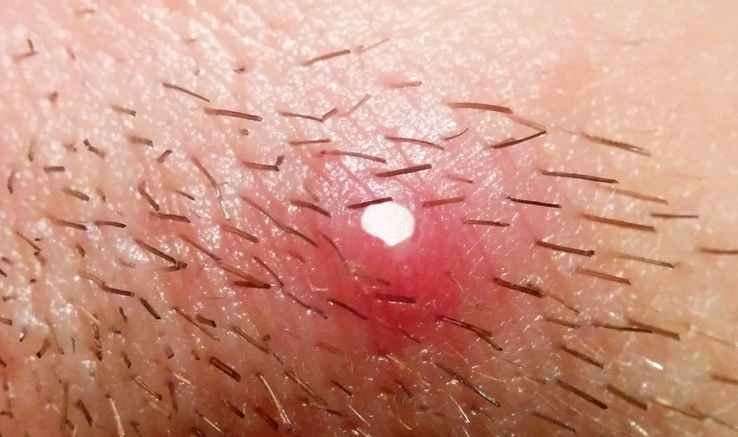
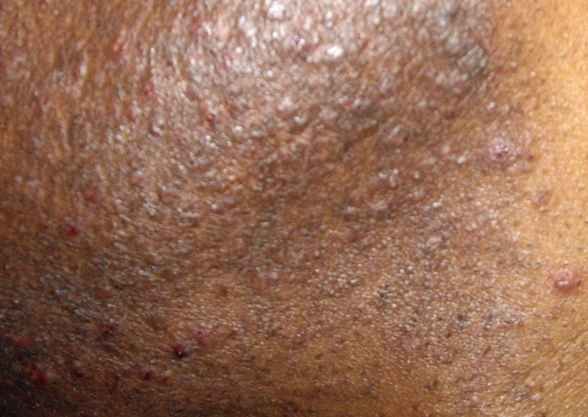
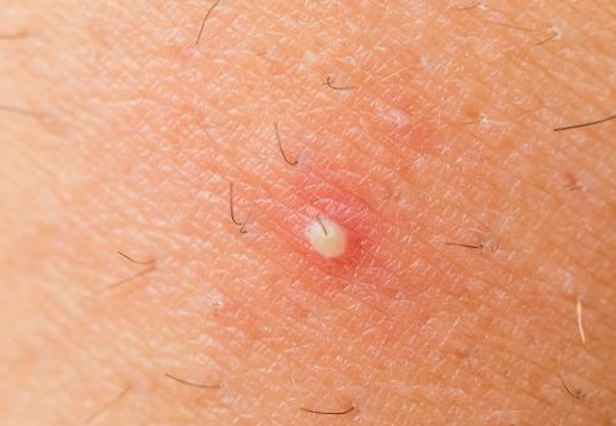
Infected Hair Follicle
Have you had an outbreak of clusters of small red bumps or white-headed pimples on your forehead, head, armpit, chest, elbow, or any other hairy part of your body recently? Is the development making you feel uncomfortable in the midst of friends? Well, infected hair follicle can be really embarrassing. Apart from the pains, the ugly-looking pimples and the itching can be terrible.
You may have tried knowing the actual cause of your problems. I understand your plight; a lot of people in your shoes will never rest until they have a proven solution. Don’t worry; we are here to give you as much help as we can. After our years of researches, we have been able to document the causes, types, symptoms and treatment of infected hair follicle. So, take your time to go through this post because all that you need have been carefully discussed below.
Symptoms of Infected Hair Follicle
Infected hair follicle otherwise known as folliculitis comes with some symptoms amongst which are:
- Clusters of small white-headed pimples or red bumps appearing around hair follicles.
- Red, inflamed skin
- A large swollen mass or lump
- Burning or itching of the skin
- Blisters filled with pus, which breaks open and crust over
- Pimples which drain pus, blood, or both
- Tiny pustules which may itch initially
- Furuncles develop yellow or green pus which can be expressed with a core plug of dead tissues.
Carbuncles can present with fever and swelling of the lymph nodes (lymphadenopathy).
What Causes Infected Hair Follicle?
Infected hair follicles have different causes, including infections from bacteria, fungi or yeast. However, other factors that cause folliculitis are the use of improperly treated hot tub, swimming pool or whirlpool, wearing tight clothes, diabetes, HIV infection, and the use of substances that block or irritate the hair follicles (including motor oil, makeup, creosote, tar, and cocoa butter).
In order to make it clearer to you, we are going to group infected hair follicles into superficial and deep folliculitis, and also list the various causes.
Superficial Folliculitis
The infection of the hair follicles is usually on the surface of the skin and the problems are not deep-rooted. The major types and causes include:
Bacterial folliculitis (Folliculitis barbae)
These are caused by bacterial infection of the hair follicles, especially by Staphylococcus aureus. The symptoms include itchy, white bumps filled with pus. Usually, the Staphylococcal bacterium lives on the human skin. Notably, staphylococcus can be found on the anterior nose, pubic area, armpit, or on other skin lesions like eczema, psoriasis, etc. But they cause problems when they penetrate into your body through an open wound or a cut. When the hair follicles in a man’s beard area are infected by bacteria, it is referred to as Barber’s itch. The infection usually results from shaving which leads to a broken skin. Sometimes, it occurs even when the hair is not shaved.
Pityrosporum folliculitis
They are mostly found in adult men and teens. It is caused by a yeast infection, and its symptoms include chronic, red, itchy pustules which are mostly on the chest and back but can also be found on the shoulders, neck, face and upper arm.
Hot tub folliculitis (Pseudomonas folliculitis)
They result from pseudomonas infection (a form of bacterial infection). One can easily get in contact with these bacteria in several places like heated pools and hot tubs where the chlorine and the pH levels are poorly regulated. The symptoms of hot tub folliculitis include rash with red, round bumps that are usually itchy in nature. They develop one to four days after one has been exposed to the organism. The rash may later develop into pustules (small blisters filled with pus). The rashes are usually more on the areas where the skin got in direct contact with contaminated water – mostly the back of the thighs.
Razor bumps (Pseudofolliculitis barbae)
This is an inflammatory reaction due to ingrown facial hairs, which usually result from shaving. It is not limited to the face; it can as well occur in any part of the body where hair is shaved or plucked such as the pubic area, leg, and armpit. It can be referred to as razor bumps or shaving rash. It is possible for folliculitis barbae and pseudofolliculitis barbae to occur at the same time in an individual.
Deep Folliculitis
In deep folliculitis, the whole hair follicle is inflamed. This type of infected hair follicle manifests differently. Some of the causes and symptoms are:
Gram-negative folliculitis
Most of the times, this problem occurs when you are on a long-term treatment of acne with antibiotics. The bacteria present in the human nose are usually harmless under normal conditions. But with antibiotics treatment, the bacterial balance can become altered thereby leading to an overgrowth of the gram-negative bacteria which are normally harmful. They can spread from the nose to the skin surrounding the nose and mouth and cause new, harsh acne to break out.
Sycosis barbae
This usually affects men who shave. Initially, small pustules develop on the chin, upper lip and under jaw. They spread and become more pronounced as time goes by and as one continues to shave. Scarring may occur with severe sycosis barbae.
Eosinophilic folliculitis
This is commonly seen in people with HIV infection. The presenting symptoms are recurring patches of inflamed sores filled with pus, and itching on the face, upper chest, scalp and neck. The sores spread, leaving behind areas of hyperpigmentation (darker than the normal skin) after healing. The actual cause of eosinophilic folliculitis is unknown. However, there are suggestions that it may be caused by the same yeast-like fungus that causes pityrosporum folliculitis.
Boils (furuncles) and Carbuncles
They are caused when staphylococcal bacteria deeply infect hair follicles. There is a sudden appearance of a boil which can be red or pink and really hurts. This can start with a hard lump that is painful to touch. There could be redness and swelling of the surrounding skin as well. The boil is then filled with pus as it increases in size and causes more intense pain before rupturing and draining. If it involves a large boil, healing may be accompanied by a scar, but for the smaller boils, there may be no scar formation.
Carbuncles are clusters of boils. They are often found on the shoulders, thighs, neck or back. Carbuncles give rise to more severe and deeper infections than single boils. That is why they develop and heal more slowly than boils. They usually leave a scar behind after healing.
Treatment
Infected hair follicle can be treated in diverse ways. Some of the few ways of treating them include:
- Antiseptic: You can use antiseptic lotion such as povidone iodine or a topical antibacterial such as fucidin or mupirocin over the affected part. They help to fight against the bacteria population and put the infection under control.
- Oral antibiotics: In severe cases, you can make use of oral antibiotics like Erythromycin or Cloxacillin. These would typically fight the infection from within and put the growth and spread under control. For carbuncles, you may need to start with intravenous or intramuscular antibiotics injections and then change to oral antibiotics as the situation improves.
- Analgesics: Potent analgesics will help to minimize pains and reduce further inflammation that comes with the infection process.
- Antiseptic soaps: Antiseptic soaps and bath preparations often help a lot in taking care of the infection. They work in the same way as antiseptic lotions. You can use the soap to wash the area. This can be done alone or you use them alongside taking the oral antibiotics.
- Medicated shampoos: This is helpful in the management of folliculitis of the beard or scalp. Simply apply the shampoo as you are about to take your bath. Allow to stay for a few minutes and then wash off as you bathe.
Removal
You can skillfully remove the boils, carbuncles or furuncles, using a few steps I am going to highlight below.
Removal of boils, carbuncles or furuncles which are brought about by infected hair follicles should not be done forcefully. Do not attempt to squeeze out the pus in the boil or furuncle as this would help to spread the infection further. Instead, you should look for a way to hasten the ripening process so that the pus, the infecting organisms, and the dead tissues can all be expelled naturally by the body. You should only pop the boil if it develops a head (the pus is visible at the top) or when it becomes really soft.
When it is not yet soft, apply warm compresses as explained under the ‘Home remedies’ below. Do this several times a day until it becomes soft and ready to be popped. If it is soft, clean the boil, furuncle or carbuncle and the surrounding tissues with an antiseptic lotion to minimize the spread of infection to the surrounding tissues.
Put your cotton or gauze swab around the affected area and gently apply pressure from both sides of the boil to empty its content into the cotton swab, making sure that the pus does not drain onto the nearby skin as this can lead to a further spread of the infection. After draining the pus, clean up the skin with the antiseptic lotion and apply a soothing cream like hydrocortisone to the boil. You can also apply white vinegar to the itchy skin to minimize the skin irritation. Wash your hands with warm, soapy water and dry them.
Home Remedies
There are a lot of things you can do at home to help get rid of the infected hair follicles or reduce the discomfort that comes with the problem. Some of the home remedies to employ include:
Turmeric
Turmeric is good for boils and staphylococcal infections. It is a traditional Ayurvedic spice that is used as an anti-inflammatory therapy and blood purifier. You can easily purchase the powder form from any grocery store. Mix a glass of warm water with 1 teaspoon of turmeric powder. Drink it three times daily. You will start noticing the healing in a matter of hours. This should be repeated for 3 days. You can get the capsule if you don’t love the taste of the turmeric mixture.
Onions
They can be employed in the treatment of boils. They have antiseptic chemicals that work as antimicrobial irritants. When applied to boils, they heat up the boil and increase blood flow to the area of infection, making it faster to cure the ailment. All you need to do is to cut a slice of onions and place it over the boil. Hold it in place with a piece of clean cloth (wrap it around). The onions should be changed every three to four hours until the boil forms a head and begins to drain.
Tea tree oil
This has served as an antibacterial, antiseptic and antifungal agent for several centuries. It is quite useful in relieving discomfort and speeding up the healing process of boils and carbuncles. Dab a piece of cotton swab into the tea tree oil. Apply it gently to the boil or carbuncle. Discard the used swab, making sure it has no contact with uninfected skin areas. Repeat the procedure several times daily.
Echinacea
This is an herbal remedy that works fine on boils and helps them to heal faster. Its active ingredients help to cleanse the lymph gland and the blood, thereby making it easier for the antibiotics to circulate and get rid of the infections. To get rid of boils, take 2 capsules of 300mg of Echinacea. It is advisable not to take the preparation continuously for over 2 weeks.
Black oil
Boils and carbuncles have been successfully fought for centuries using the black oil. Add half a teaspoon of black oil to a glass or cold or hot drink. Drink it two times every day during the active phase of a boil infection.
Hydrotherapy
Apart from the above-listed home remedies, there are other steps you could take to help heal your folliculitis faster. The procedure is called hydrotherapy – the use of water to treat the inflammation and pain associated with the boils and carbuncles. But how do you use the water? I shall quickly talk about that below.
Warm compresses
Applying warm compresses to the areas of inflammation would help to improve blood supply to the area and help the body’s immune system to take care of the problem fast. Warm compresses can also soothe the itchy skin. Pour water into a bowl and add salt to the water. Soak a hand towel or napkin in the warm salty water. Wring out the excess water and apply the towel over the affected area.
Tea compress
Apply a warm tea bag over the boil for a period of about 15 minutes on a stretch. Repeat it several times daily.
Bread compress
This is an old method of treating boils. Even though it is old, a lot of people testify that it truly works on boil. Soak a piece of bread in warm milk and then paste it directly on the boil. Replace the warm slice of bread continuously for 15 minutes at a go. Repeat this up to four times daily.
Vegetable compress
This involves the application of heated slices of raw onions, tomatoes, outer leaves of cabbage, or mashed garlic directly to the surface of the boils, carbuncles, or furuncles. Place the heated vegetable on the boil and leave it for about 15 minutes at a time. If the vegetable begins to feel cold, replace it.
Waxing an infected follicle
Waxing an infected follicle is a potentially dangerous practice that must be avoided at all cost. Waxing is a semi-permanent hair removal which involves removing hair from its root. When waxing is done, new hairs will usually not grow on the waxed area for at least four to six weeks. One can wax any part of the body like the face, eyebrow, pubic area (known as bikini waxing), feet, arm, abdomen, leg, back, nose, and behind ear.
However, waxing can lead to ingrown hairs, minor bleeding, and red bumps. One can easily get hair follicle infection from waxing, because of the destruction of the skin integrity (by pulling off tiny pieces of the skin’s outer layer) which creates an opening for microorganisms to infect the follicles thereby causing folliculitis, boils, carbuncles or furuncle. You must avoid waxing the eyelashes and the eyelids because the skin in these areas is quite sensitive.
Conclusion
Infected hair follicle is a common health condition that causes you an embarrassment in public, as result of the ugly skin development. The pain and the itchy skin could make things unbearable for one. However, following the advice in this post can save you a whole lot of pain. Should you at any time be confronted with infected hair follicle, try the home remedies we outlined above. They will sure be of great help to you.