipedema:
- Seaweed (brown and green)
- Reduce the excess lymph accumulated in the legs
- Horse chestnut
- Recommended choice – capsules
- Pain relief (in the legs) and reduction of inflammation
- Bio-rutin
- Improving of blood circulation
- Allows the small vessels of blood (capillaries) to remain open
- Reduces the risk of bruising or bleeding, due to the capillary fragility
- Cayenne pepper
- Active ingredient – capsaicin
- Recommended choice – tincture
- Improves the blood circulation, reducing the risk of bleeding due to fragile capillaries
- Colloidal silver
- Reduced risk of infection
- Recommended – daily intake
- Bioflavonoids
- Strengthen the walls of the capillaries
- Antioxidant effect.
Diet
Even though the diet alone is not sufficient to improve the symptoms of lipedema, this does not mean that one should not consider a change of the eating habits. A healthy and balanced diet is essential in patients with lipedema, especially if they want to avoid complications. The diet, in combination with the physical exercise, the treatment and the natural cures can improve the overall quality of life. One should learn to include fresh fruits and vegetables on the diet, eliminating processed foods, those that are in rich in carbohydrates (sugar) and gluten. Unhealthy oils, fast food and spicy food should not be included in the diet. Sugary drinks and sweets are not recommended at all. Drinking plenty of water, as well as unsweetened herbal tea, is recommended at all times.
Lipedema Pictures
Take a look at some of the pictures of Lipedema…