Infected Cut
Infected cuts may be caused due to certain medical conditions such as diabetes, inadequate hygiene or even psychosocial factors. If you are recovering after an injury or a surgery, it is important to take due care to prevent your cuts or wounds from getting infected. Infected cuts occur when bacteria enters your skin through the cut and multiplies within. This may delay the process of wound healing.
What are the Causes of Infected cuts?
Infected cuts are caused when the cuts or wounds on your skin are contaminated by bacteria. In most of the cases, infections in cuts occur due to bacteria present in the skin or other parts of the body or the bacteria originating from the environment. The normal microbial flora present on the skin and body are harmless when their numbers are in control, in fact it is considered to have some beneficial effects for the skin and the body. However, when there is a cut or wound on the skin, these normal microbial flora get the opportunity to multiply and grow within the injured area. This causes infection in the cut that may prolong the healing time.
Infected cuts are generally caused due to bacteria belonging to Staphylococcus species, especially Staphylococcus aureus. Poor dressing of wound or inadequate hygiene in general may increase the risk of developing infected cuts. Elderly people, people with compromised immunity and diabetics are at increased risk of developing infected cuts.
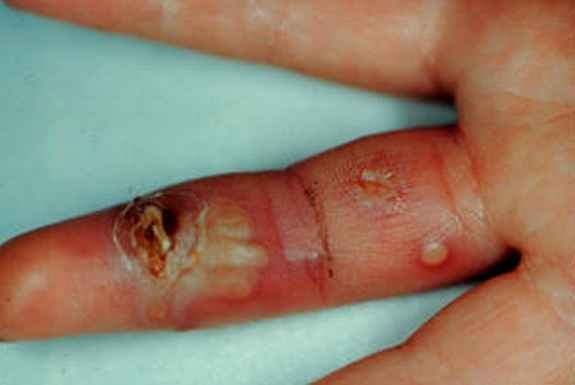
Infected cuts on hands
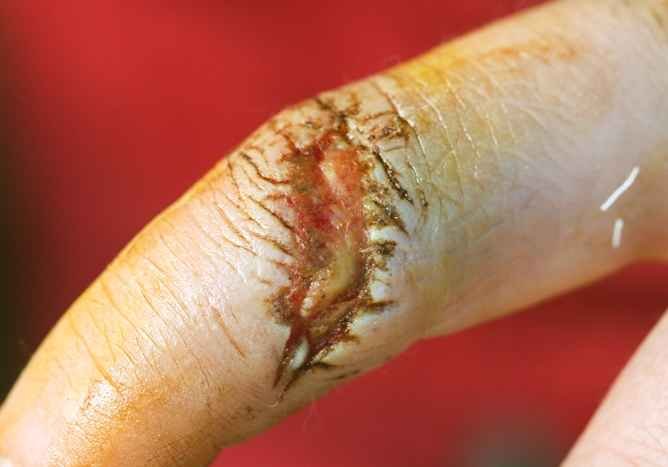
Fingers are very prone to get cut, either due to a knife, glass or metal object. It is normal to see some amount of blood oozing out of the cut on your finger. Oozing of blood generally stops on its own and does not require any special medical help. However, if you are a diabetic or are immune compromised, you should take due care to prevent any infection. Your elbows are also very vulnerable to scratches and cuts, especially if you are a sportsperson. If ignored, the minor scratches and cuts on your elbow may get infected and may cause serious complications.
Infected cuts on foot
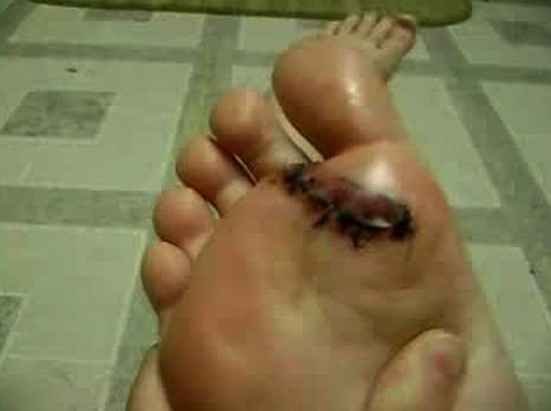
Feet, knees and ankles are very vulnerable to cuts, bruises and wounds due to sharp objects or if you fall while running or playing. Moreover, cuts on feet are also subjected to repeated trauma. Therefore, cuts on feet or feet lacerations may get infected easily.
Infected cuts on mouth
You may get minor cuts on your mouth, especially the lips while participating in sports or playing. Children are very vulnerable to getting cut on the mouth. Sometimes, there may be immense bleeding from the mouth if the tongue, gums or lips have got cut as these areas are rich in blood supply. Just like cuts on any other part of your body, it is important to ensure proper healing of the cuts on your mouth in order to prevent it from getting infected.
What increases the Risk of Infected cuts?
Anything that interferes with or diminishes your body’s natural ability of healing will expose you to the risk of getting your wound infected. The risk of cuts getting infected may increase greatly due to one of the following reasons or a combination of them.
Foreign objects
If you have got a cut due to pricking of glass or some metal on your skin, some part of the foreign object may get retained on your skin or may even enter the cut and may go unnoticed. This foreign object later interferes with your body’s ability to heal the wounds and may delay the process, thereby causing infection.
Medical conditions
Certain medical conditions such as diabetes, cancer, improper functioning of liver, kidney or lungs may slow down the process of healing and may increase the risk of infections in the cuts.
Compromised immunity
Your body’s ability of healing cuts and wounds decreases if your immune system is weak. Your immunity may get compromised if you are suffering from diabetes, HIV or are undergoing chemotherapy. If you have any medical condition that compromises immunity, you should be extra cautious when you have cuts in order to prevent them from getting infected.
Repeated injury
If you already have a cut and if you subject the cut to repeated trauma, it may not get the time to heal properly due to repeated stress. This may worsen the situation by giving way to infections to occur within and around the cut.
Reduced supply of blood to the wound
Proper blood supply is required for quick healing of cuts and wounds. If you have cardiovascular disorders such as blood pressure, narrow blood vessels or some heart conditions, you may be at an increased risk of getting your wound infected. Smoking may all the more worsen the situation.
Symptoms of Infected cuts
If a cut does not heal quickly, it may spread and the skin surrounding it may become red and tender. In some cases, you may see rashes or blisters on the surrounding area. The infection may also spread inside the skin. This process is known as cellulitis. As the infection spreads through the blood into your whole body, you may observe various symptoms such as fever and weakness. The symptoms that are generally presented during an infected cut are as follows
Malaise
Malaise is described as a feeling of lethargy and tiredness. It may occur as a non- specific symptom of a localized bacterial infection. You may feel very lazy and may end up sleeping more than usual. If you have undergone a surgery recently, malaise may also occur due to the stress your body has gone through during the surgery. However, if the cuts made during your surgery are not infected, you will start feeling better and more energetic with every passing day. If you do not feel better with time after surgery, talk to your doctor to make sure you have not contracted some infection which has entered your body through the cuts.
Fever
Elevated body temperature i.e. fever and loss of appetite are generally considered to be a symptom that your body’s immune system is trying to fight some sort of infection. If you have had a surgery recently, a slightly raised body temperature of around 100 ° Fahrenheit may be considered to be normal. In some cases, fever may be accompanied with sore throat. However, if the temperature of your body goes beyond 101 ° Fahrenheit, there is a possibility that you have infected your surgical cut or wound.
Drainage of fluid
Irrespective of whether the cut is due to an injury or surgery, some extent of fluid draining out from the cut is considered to be normal. The fluid that generally comes out of the cuts is either clear or slightly yellow in color. The normal drainage can be taken care of by using hydrocolloid containing absorbent dressing or by negative pressure therapy. However, green or cloudy fluid with a stench should be considered as an alarm that you may have possibly infected the cut.
Pain
It is very common to experience pain when your skin gets cut. However, the pain should alleviate as time passes. If your skin around the cut starts turning red and inflamed and is accompanied by continuous pain that increases with time, there are chances that the cut is infected. In case of infected cuts, you may even feel that your skin around the cut or wound has turned warm and is emitting heat. This occurs as sequelae of your immune system trying to get rid of the infection.
What are the Complications caused due to an Infected cut?
If the infected cut is ignored and left untreated, it may develop into a serious infection known as sepsis. In severe cases, the cut may turn in a tender or itchy and pus containing painful lump called as abscess. If you have an infected cut from metal object or any other sharp foreign body, there is a very rare possibility of developing tetanus infection. Consult your doctor to know whether you need to take a tetanus injection to prevent further complications. In extremely rare cases, infected cuts may lead to an infection called necrotising fasciitis, also known as flesh eating bug. In this condition, a large area of the skin gets damaged and the condition is very painful.
How is an Infected cut Diagnosed?
If you suspect that your cut has got infected, visit your doctor immediately. In most cases, the physician will be able to diagnose infected cuts just by looking at it and by assessing your medical history. If required, the physician may prescribe the following tests for confirmation of infected cuts
Blood tests
Generally if you have any form of infection in your body, it can be diagnosed by carrying out a complete blood count determination. An elevated leukocyte count indicates presence of infection.
X- ray, CT scan or MRI
If you have a very deep cut, the physician may ask you to get an X-ray, CT scan or MRI done of the area in which you have the cut. These tests enable the proper visualization of the tissues and bones of the affected area which may help in determining the presence of infection. It will also help in determining whether there is some foreign object left inside the cut. You may be administered a contrast dye during CT scan. Inform your healthcare provider if you have had any allergies to the contrast dye.
Culture test
A small swab of fluid will be taken from the affected area to carry out some microbiological tests that will help in establishing the presence of infection in the cut, if any.
Infected Cut Treatment
The course of treatment of infected cut will depend on how severe and deep the cut is. The basic steps involved in treatment of infected cut would be as follows:
Cleaning the cut
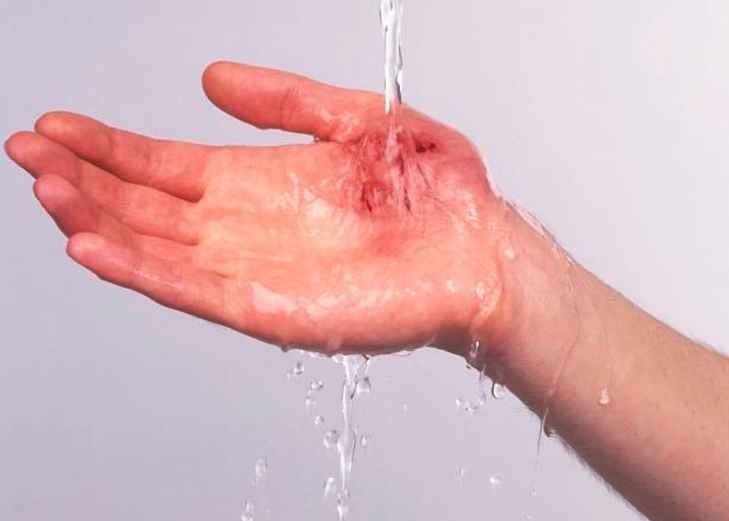

It is important to clean the cut using clean water and antiseptic solution. Make sure you use clean cotton balls for cleaning your wound. If you observe some foreign objects in the affected areas, take care not to wipe the affected area vigorously in order to prevent small particles of the foreign object from entering your body through the cut.
Oral antibiotics and painkillers
If you have an infected cut, your doctor may prescribe oral antibiotics to get rid of the infection. If the infection is caused due to an open wound or cut, impregnated dressings containing natural antibiotics such as honey or silver may be helpful.
Your doctor may also prescribe some painkillers to reduce the pain and swelling. It is important for you to know that painkillers cause stomach ulcers and bleeding inside the stomach. Therefore, do not take pain killers unless your physician prescribes it. If you have high body temperature, your doctor may prescribe some medicines like paracetamol so that the fever subsides.
As already mentioned in this article, in most of the cases, infected cuts are caused due to Staphylococcus bacteria. Note that there is a resistant form of these bacteria known as methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). If your cuts have been infected with these bacteria, you may not respond to the normal antibiotics prescribed to you. If your cuts do not start healing within 5 days of initiation of treatment, consult your doctor to know whether culture test for MRSA is required.
Home remedies
If you have a cut due to a foreign object that has embedded deep inside the cut, do not try to pull it out. You may end up damaging the skin and tissues around the cut. Seek help immediately in such cases.
However, if you have a minor cut, do not have to take a tetanus injection and are not at risk of infecting the cut, you may treat the infection using simple home remedies. You may try using the following home remedies to speed up the healing process
Stop bleeding
Minor bleeding may occur when you get a cut on your skin. First, stop the bleeding by applying pressure on the cut. You should use a clean bandage or cloth to cover the cut to stop bleeding. If the first layer of bandage or cloth gets soaked in blood, apply a new bandage over it without pulling the first layer off. Pulling the first layer of bandage off the cut may undo whatever clotting or stoppage of bleeding has occurred.
Clean the skin around the affected area
Once the bleeding ceases, clean the cut using a clean cotton ball. You may use a mild topical antiseptic solution to ensure that the area is free of germs. Avoid using rubbing alcohol, iodine or hydrogen peroxide to clean the cuts as these chemicals may harm the tissue and slow down the healing procedure. If you see some dirt sticking inside the cut, use a clean tweezer to remove it. Take care not to hurt yourself further while using the tweezer.
Apply natural antibiotics on the cut
You may apply essential oils such as peppermint, cinnamon or garlic oil which are known to have antimicrobial properties. Applying peppermint, garlic or cinnamon oil may cause some amount of burning sensation and irritation in the affected areas. Honey, lavender oil, apple cider vinegar and tea tree oil are also excellent antibacterial agents and will help in curbing the infection in the cuts without causing much irritation to the skin. You may also apply the age- old home remedy i.e. turmeric to your wound. It has been known since antiquity that turmeric contains curcumin as a major constituent, which acts as a natural antibacterial and wound healing agent. Alternatively, you can use powdered sugar for quick healing. Intake of excessive sugar is considered to be bad for your health However, when powdered sugar is applied on cuts or wounds, it acts as an absorbent which absorbs all the pus or water that is accumulated within the cut.
Cover the wound
Some people believe that keeping the wound covered may delay the healing process. However, it is advisable to cover the cuts using a clean bandage after application of natural antibiotics so that the medicine stays on the skin and can provide the necessary action. You may remove the bandage after a few hours.
Most importantly, if you have a cut, take care not to injure the affected area again, at least till the time the first cut heals! Follow adequate hygiene to avoid your cuts from getting infected. Small steps such as refraining from walking barefoot with a cut on the feet or entering public swimming pools when you have an open cut may help you in preventing the cut from getting infected.
When to get worried about an infected cut?
If you observe blots of blood on your bandage or dressing or you have severe pain, consult your physician immediately. You should seek a physician’s help if the area around the cut starts turning numb or if you face difficulty in moving the limbs below the cut. Inform your physician if you observe yellow or green pus or a bad odor coming out of the cut.
Bear in mind that cuts and wounds heal better when the area around it is kept clean and free from germs. So, if you have a cut, ensure that you clean the area regularly to have a happy healing!