Carotenemia
What is Carotenemia?
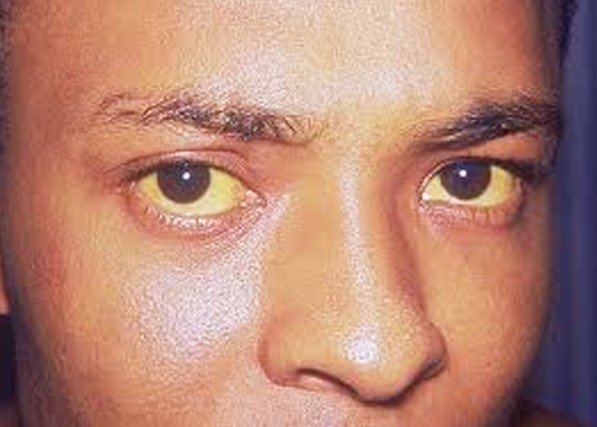
This medical condition is having the presence of excess carotenoids in your blood and causes a pigmentation of skin that resembles jaundice. The one way that you can differentiate whether it is jaundice or carotenemia is that the conjunctivae are not discolored when a person has carotenemia. It also does not affect your mucus membranes which include your nostrils, mouth, and eyes. Carotenoids are the yellow colored lipid-soluble compounds that are found in orange, green, red, and yellow fruits and vegetables.
The different carotenoids that are found in fruits and vegetables include:
- Alpha-and beta carotene
- Beta-cryptoxanthin
- Lycopene which is the red color found in tomatoes
- Lutein
- Zeaxanthin
- Canthaxanthin
- Astaxanthin
Carotenoids are found in milk products and many plants. It is also a major source of vitamin A, a necessary vitamin that your body needs. The reason that your body needs vitamin A is that carotenoids help to contribute to the normal color of your skin. Carotenoids will also help to protect your skin from being sunburn. It can happen to people of all ages, gender, and race although it is hard to see in people who have dark skin. Carotenemia is many times found in babies and infants who are fed large amounts of carrot and sweet potato processed baby food. These two vegetables are normally the first vegetables that are fed to babies and infants. It is also more prominent in people who are vegetarians.
Carotenemia Symptoms
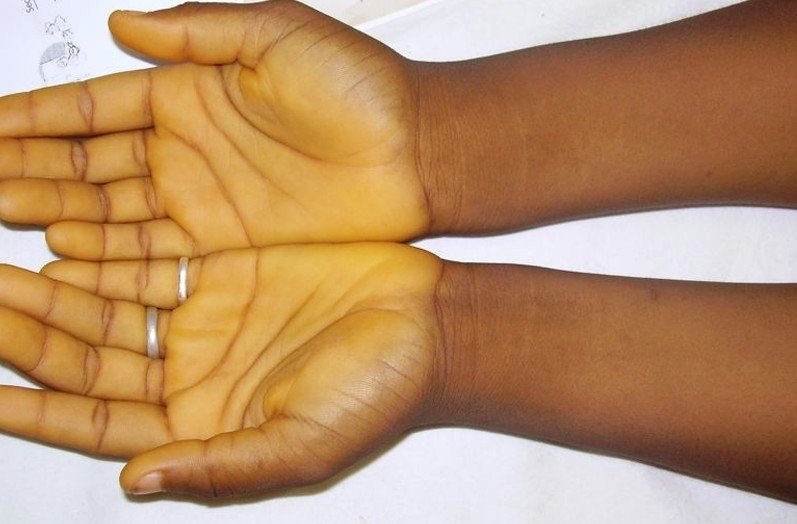
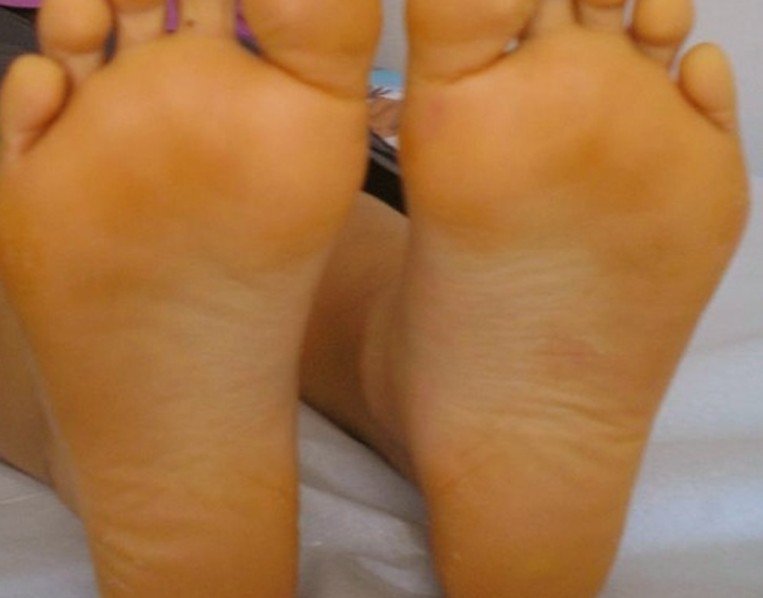
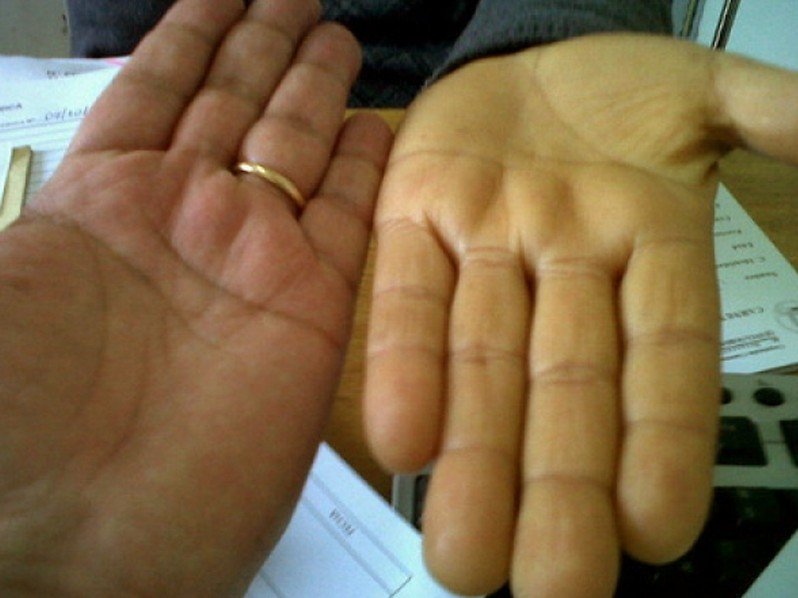
When you have carotenemia there are no actual symptoms but there are certain characteristics that could indicate carotenemia. This medical condition is characterized by the yellowing of the soles of your feet, face, other areas of your skin, and the palms of your hands. Sometimes these areas can even be slightly orange in color.
Carotenemia Causes
Carotene is absorbed by your gastrointestinal tract and then overtime it is converted to usable vitamin A. Your body gets rid of the extra carotenoids in your urine, feces, sebum, and sweat but if your small intestine becomes overwhelmed with excess carotene before your body can get rid of it the pigment will saturate your skin and blood. When this happens your skin will develop carotenemia. Although carotenemia is almost always associated with your diet and having excess carotene in your body it can also be a sign of a more serious medical condition like hypothyroidism, kidney disease, liver disease, and diabetes. Any of these medical conditions can alter the carotene levels in your body. There is also a genetic metabolic that inhibits the conversion of carotene to usable vitamin A and cause these same characteristics. It can also be caused by nephritic syndrome which prevents your body from excreting the excess carotenoids in your urine.
Carotenemia Treatment
If you notice any of the characteristics of carotenemia in yourself or your children you should see your physician to rule out any underlying medical problems. In most cases of carotenemia the physician will not recommend any treatment plan because it is usually the result of having a healthy diet and it is a harmless medical condition. To help reduce the yellowing of your skin you should moderate foods that are rich in carotene like:
- Carrots – by just eating a cup of this vegetable give your body more than six hundred percent of the recommended daily allowance of vitamin A.
- Squash – by eating a cup of this vegetable it provides your body more than one hundred forty-five percent of the recommended daily allowance of vitamin A
- Cucumbers
- Sweet potatoes
- Oranges
- Cantaloupes
- Green beans
- Leafy greens – these types of vegetable are very high in vitamin A and carotene with one cup containing three hundred seventy-seven percent of the recommended daily allowance. Leafy greens can include romaine lettuce, collard greens, broccoli, and kale.
When modifying your diet your skin color will return to normal within the first fourteen days but it could take as long as a few months because of the accumulated carotene that is in your tissues. Once your skin returns to normal you need to be sure that you do not overeat any fruit or vegetables that have a high level of carotene.
Carotenemia Pictures
Collection of pics, photos and pictures of Carotenemia…