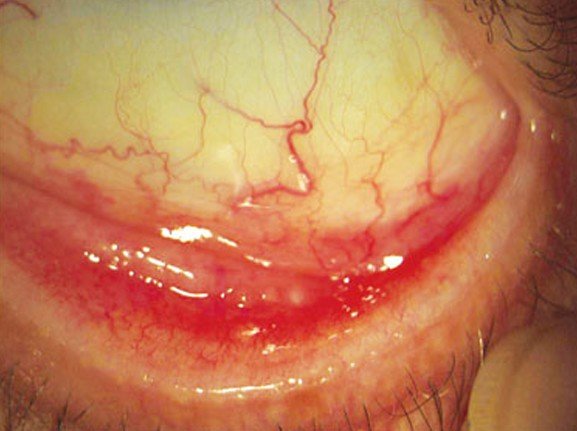
Conjunctival Hyperemia
Definition
Conjunctival Hyperemia is a medical condition in which the sclera of the eyes is characterized by redness. What happens is that the blood vessels of the eyes become dilated, hence the characteristic aspect.
Symptoms of Conjunctival Hyperemia
Apart from the characteristic redness, these are the most common symptoms associated with conjunctival hyperemia:
- Pain in the eye
- Blurry vision or loss of vision
- Increased sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Systemic symptoms (swollen lymph nodes, fever, nausea and vomiting) are encountered in acute cases (suggestive of infection)
- Discharge from the eye
- Green, purulent in case of bacterial infection
- Watery discharge if the main cause is an allergy (associated with tearing and nasal congestion)
- Facial rash might also be present in case of infection or allergies
- Tenderness upon palpation of the eyes or the eye might feel hard to the touch (closed eyelids)
- Significant differences in the pressure of the eyes (glaucoma in one eye)
- Sensation of having something in the eye (patients describe this sensation as ‘sand’ or ‘dust’ in the eyes)
- Severe throbbing sensation (acute glaucoma)
- White infiltrate under the corneal epithelium (infection)
- Inflammation of the eyelids margins (blepharitis)
- Dry eye, with reduced production of tears
- Diffuse or limited inflammation of the sclera.
Causes
These are the most common causes that lead to the appearance of conjunctival hyperemia:
- Exposure to irritating substances (chemicals, dust, debris)
- Conjunctivitis
- Infectious – bacterial, viral; gonococcal, chlamydial
- Recurring (chronic conjunctival hyperemia)
- Allergic – direct exposure to different allergens (pollen, dust mites or dander from pets)
- Trauma or injury
- Endogenous ocular health problems (suggestive of a systemic disease)
- Inflammation of the eye sclera (scleritis or episcleritis)
- Leads to the dilatation of the blood vessels in the eye
- Commonly associated with autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis
- Keratitis – most commonly caused by bacterial or viral infection
- Associated risk factors include: wearing contact lenses, trauma to the eye, surgical intervention on the cornea, reduced immunity
- Intraocular inflammation
- Subconjunctival hemorrhage
- Sepsis (especially if there are systemic symptoms present)
- Systemic autoimmune disorders
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Connective tissue diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, Sjogren’s syndrome)
- Medication
- Anticoagulants (aspirin, other NSAIDs, warfarin)
- Intraocular surgery
- Wearing contact lenses
- Glaucoma (with or without increased intraocular pressure)
- Corneal abrasion
- Infectious corneal ulcer
- Blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelid margins, caused by bacterial infection – most common: staphylococcus)
- Anterior uveitis (inflammation of the anterior segment of the eye)
- Potential causes – infectious microorganisms, autoimmune disorders, exposure to toxic substances, cancer, trauma or injury
- Chemical burns
- Rapid penetration of the chemical substance into the cornea
- Other conditions
- Cancer (sebaceous cell carcinoma)
- Senger’s disease
- Amyloidosis
- Occupational or environmental factors
- Foreign bodies in the eye.
Treatment
These are the most efficient measures of treatment recommended for conjunctival hyperemia:
- Compresses
- Cold compress – recommended for the relief of the symptoms caused by eye allergies or in case of inflammation
- Warm compress – recommended in patients who have red eyes because of blepharitis (+ excellent hygiene for faster recovery)
- Eye patching
- Recommended to be worn as a protective measure in case of corneal abrasion (+ topical antibiotics)
- Variant – eyeshield – recommended to prevent the contact with the eye (suspicion of globe rupture)
- Removal of the eye patch is possible when the condition improves
- Double eye patching + dim light + analgesic medication – treatment protocol for burns of the cornea caused by the intense or prolonged exposure to UV rays
- Eye patches – not recommended in patients diagnosed with infectious conjunctivitis
- Removal of foreign bodies (visible with the naked eye)
- Before the foreign body is removed, a local anesthetic is going to be removed
- Antibiotic ointment – reduce the risk of secondary bacterial infections
- Elimination of the medication that caused the eye to become red
- The patient should talk to the doctor about the possibility of using other similar medication, one that does not have such side-effects
- Antihistamines
- Recommended in case of allergies
- Administration – oral and topical
- Avoidance of the allergen
- Other medication for eye allergies includes:
- Topical vasoconstrictors
- Mast cell stabilizers (cromolyn)
- Topical corticosteroid ointments
- Steroid eye drops
- NSAIDs (ketorolac)
- Protective sunglasses
- Recommended measure for those who suffer from the dry eye syndrome
- Artificial tears, anti-inflammatory medication (corticosteroids, cyclosporine)
- In case of chemical exposure:
- Irrigation with saline solution (high quantities)
- Pain management (depending on the intensity of the pain – narcotics or NSAIDs)
- Antibiotics
- Recommended for acute cases of bacterial conjunctivitis
- Available for oral and topical administration
- Broad spectrum antibiotics are generally prescribed (gentamicin, tobramycin)
- Severe cases – topical administration of fluoroquinolones (ofloxacin, ciprofloxacin)
- Antibiotic eye drops – for persistent or recurring cases of conjunctivitis
- Miotic drops
- Recommended for acute glaucoma.
As you have seen, conjunctival hyperemia can either by caused by acute or chronic conditions. Recognizing the early signs and symptoms of different conditions is essential, so as to prevent the more serious complications that can occur with the passing of time (loss of vision, chronic glaucoma). It is also important to understand that there are many external factors that can lead to the appearance of such problems, such as airborne allergens, occupational or environmental exposure to different toxins and so on.
If you work in an environment with a high risk of exposure to chemical or toxic substances, you need to wear protective gear. Don’t take your chances and think that such things will not happen to you. It is for the best that you protect yourself – it is often easier to prevent rather than treat. Also, if it happens that you are in accident and someone close to you has a foreign body in the eye, avoid handling such problems yourself. Wait until the ambulance arrives and let the doctors handle the removal of the foreign body. By trying to remove it yourself, you will probably do a lot of damage to the respective eye, causing the permanent loss of vision. Plus, you will cause a lot of pain to the person. With such matters, it is for the best to leave matters in the hands of specialists. The eye remains one of the most sensitive parts of the human body and you need to always remember that.