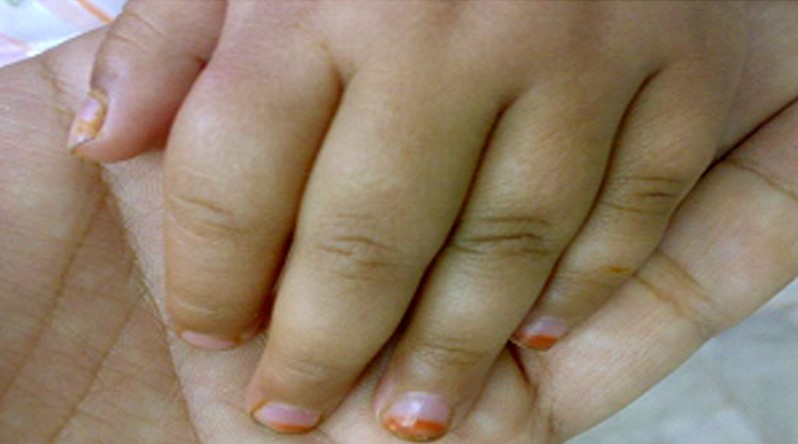
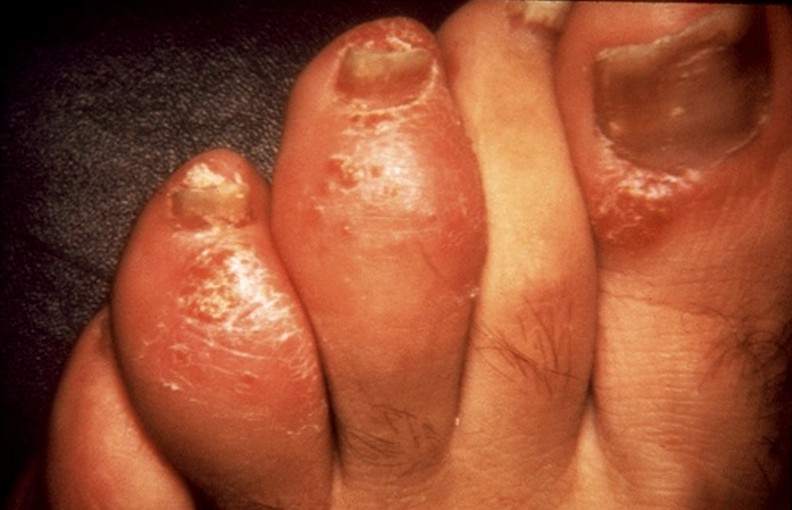
Dactylitis
Dactylitis is a medical condition in which a digit (finger or toe) becomes inflamed, taking the shape of a sausage and causing a lot of pain. The name of the condition comes from the Greek word ‘daktylos’, meaning finger. However, in the medical literature, it is known that both the finger and the toe can be affected. The diagnosis can be made with the help of a dactylitis score sheet (finger/toe involvement, circumference of the involved digit, contralateral digit, tenderness).
Dactylitis Symptoms
These are the most common symptoms of dactylitis:
- Inflammation of the finger or toe – the severity of the inflammation depends on the underlying pathology can leads to the appearance of this condition but also from one patient to the other
- Fingers and toes can be affected at the same time
- Painful swelling commonly appears along the flexor tendons (the patient is unable to flex his or her finger)
- Diffuse inflammation of the digital soft tissue (pseudosynovitis)
- Sausage-shape or puffy-like appearance of the inflamed digit
- The inflammation can extend to the other digits of the palm (suggesting involvement of digital and palmo-carpal synovial sheaths)
- If a finger is involved in the inflammatory process and its synovial sheath is communicating with the ulnar bursa, then there is a very good chance for the swelling and pain to extend to the palm of the hand
- The inflammation of the thumb and the fifth finger can lead to the teno-synovial inflammation of both the radial and ulnar bursa (according to the synovial sheath territory)
- Joint synovitis can also be present, accompanied by tenosynovitis and inflammation of the soft tissues
- Involvement of connective tissue has also been encountered in some patients
- Intense pain – the pain can be so intense that the patient will refrain from doing a lot of usual activities, avoiding using the affected toes or fingers
- Tenderness – this can evaluated with the tenderness test or the response of squeezing. The scores are as follows:
- 0 – no tenderness identified through squeezing the affected digit
- 1 – tenderness
- 2 – tenderness and wincing through squeezing
- 3 – extreme tenderness and immediate withdrawal when the affected toe or finger is squeezed
- The digits are warm to the touch – this is because there is a lot of blood in the area but the circulation is blocked. Also, the warmth can be a sign of bacterial infection in the area.
- Symptoms last for one to four weeks
- Sudden onset
- If the toes are affected, the child will refuse to bear weight. Older patients can be affected as well, refusing to walk on the affected toes.
- If the fingers are affected, the patient will refrain from using his or her hands as he or she would normally have (for example, a child will refuse to pick up toys or hold a drinking water bottle or cup)
- Systemic symptoms include: fever, increased number of white blood cells and mild anemia. These appear most often in bacterial infections and in children.
What are the Causes of Dactylitis?
The main cause behind the appearance of dactylitis is the blocked blood circulation. Another potential cause of dactylitis is the flexor tenosynovitis, without the distension of the joint capsule. The following medical conditions have been associated with dactylitis:
Tuberculosis
- Dactylitis is a rare manifestation of this condition
- It can affect the short and tubular bones in the hands/feet
- Radiologic sign – spina ventosa (particular lesion)
Syphilis
- Dactylitis can be one of the symptoms of congenital syphilis
- Similar to the dactylitis in tuberculosis, the difference being represented by the bilateral and symmetrical involvement
Sarcoidosis
- Dactylitis affects a small percentage of the patients diagnosed with this medical condition
- Associated with other types of lesions (nodules, plaques)
- The digits swell to take a sausage-like appearance
- The involvement is bilateral
Bacterial infection
- The anterior fat pad of the distal portion of the finger is infected and swollen
- Type of dactylitis that commonly affects children
- Most common bacteria involved in this type of dactylitis are: Streptococcus A beta-hemolytic and Staphylococcus aureus
Rheumatologic disease (spondyloarthritis, psoriatic arthritis)
- Dactylitis affects a third of the patients who are diagnosed with a rheumatologic disease
- The toes in the feet are the ones that swell and take the form of a sausage
Sickle cell disease
- This condition affects children under four years of age (most often children between six and nine months)
- Dactylitis is often the first symptom
- The inflammation of the digits is used for confirmation of diagnosis
- May be confused with other disorders (acute osteomyelitis, cellulitis, leukemia, rheumatic fever)
Treatment
These are the most common courses of treatment undertaken for dactylitis:
- Anti-inflammatory medication – this is recommended in order to alleviate the upsetting symptoms, such as pain and inflammation. Not only will this treatment bring the necessary pain relief, but it will also improve the range of mobility in the affected finger/toe and it will allow for the bearing of weight on the affected toes. The most recommended anti-inflammatory drugs are ibuprofen and acetaminophen.
- In severe cases, emergency medical treatment might be recommended. Going to the emergency room is recommended if the pain is not relieved by the usually administered anti-inflammatory medication, if inflammation occurs in other parts of the body other than the finger or toes and if the patient runs a high fever. The treatment in the emergency room will constitute of more powerful anti-inflammatory medication and intravenous fluids to maintain proper hydration. Reducing the fever will also be an immediate objective of treatment.
- Antibiotics are recommended in cases of bacterial infections, caused either by streptococcus or staphylococcus. It is important that the treatment is taken for the recommended period of time; otherwise, the bacteria might develop resistance of the administered antibiotic and the treatment will no longer provide the desired results.
- Proper hydration can guarantee a faster recovery from this condition. This is especially recommended for children, as they can get dehydrated easily.
- In many patients, the swelling and inflammation subside on their own, without any medical or surgical treatment.
Pictures of Dactylitis
List of pictures collection of Dactylitis…