Actinomycosis
Actinomycosis is a polymicrobial infection that occurs extremely rare in humans and more often in animals. The infectious bacterial disease, when it affects humans, can range from sub-acute to chronic. It has different clinical forms, including the one affecting the cervical and facial area, the thoracic and abdominal form. In women, there is a pelvic form that can be developed. The fact that this is a polymicrobial infection means that there are actually several bacterial species causing the problem (usually somewhere between five and ten).
The bacterial species that commonly cause this infection are part of the regular flora of the oral cavity; they are also found in other parts of the body, including the gastrointestinal tract and the genital tract of females. However, in this area, their percentage is reduced. What happens is that these bacteria cannot breach the skin if the mucous membrane is whole; however, if the mucous membrane is not whole anymore because of various reasons, then the bacteria can enter the deeper tissues of the body and cause the polymicrobial infection. This is a severe infection, in which the body develops a powerful inflammatory response and a wide range of clinical features are present.
Actinomycosis Symptoms
These are the symptoms of actinomycosis, depending on the actual form of the disease:
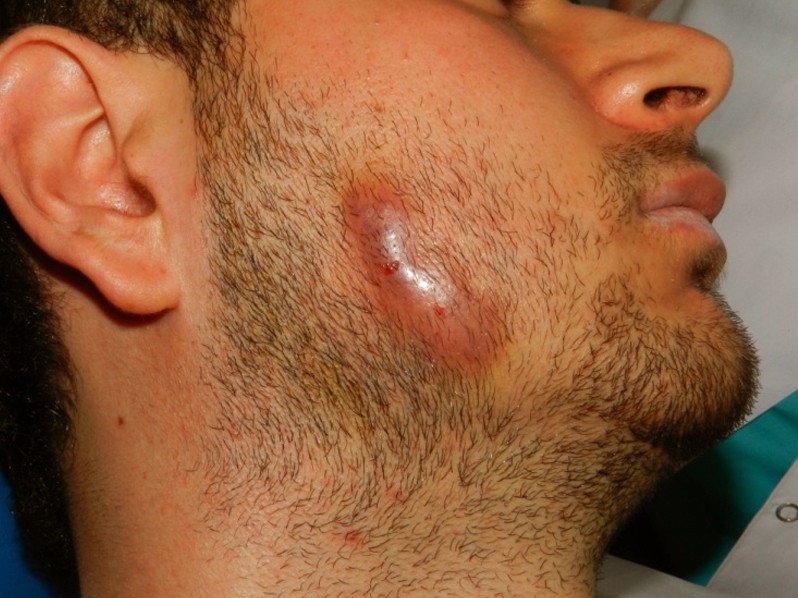
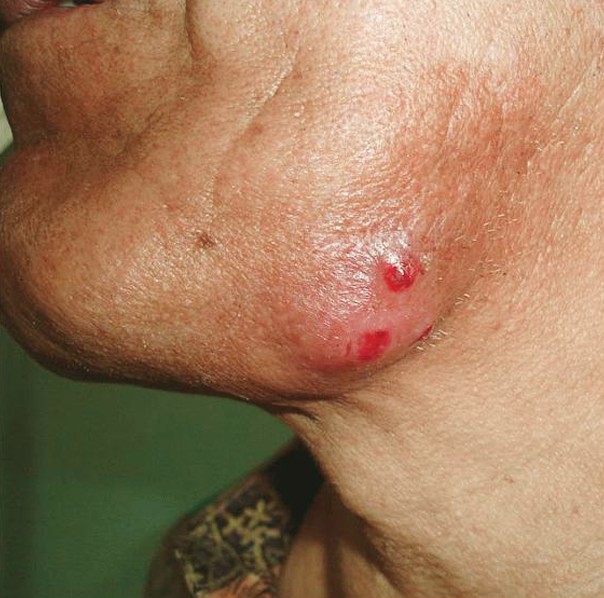
Cervico-facial actinomycosis
- This condition is also known as a lumpy jaw
- In a lot of cases, this form is not accompanied by pain
- Pain might arise along with the inflammation of the soft tissues from the submandibular or peri-mandibular region
- Abscess formation with formation of sinus tracts and pus discharge
- Pus contains sulfur granules
- The condition can enter into remission and re-occur after a period of time
- The skin in the affected area is discolored
- Nodular lesions in the angle of the jaw
- No swollen lymph nodes
- The patient can also present fever
- The mastication might be impaired, as the muscles responsible for the process are affected as well.
Thoracic actinomycosis
- Cough (dry or productive)
- Sputum with blood
- Difficult breathing
- Pain in the chest
- Fever
- Weight loss
- Abnormal sounds in the chest
- Sinus tracts can form on the chest as well, with pus discharge.
Abdominal actinomycosis
- Fever (low in intensity)
- Weight loss
- Overall weakness
- Bowel movement is affected
- Abdominal discomfort
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Palpable mass in the abdomen
- Sinus tracts are formed in the abdomen, with pus discharge.
Pelvic actinomycosis
- Abdominal discomfort (lower region)
- Abnormal bleeding from the vagina
- Discharge from vagina
- Palpable mass in the lower abdomen.
What Causes Actinomycosis?
Actinomycosis is a polymicrobial infectious disease. Below, you will find the bacterial species incriminated in the appearance of the disease:
- Actinomycetales, family Actinomycetaceae, genus Actinomyces:
- Actinomyces israelii
- Actinomyces gerencseriae
- Actinomyces turicensis
- Actinomyces radingae
- Actinomyces europaeus
- Other Actinomyces: naeslundii, odontolyticus, viscosus, meyeri
- Propionibacterium
- Propionibacterium propionicum
- Actinobaculum
- Bifidobacterium
- Other bacterial agents that accompany the original bacteria:
- Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans
- Peptostreptococcus
- Prevotella
- Fusobacterium
- Bacteroides
- Staphylococcus
- Streptococcus
- Enterobacteriaceae.
Diagnosis
These are the most common methods used for the diagnosis of actinomycosis:
Complete blood count
- Anemia
- Leukocytosis
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate is increased
- C-reactive protein is increased as well
Chemistry levels
- Normal in most cases
- Hepatic actinomycosis: Increased alkaline phosphatase
Bacteria culture
- A sample of the bacterial culture is necessary for the confirmation of the diagnosis
- The sample can be taken from the following sources:
- Sinus tract with pus discharge
- Deep tissue (through aspiration)
- Other possibilities: swap in the oral cavity, sputum sample, urine specimen.
- Gram-stained smear is also used for the confirmation of the diagnosis
- Nucleic acid probes
- Polymerase chain reaction
Examination of sulfur granules under the microscope
Papanicolaou test is recommended in case of suspicion of pelvic actinomycosis. However, this is a not a test used for diagnosis.
X-rays
- Recommended in case of pulmonary affectation
- Used for the diagnosis of thoracic actinomycosis
- The X-ray can reveal a mass-like lesion
- This lesion can affect the pleura (lining of the lungs and anterior thoracic wall), the thoracic vertebrae, the ribs or the sternum
Computer tomography
- CT can detect an infiltrative mass, in different regions in the body
Ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration
- This is used for the biopsy necessary for the confirmation of diagnosis
Surgical exploration
- Thoracotomy
- Open lung biopsy
- Exploratory laparotomy.
Actinomycosis Treatment
These are the most common methods of treatment used for actinomycosis:
Antibiotics
- This the number one course of treatment
- Penicillin G is often effective in treating the polymicrobial infection
- Administration of high doses
- Treatment is required to be followed for prolonged periods of time (up to one year)
- The patients diagnosed with the cervico-form of actinomycosis can take the antibiotic treatment for shorter periods of time (six months)
- Minimum risk of the patient developing resistance of the treatment with antibiotics
- Given the fact that this is a polymicrobial infection, it might be necessary to add a secondary treatment to the course of treatment. This happens when one of the bacterial species is resistant to the first course of treatment.
- Other antibiotics that can be administered include:
- Metronidazole
- Aminoglycosides
- Aztreonam
- Co-trimoxazole
- Other penicillins: methicillin, oxacillin, cloxacillin
- Cephalexin
- Fluoroquinolones: ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin.
- In more severe cases, intravenous antibiotics will be administered through a peripherally inserted central catheter.
- The response to the given antibiotic therapy is monitored to the usage of imagining methods, such as the CT and MRI.
Surgery
- Incision and drainage of skin abscesses
- Sinus tract excision
- Removal of fibrotic lesions
- Cleaning of infected areas through surgical methods
- Decompressive surgery in case of pelvic actinomycosis affecting the uterus
- Emergency medical treatment in case of peritonitis (this appears in patients diagnosed with abdominal actinomycosis)
Actinomycosis Pictures
Images, Photos and Pictures collection of Actinomycosis…