Swollen Upper Lip
Swollen upper lip is a condition when the upper lip of a person gets bigger in size along with a feeling of numbness and pain in it. The swollen region can be either a part of the upper lip, the whole lip, or the inside portion of the lip. Sometimes the swelling happens overnight and the person is unable to find the reason. This problem is common in adults as well as in babies. The swelling in the upper lip is usually caused by different factors that can be directly and indirectly linked to the lip. The swelling can sometimes be seen as one of the symptoms of a different disease.
Symptoms of Swollen Upper Lip
The symptoms are:
- Numbness and Tingling: In some cases the swollen lip might feel numb and have a little tingling sensation to it. This usually happens when the whole lip is swollen and you cannot feel anything while touching or moving your mouth.
- Increase in the size of lip: Swelling in itself means that the lips get filled with fluids and become bigger in size. But in some cases, the swelling comes overnight and makes the lip very large. This can increase the size of the lip in a particular area like just below the nose or the whole lip.
- Pain: With the swelling and numbness comes pain. There is a slight pain in some cases on the swollen lips and the areas around it. You might also feel some tingling sensations. The pain might exceed if the area is touched or some force is applied to it.
- Dryness: Especially during the winters, the lips tend to dry out. If the swollen lips happen during the winter, there is a huge chance for them to get dried and chapped. The chapped lips might sometimes bleed and pain on moving or touching.
- Itchiness and Inflammation: The swollen, dried and chapped lips usually itch and that itch is followed by inflammation. The inflammation increases if any acidic substance or any food that has acid content touches them or if the person stretches them.
- Filling of pus: Among the other fluids whose filling can cause swollen upper lips, pus is the most common. The upper lips get filled with pus and appears a little yellow in most cases. The pus filling usually happens in the cases of bug bite, insect bite, and injuries.
- Change in color: The color of the lip may change depending on the cause of the swelling. The lips might turn from yellow to blue or red. The blue bruising, in addition to the swelling, usually happens in the cases of an injury.
- Blisters: Blisters are not a symptom of the swollen upper lip but usually happen with it. If the blisters happen on the inner side of the lips, it might give an appearance that the part of the lip is swollen and is very painful. Cold sores also appear on the lips causing it to swell and are usually filled with fluids.
- Fever and Nausea: Fever is another symptom associated with the swollen upper lip. Many times the swelling is followed by high or low fever depending on the cause of the problem. The person might also feel nauseous along with high fever and weakness.
- Swelling of the tongue or gums: in cases of the allergies the gum and the tongue also swell along with the upper lip. This is one of the defensive responses of the body against any foreign substance that has been fed or inserted in it.
Causes of Upper Lip Swelling
There is not one but many causes for swollen upper lips. The swollen upper lip may sometimes be the disease in itself but mainly is a symptom of other diseases. Upper lip swelling might happen for no reason at times and might go away with time. Some of the biggest reasons for this condition are:
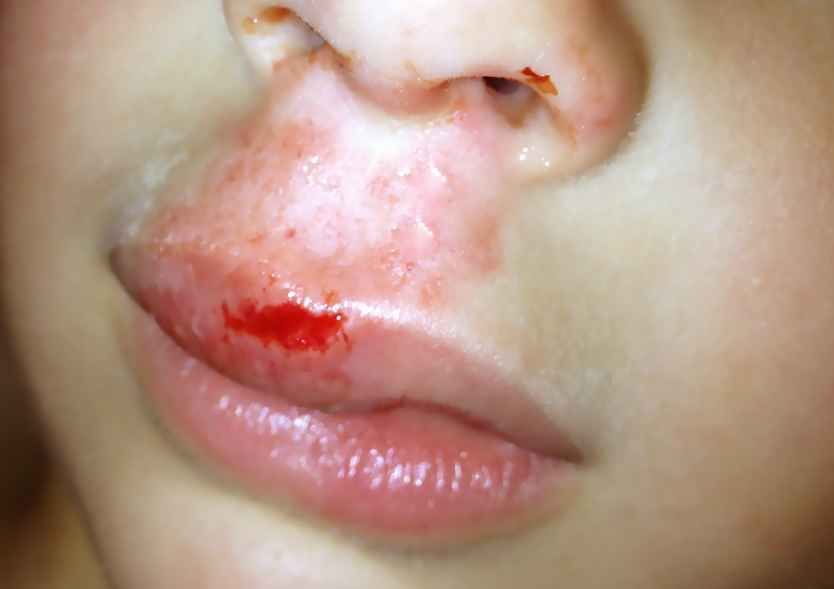
Injury
Picture 1: Swollen Upper lip from Injury
The most common cause of a swollen lip is a lip injury or a trauma. It might happen when the lip gets hit by a sharp or a blunt object or gets bruised due to any activity like sports or biting the lip or playing musical instruments. This leads to bruising and swelling. This swelling is painful and usually happens at one part of the lip that has been injured. It usually goes overtime on itself or on applying hot and cold compress on it. No special medical assistance is required unless there is a cut on the lip.
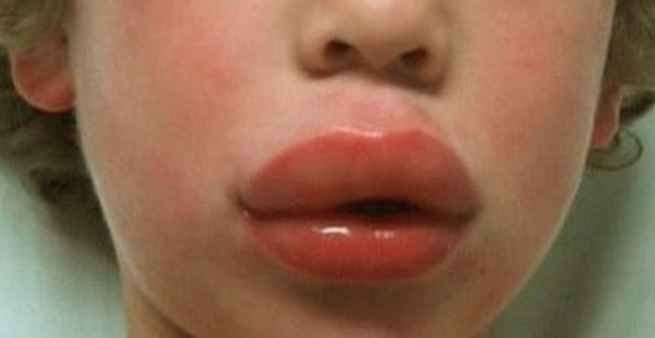
Allergy
Picture 2: Upper lip swelling as a result of allergic reaction
Allergy is the second most common causes of the swollen upper lip. Many people are allergic to certain kinds of foods, medicines, pet hair or dander, different lip cosmetics etc. If you suddenly start having swollen lips, then allergies are the most common reason. If you apply a certain type of lip care product or sleep on a bed with animal dander, your lips will swell overnight and you will have swollen lips in the morning. Similarly, after eating the food or medicine that your body is allergic to, the lip will start to swell as a natural response of the body to a foreign substance. Anaphylaxis which is one of the most dangerous allergy mostly caused by foods or medicines also leads to the swollen upper lip. The allergy can be identified easily because apart from the lip, it will affect the other parts of the body as well. This allergy requires immediate medical assistance since it is life threatening.
Surgery(Rhinoplasty or Lip Augmentation)
Rhinoplasty, in common terms, is a nose job which is done to fix various deformities in a person’s nose. After rhinoplasty, there might be a slight swelling below the nose in the area between the nose and the lips. This goes with the time as the operated part heals but can sometimes stay for a longer period of time when the surgery has gone wrong. Same is the case with lip augmentation which is done in different ways such as surgery and lip injections. The chemicals present in the injections are not suitable for all types of people and lead to reactions and hence swollen upper lip.
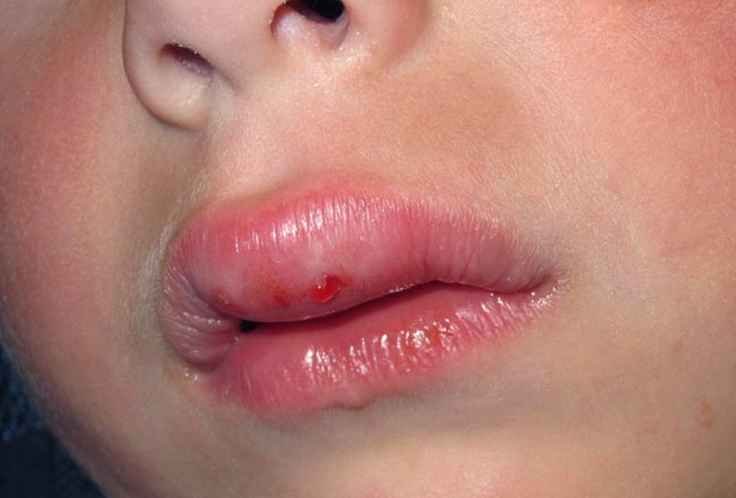
Cold Sores
Picture 3: Upper lip swelling from cold sores
Cold sores are small blisters that form around the mouth and occur in groups. They are usually pus filled and the area around them is always swollen. The cold sores are very painful and cause the upper lip to swell. They are the symptoms of the herpes virus the HSV or the HIV that is the AIDS virus. These sores usually take a lot of time to heal i.e. from six to seven days to about two to three weeks. These should get checked immediately and medical assistance should be taken. Cold sores may also bring with them fever and swelling of the gums and throat.
Lip Cancer
In lip cancer, there is an abnormal growth of cells on the lip and may turn into a tumor. The lips usually become large and swollen and there are blisters in and around them. This is the most common type of oral cancers and can be easily treated if diagnosed early.
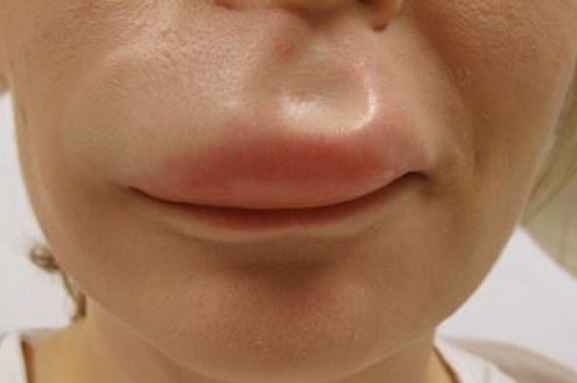
Lip Pimple and Insect Bites
Picture 4: Insect bites causing upper lip swelling
A Lip pimple is not very common but a possible reason for the swelling of the upper lips. A pimple can take place on anybody’s lips but usually happens in the cases of the people with oily skin. In addition to this, insect bites and bug bites can also cause swollen upper lips. The chemical secreted as a poison by the insect into the body while biting it causes reactions in people and lead to swollen lips.
Organ Failure, Blood Transfusion reaction and Infections
Certain conditions like kidney, liver and lung failure can also lead to the swelling of the upper lips along with the other dysfunctionalities in the body. Sometimes wrong blood transfusion occurs leading to the reactions in the body and causes the swelling. Similarly, some skin infections like cellulitis can also cause swollen upper lips. Cellulitis is a skin infection that takes place in the inner layers of the skin.
Treatment
The basic cause of the lip swelling is the body not being able to adjust itself with the foreign particles that have entered it in various ways. So, treating the swollen upper lip is not that tough and can be done easily by any medical professional. The different medical treatments are:
Adrenaline
Adrenaline injections are the most common treatment used to cure swollen upper lips as adrenaline is very effective in managing any kind of infection and allergy. It usually counters the harmful effects that the immune system can cause on the body in case of an allergic reaction. Although, it should be noted that if you have any health problems that do not allow you to take adrenaline injections, discuss it with your doctor so that he can arrange for an alternative remedy for you.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines are also called anti-allergics and are the drugs specially designed to treat allergies like food allergies and medicinal allergies. In the case of the swollen upper lips caused due to allergy, these are used. These are the quickest of all the drugs in relieving a person from the allergic symptoms. They can be of the oral or injectable types. The oral ones are the most common and are usually prescribed by the doctors. There are different antihistamines for different types of allergies and the doctor has to determine which one you are having before giving you any medicine.
Anti-Inflammatory drugs
The next type of drug that is given to a person with swollen upper lips is the anti-inflammatory drugs. As the name suggests these are the drugs that usually brings down the inflammation and the pain. They also help in reducing the swelling that is caused due to an injury or trauma. The anti-inflammatory drugs are combined with an antibiotic to make its side effects minimum. So, it is very important to consult your doctor before taking any anti-inflammatory drug over the counter.
Home Remedies
Since the swollen upper lip mainly gets treated on its own, there are some home remedies that can help the treatment happen faster and reduce pain.
- Turmeric Powder: Turmeric has healing properties. A paste of turmeric with water when rubbed on the swollen lips, helps them heal faster and better. Turmeric also helps in reducing the pain and if there is any injury to the lips, turmeric helps in healing since it has anti-inflammatory properties.
- Warm Compress: If the lip swelling does not go within a week, it is advisable to apply warm compress from time to time to bring it down. This warm compress is very effective in increasing the blood flow to the lips and reduces any accumulation of the fluids inside the lips. The fluid accumulation is the cause of the swollen lip and when the fluid gets drained out, the lips become normal.
- Aloe Vera Gel: Aloe Vera has cooling properties and may also act as an anti-inflammatory ointment. In the case of an insect bite or a wasp sting, immediate application of Aloe Vera is very effective since it stops the poison from spreading into the whole lip and reduces the pain and inflammation. Just take fresh Aloe Vera gel and apply it on the affected part for best results.
- Black Tea: Tea has a compound called tannins that helps in reducing the swelling by acting as an astringent to the lips. The black tea soaked in water should be directly applied on the lips for best results.
- Baking Soda: Baking soda, another substance found in everyone’s kitchen, is very effective in the treatment of the swollen upper lip. Baking soda paste which is made by mixing it in water should be applied on the upper lip for 15 to 20 minutes and the swelling will reduce after a few times of application.
- Honey: Honey is also very effective in treating the inflammation of the lips. Application of honey on the lips not only reduces the pain but also helps in subsiding the swelling.
- Cold Compress: To reduce the inflammation in the swollen lips, cold compress is the easiest and the most effective way. Gently apply a cold compress to the lips every hour and the inflammation, as well as the swelling will reduce in no time.