Angiolipoma
Angiolipoma can be defined as a benign subcutaneous tumor, being primarily composed of blood vessels and fat. According to the studies made on patients diagnosed with this condition, it seems that this condition can be inherited (5% of all the cases). Angiolipoma is more often diagnosed in people who are young.
In the medical world, this condition is also known as hemangiolipoma, fibro myolipoma or vascular lipoma. Depending on its characteristics, the soft tissue tumor can be classified into two main categories, meaning infiltrating and non-infiltrating.
Symptoms of Angiolipoma
It is possible that the angiolipoma does not cause any symptoms. In some patients, the growth can be tender to the touch. Due to the similar aspect with the lipoma, the diagnosis is often mistaken. The lesion is soft to the touch, having a similar color with the one of the skin and appears as a plaque or a nodule. As for its actual location, it is commonly found on the forearms, arms and trunk. Solitary growths are uncommon, as multiple growths are present in the majority of the people.
The growths are rather small in size, being in general under 2 cm in diameter. Apart from the above-mentioned areas, the angiolipoma is frequently encountered in the subcapsular area. The blood vessels that are part of the angiolipoma are actually capillaries and it is possible that small fibrin thrombi are also present.
Angiolipoma Diagnosis
As it was already mentioned above, the different diagnosis can be made with lipoma; however, due to the clinical resemblances, it can be quite hard to decide on the final diagnosis. The confirmation of the diagnosis is obtained through biopsy, showing the composition of blood vessels and fat, which is characteristic for angiolipoma.
Apart from the lipoma, the differential diagnosis can be made with any of the following conditions: Kaposi sarcoma, spindle cell hemangioendothelioma, angioleiomyoma and angiomyolipoma.
Imaging studies can be of use in confirming the diagnosis of angiolipoma, showing the mixture of fat cells and blood vessels. The MRI is generally performed with contrast, so as to highlight the prominent supply of blood. As for catheter angiography, this demonstrates the blood vessels that are part of the tumor as well.
Treatment for Angiolipoma
The standard treatment for angiolipoma is represented by the surgical intervention. However, given the fact that we are talking about a benign growth, the surgical intervention is recommended only in the situation that the patient experiences discomfort or is bothered by the aesthetic appearance. The surgical removal of angiolipomas is not difficult to perform and there are no complications associated to it. The only situation in which the surgical removal is difficult is if there are too many nodules that have to be cut. It is also considered that infiltrating angiolipomas are more difficult to be removed. However, in the situation that the angiolipoma has been successfully removed, there is no risk of recurrence. On the other hand, it is possible that new tumors appear, without any connection to the ones that already exist.
Pictures of Angiolipoma
Angiolipoma Pictures – How does Angiolipoma look like?
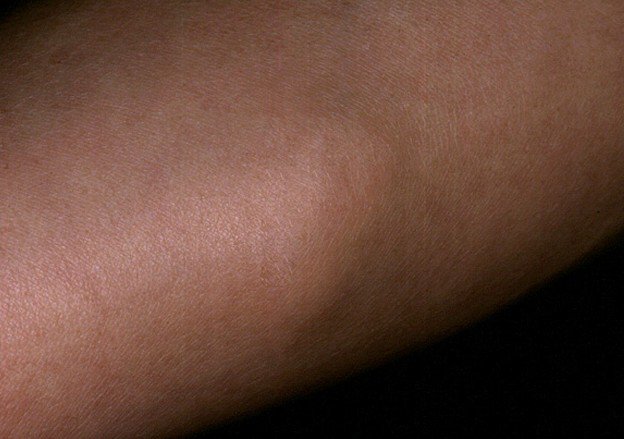
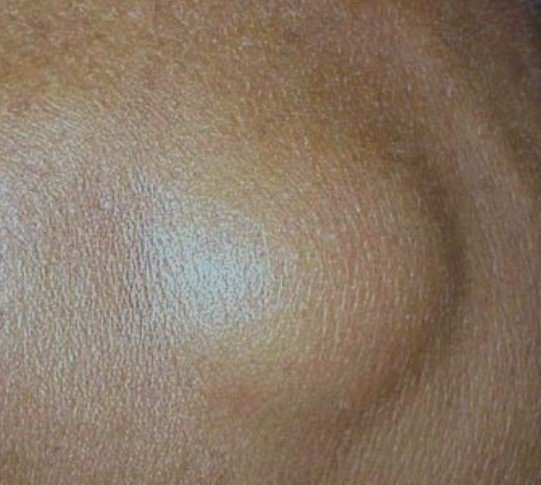
Epidural angiolipoma
The epidural angiolipoma is a distinct medical condition, having a similar composition as the rest of the angiolipomas (fat cells and blood vessels). However, epidural angiolipoma is more often diagnosed in women, especially in those who have reached the middle age. This benign tumor is characterized by gradual growth, with some of the most common symptoms including paraparesis and back pain (as the growth compresses the spinal cord). Sensory changes and exaggerated reflexes are highly likely to occur, particularly in the lower limbs.
This particular type of angiolipoma can be divided into infiltrating and non-infiltrating as well. However, the non-infiltrating angiolipomas are more commonly seen at the level of the epidural space. These are found in the thoracic region, more specifically in the dorsal part of the epidural space. On the other hand, the infiltrating angiolipomas are seen in the anterior part of the epidural space. Characteristic for this type of angiolipoma is the fact that it infiltrates not only the soft tissues but also the vertebrae in the area.
The diagnosis of epidural angiolipoma can be made with the help of imaging studies. On the CT scan, the components of epidural angiolipoma are revealed. The MRI can be used for similar purposes, demonstrating the prominent vascular supply of the benign growth. As for the differential diagnosis, this can be made with the following conditions: epidural metastases, lymphoma, multiple myeloma, epidural lipomatosis, Hirayama disease and spinal meningioma.
The treatment for the epidural angiolipoma is represented by the surgical resection. This is especially recommended for the tumors that fall in the non-infiltrating category. Epidural angiolipoma does not present any risk for malignant transformation. In some patients, for which the surgical removal would be mutilating, interferon therapy is used to reduce the size of the tumor. Once the tumor has been reduced in size, it can be more easily removed.
Prognosis
In the majority of the cases, it is possible to completely remove the benign growth, which guarantees the disappearance of the symptoms and, thus, an excellent prognosis. It is possible that some tumors are difficult to remove, especially if they have infiltrated into the adjoining tissues. The total resection of the tumor is especially important in the patients diagnosed with epidural angiolipoma, as this can guarantee the relief from the symptoms caused by the spinal cord compression. The fact that these tumors grow slowly is also one of the reasons why the prognosis is considered positive. Moreover, these tumors do not present any change for malignancy, which is another advantage.
In conclusion, even though this condition does not threaten life, it can have a negative impact on the quality of life. One must seek out medical advice as soon as possible, before the tumor grows even further. The doctor will perform the necessary investigations, in order to determine whether the tumor belongs to the infiltrating or to the non-infiltrating category. Once this has been established, the doctor can present you with all the information that you need to know on the surgical resection or with other therapy alternatives (such as interferon therapy).