Eosinophilic Folliculitis
What is Eosinophilic Folliculitis?
Eosinophilic folliculitis is a skin disease, primarily characterized by skin rash, itchiness and frequent recurrences. Its exact cause has yet to be identified. This medical condition is also known as eosinophilic pustular folliculitis, sterile eosinophilic pustulosis or Ofuji disease. The name of the disease comes from the eosinophils, which are immune cells found around the hair follicles. A skin biopsy performed on a patient suspected to have eosinophilic folliculitis will reveal the presence of eosinophils around the hair follicles.
This medical condition is rare and it seems that it affects predominantly more males than females. There are several main types of eosinophilic folliculitis, each with its own set of particular characteristics. The first is the classic type, commonly found and diagnosed in patients from Japan. The second is encountered in patients who are infected with the HIV virus. The third appears only in small children and particularly in infants. The fourth appears in patients who suffer from different forms of cancer. The fifth appears as a direct result of certain medications.
What does eosinophilic folliculitis look like?
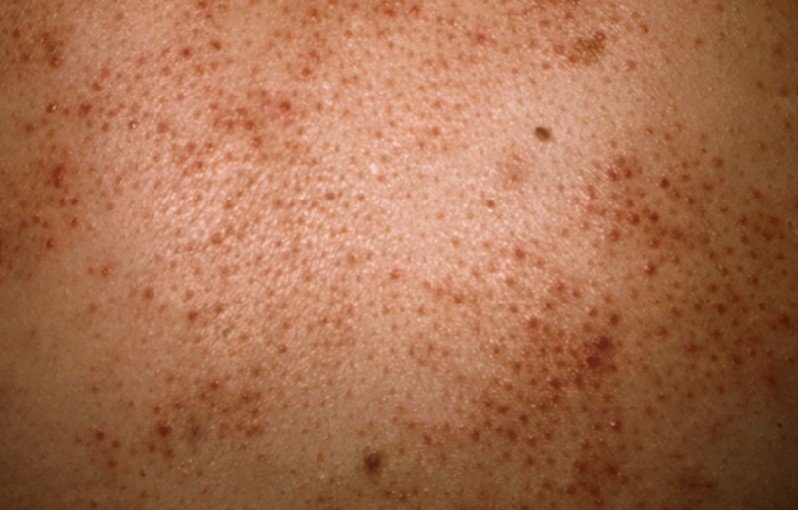
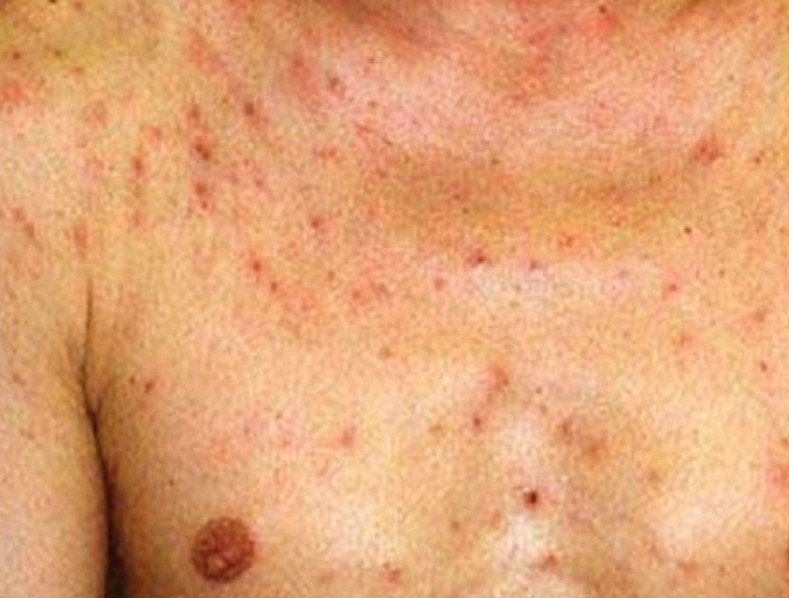
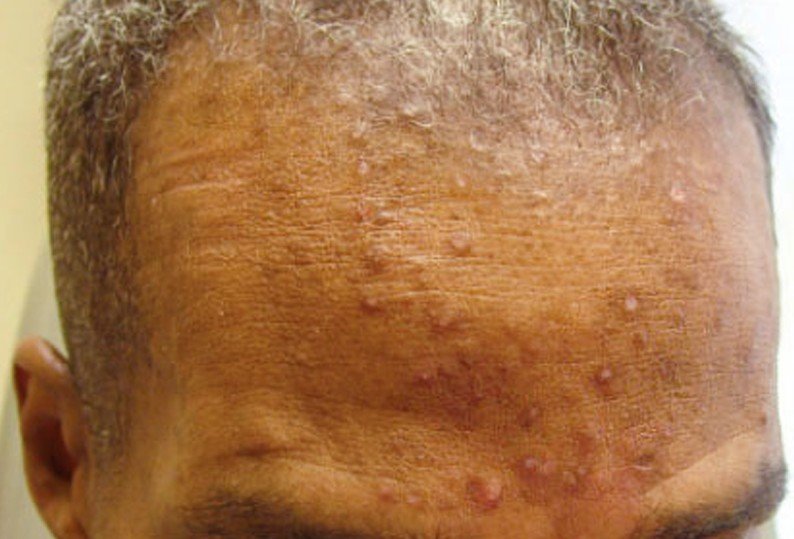
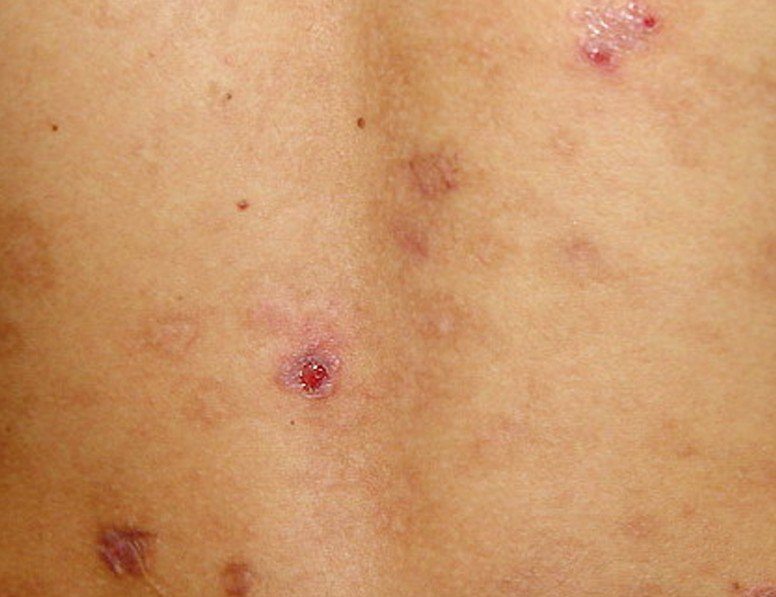
Affecting in general the upper part of the body, the lesions in eosinophilic folliculitis are represented by bumps or papules that are red and itchy. These lesions are centered on the follicle of the hair. Sometimes, they can have the color of the skin and they can take the shape of a dome. Most of the times, the lesions transform into pustules and they are easily confused with some form of acne or even other forms of folliculitis. The main areas where the lesions appear are on the face, scalp, neck and trunk. In rare cases, the lesions might be more extensive, the skin presenting large patches that are red and irritated. A patient might also present lesions on the palms and soles, but this happens only rarely and it is technically not folliculitis, because there are no hair follicles on those areas.
Symptoms of Eosinophilic Folliculitis
These are the most common symptoms of eosinophilic folliculitis:
- Skin lesions of different types: bumps, papules, pustules. These are sterile and centered on the hair follicle
- Lesions present on the upper part of the body, mainly on the face, scalp, neck and trunk
- The lesions are red or they can have the color of the skin
- Urticarial lesions appear in rare cases, with red and irritable patches of skin
- Itchiness is one of the most common symptoms, encountered in all forms
- Lesions on the palms and soles in rare cases
- In children, the scalp and especially the vertex are the most frequent areas affected
- The papules and pustules can have a diameter of between 20 and 50 mm in the classic form. The diameter is smaller, ranging from 1 to 3 mm, in patients who have been diagnosed with HIV infection
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation of the skin may also appear
- Internal organs are not affected
- Atypical cases, with urticarial lesions or lesions on the palms and soles, appear mostly in patients with HIV infections or small children (infants in particular).
Possible Causes
These are the most common causes of eosinophilic folliculitis:
- Immunodeficiency, such as HIV infection, Sezary syndrome, Hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome
- Prolonged cases of dermatitis, especially if there is a lot of itching and scratching involved
- Even though secondary infections of any kind (viral, bacterial or fungal) have not been found to be causes of this medical condition, one recent study has indicated that the hair follicle mite might be a culprit in its appearance
- Another study has shown that immune system changes can lead to the eosinophiles attacking the sebum producing glands
- Silicone breast augmentation
- Stem cell transplants
- Bone marrow transplants
- Allopurinol – this induces a generalized form of eosinophilic folliculitis.
How is eosinophilic folliculitis diagnosed?
This medical condition can be diagnosed by performing:
- Skin biopsy – this will identify the eosinophiles around the hair follicle
- Blood test – this will identify a rise of eosinophilic cells. However, this increase never reaches alarming levels. The same test will reveal an increase of IgE and a decrease of IgG and IgA
- In patients who suffer from an HIV infection – the levels of CD4 lymphocytes are decreased
- Clinical symptoms can also be used for the initial part of the assessment.
Treatment
These are most common courses of treatment, depending on the type of the eosinophilic folliculitis:
- HIV infected patients benefit from a reduction of the existent symptoms by receiving HAART (Highly active antiretroviral treatment)
- Anti-inflammatory medication can help reduce the inflammation.
- Antibiotics are recommended in cases of secondary bacterial infections, including oral Metronidazole.
- Oral antihistamines are indicated in case the lesions are accompanied by severe pruritus.
- Topical creams are especially recommended for patients who also suffer from HIV infections.
- Indomethacin – topical and oral administration.
- Naproxen has shown promising results.
- Anti-mite drugs, such as Permethrin, are recommended in case of hair follicle mites.
- Topical Tacrolimus can help as well. This treatment is recommended in order to suppress the response of the immune system and topical preparations seem to deliver the best results.
- Phototherapy – here there are two recommendations. The first is UVB light and it has shown promising results. The second is the UVA light but this is indicated to be used along with psoralen.
- Corticosteroids – topical and oral administration. These should not be administered for prolonged periods of time, as they can have serious side-effects.
- Calcineurin inhibitors – these are prescribed for various inflammatory conditions, reducing the response of the immune system.
- Colchicine – this is a drug often recommended for patients who suffer from gout, having a powerful anti-inflammatory effect. This is why it also works wonders on this medical condition.
- Retinoids – these should be taken only under the careful supervision of a doctor, as taken for prolonged periods of time, they can have serious side-effects.
- Itraconazole is recommended as anti-fungal medication.
Eosinophilic Folliculitis Pictures
Here are some of the pictures of Eosinophilic Folliculitis…